HTTP headers | Content-Encoding
Last Updated :
23 Oct, 2019
The HTTP headers Content-encoding is used to compress the media type. It informers the server which encoding the user will supported. It sends the information to the Accept-encoding. The server selects any one of the proposals, uses it and informs the client of its choice with the Content-Encoding response header.
Syntax:
Content-Encoding: gzip | compress | deflate | br| identity
Note: Multiple algorithms can also be applied.
Directives:
- gzip: It uses Lempel-Ziv coding (LZ77), with a 32-bit CRC format. It is the original format of UNIX gzip program.
- compress: It uses Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) algorithm. Due to patent issue, many modern browsers don’t support this type of content-encoding.
- deflate: This format uses zlib structure with deflate compression algorithm.
- br: It is a compression format using the Brotli algorithm.
- identity: It is used to indicate that there is no compression.
You can check how good your Accept-Encoding and Content-Encoding is working on this site.
Example:
Single Compression:
Content-Encoding: gzip
Content-Encoding: compress
Multiple Compression:
Content-Encoding: gzip, compress
To check the Content-Encoding in action go to Inspect Element -> Network check the request header for Content-Encoding like below, Content-Encoding is highlighted you can see.
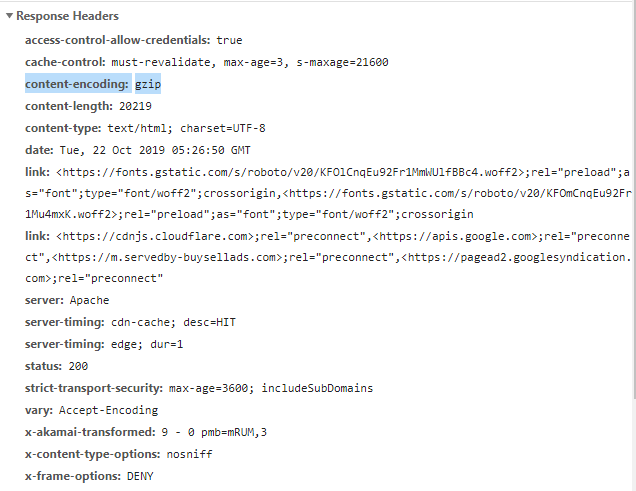
Supported Browsers: The browsers compatible with HTTP headers Content-Encoding are listed below:
- Google Chrome
- Internet Explorer
- Firefox
- Safari
- Opera
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...