How to Read a Traceroute?
Last Updated :
09 May, 2022
Traceroute is a Linux Command, used in Network Diagnostics for tracking the route chosen by a Network packet while reaching the next host, this route is called hops, for each hop, Traceroute command can give detailed information of the traveled route by packets.
Traceroute will provide the complete information regarding the path chosen by the data packets to reach the destination.
For Example, if a Machine(Computer) is in city A which is the Source and the Server resides in the city B which is the destination, Traceroute will retrieve the complete path – each hop( which involves the routers, computers, and any devices that are involved in this Network traffic) and also with the duration of time it takes to come and go back.
The Traceroute helps, in getting a better understanding of the Network Traffic Communication, which would help users and sometimes the Network Engineers in identifying Network related problems and also, in some cases serious security Vulnerabilities, for example, Log4j Vulnerability which is currently trending in the IT World.
What is Log4j Vulnerability?
Log4shell or LogJam is a Remote Code Execution class vulnerability if it can be exploited by attackers on one of the servers, they can be able to get arbitrary code and get full control of the machines, for this IT engineer suggests either upgrading Log4j to the latest patch or based on priority if Log4j is not necessary, then users can uninstall it completely.
Working of Traceroute
Traceroute works with the help of ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol) echo packets consisting of variable TTL (Time To Live) and to get accurate values each hop is queried multiple times and each hop’s response time is calculated.
The working of Traceroute command is executed by manipulating these TTL values, TTL Values are used to limit how long, These TTL values are assigned to each packet of data and whenever the packet makes a hop on the destination, the TTL value is decreased by 1. This TTL working can be seen in the below image:
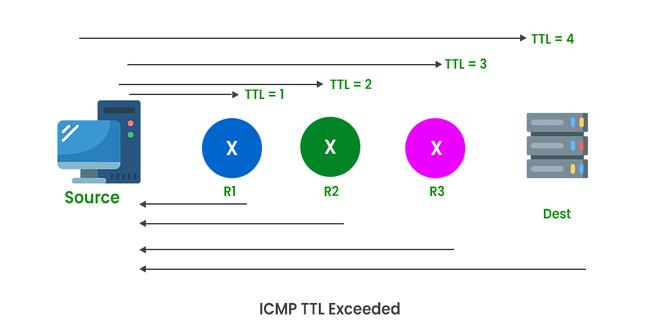
Working of Traceroute
How to Read a Traceroute?
Users can execute the traceroute command in their machines with the Traceroute Keyword accompanied by the Website name they want to test for getting the logs.
Here, Windows users use the traceroute keyword, while Linux Users use the traceroute command, windows users execute this command in the CMD terminal, while Linux Users use terminal shell and execute it,
Syntax:
For Windows:
traceroute server name or IP Address
For Linux:
traceroute server name or IP Address
Let us see the Traceroute logs by executing them, the logs extracted from both Linux and Windows machines for “www.google.com“.
Logs From Windows Machine:
Command:
$traceroute www.google.com
Output:
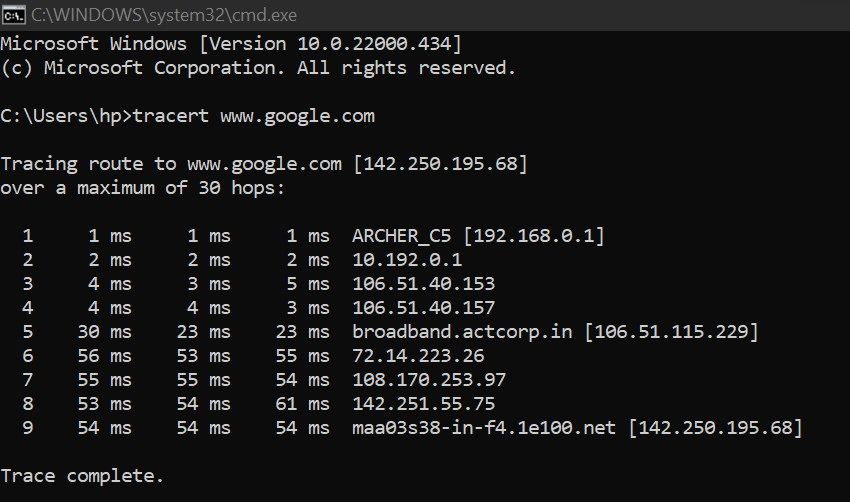
Traceroute in Windows
Logs from Linux Machine:
Command:
$traceroute www.google.com
Output:
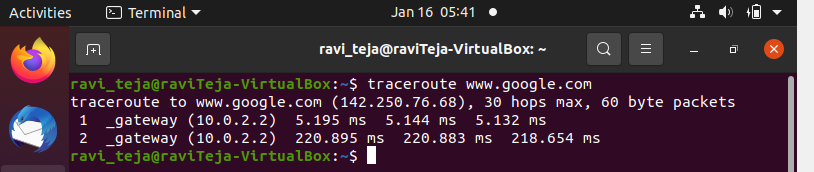
Traceroute in Linux
As we can see the traceroute logs extracted from both Linux and Windows machines, here we need to understand that network packets before reaching from source to destination travels to various routers, hence whenever a packet is forwarded to the next router a hop occurs, and generally traceroute command fetches results of maximum of 30 hops, the more the hops means it indicates slower network connection, while, fewer hops means fast access.
In the above logs,
- The first-line displays the target server’s name followed by the server’s IP address, the maximum hops that are allowed, and also the size of the packets that are transmitted.
- And the following line displays, the router in the path between source and destination.
- Each line shows the name of the server, IP address, and 3 Round Trip Times(RTT) in milliseconds.
What is RTT?
Round Trip Time is a time constant that is calculated by taking :
- The time is taken by a packet to get from Source to destination..
- Time is taken for the packet to get back from destination to source.
This RTT is calculated in milliseconds and is also often called latency. By default, 3 packets are sent for each route hence we get 3 RTTs, in every Hop.
How to check Hop Count?
Hop Count can be determined by using the Traceroute command, as discussed in above user first goes to the command terminal in their machine and for windows type traceroute and for Linux type Traceroute followed by server name or IP address. Then traceroute will display logs of max 30 hops, in that last hop will be the hop count.
Limits of Traceroute:
The Traceroute can report only a maximum of 30 hops in logs and in theory, we do have some limitations, which needs to be discussed :
1. In some cases, Firewalls can block packets in between the source and destination making traceroute to reach maximum hops without getting any result, in such cases, the logs will be displayed with an asterisk in place of IP Address.
For Example: $ traceroute google.com
traceroute to google.com (209.85.231.104), 30 hops max, 52 byte packets
1 * * *
2 * * *
3 * * *
4 * * *
2. Routers that make use of load balancers may use multiple paths for packet transmissions and the traceroute logs can be inaccurate in defining the path between source and destination.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...