How to read and write JSON file using Node ?
Last Updated :
15 Mar, 2024
Node JS is a free and versatile runtime environment that allows the execution of JavaScript code outside of web browsers. It finds extensive usage in creating APIs and microservices, catering to the needs of both small startups and large enterprises.
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) is a simple and text-based format for exchanging data between different applications. Similar to XML, it’s a commonly used method for web applications and APIs to communicate and share information.
Below are the different methods to read and write JSON files:
Method 1: Using require method:
A straightforward way to read a JSON file in a Node JS file is by using the `require()` method to include it.
Syntax:
const data = require('path/to/file/filename');
Example: Create a users.json file in the same directory where index.js file present. Add following data to the users.json file and write the index.js file code:
JSON
[
{
"name": "John",
"age": 21,
"language": ["JavaScript", "PHP", "Python"]
},
{
"name": "Smith",
"age": 25,
"language": ["PHP", "Go", "JavaScript"]
}
]
// Requiring users file
const users = require("./users");
console.log(users);
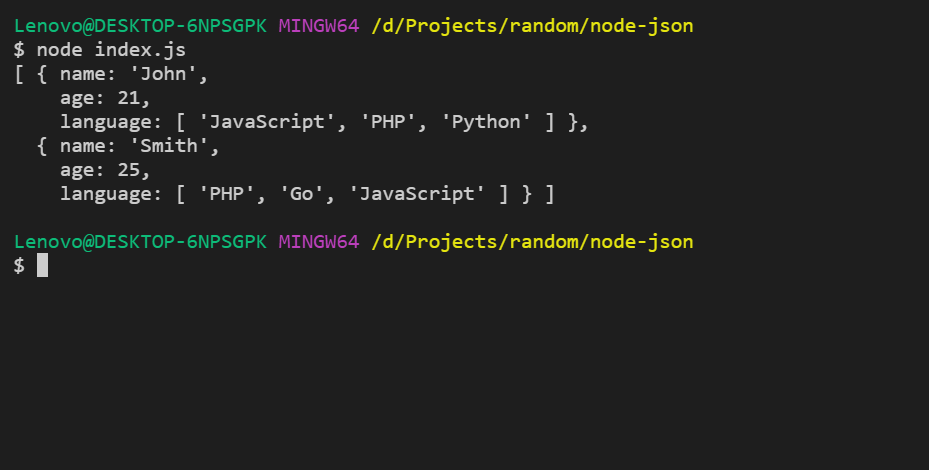
To run the file using the command:
node index.js
Output:
Method 2: Using the fs module:
Another approach to read a file in Node JS is by utilizing the fs module. The fs module provides the file content as a string, requiring us to convert it into JSON format using the built-in method JSON.parse().
JavaScript
const fs = require("fs");
// Read users.json file
fs.readFile("users.json", function(err, data) {
// Check for errors
if (err) throw err;
// Converting to JSON
const users = JSON.parse(data);
console.log(users); // Print users
});
Output:

Writing to a JSON file
We can write data into a JSON file by using the nodejs fs module. We can use writeFile method to write data into a file.
Syntax:
fs.writeFile("filename", data, callback);
Example: We will add a new user to the existing JSON file, we have created in the previous example. This task will be completed in three steps:
- Read the file using one of the above methods.
- Add the data using
.push() method. - Write the new data to the file using
JSON.stringify() method to convert data into string.
Javascript
const fs = require("fs");
// STEP 1: Reading JSON file
const users = require("./users");
// Defining new user
let user =
{
name: "New User",
age: 30,
language: ["PHP", "Go", "JavaScript"]
};
// STEP 2: Adding new data to users object
users.push(user);
// STEP 3: Writing to a file
fs.writeFile(
"users.json",
JSON.stringify(users),
err => {
// Checking for errors
if (err) throw err;
// Success
console.log("Done writing");
});
Output: Run the file again and you will see a message into the console:
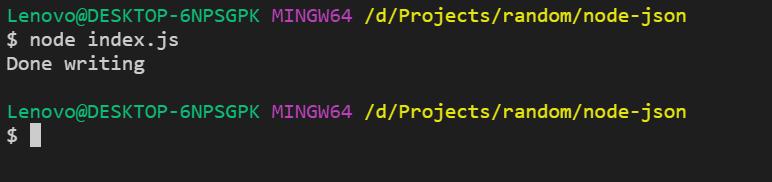
Now check your users.json file it will looks something like below:

Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...