How to insert a pandas DataFrame to an existing PostgreSQL table?
Last Updated :
22 Nov, 2021
In this article, we are going to see how to insert a pandas DataFrame to an existing PostgreSQL table.
Modules needed
- pandas: Pandas DataFrame is two-dimensional size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data structure with labeled axes (rows and columns). A Data frame is a two-dimensional data structure, i.e., data is aligned in a tabular fashion in rows and columns. Pandas DataFrame consists of three principal components, the data, rows, and columns.
- psycopg2: PostgreSQL is a powerful, open source object-relational database system. PostgreSQL runs on all major operating systems. PostgreSQL follows ACID property of DataBase system and has the support of triggers, updatable views and materialized views, foreign keys.
- sqlalchemy: SQLAlchemy is the Python SQL toolkit and Object Relational Mapper that gives application developers the full power and flexibility of SQL
we start the code by importing packages and creating a connection string of the format:
‘postgres://user:password@host/database’
The create_engine() function takes the connection string as an argument and forms a connection to the PostgreSQL database, after connecting we create a dictionary, and further convert it into a dataframe using the method pandas.DataFrame() method.
The to_sql() method is used to insert a pandas data frame into the Postgresql table. Finally, we execute commands using the execute() method to execute our SQL commands and fetchall() method to fetch the records.
df.to_sql(‘data’, con=conn, if_exists=’replace’, index=False)
arguments are:
- name of the table
- connection
- if_exists : if the table already exists the function we want to apply . ex: ‘append’ help us add data instead of replacing the data.
- index : True or False
Example 1:
Insert a pandas DataFrame to an existing PostgreSQL table using sqlalchemy. The create table command used to create a table in the PostgreSQL database in the following example is:
create table data( Name varchar, Age bigint);
Code:
Python3
import psycopg2
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
db = create_engine(conn_string)
conn = db.connect()
data = {'Name': ['Tom', 'dick', 'harry'],
'Age': [22, 21, 24]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.to_sql('data', con=conn, if_exists='replace',
index=False)
conn = psycopg2.connect(conn_string
)
conn.autocommit = True
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql1 =
cursor.execute(sql1)
for i in cursor.fetchall():
print(i)
conn.close()
|
Output:
('Tom', 22)
('dick', 21)
('harry', 24)
Output in PostgreSQL:
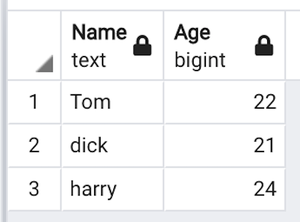
output table in PostgreSQL
Example 2:
Insert a pandas DataFrame to an existing PostgreSQL table without using sqlalchemy. As usual, we form a connection to PostgreSQL using the connect() command and execute the execute_values() method, where there’s the ‘insert’ SQL command is executed. a try-except clause is included to make sure the errors are caught if any.
To view or download the CSV file used in the below program: click here.
The create table command used to create a table in the PostgreSQL database in the following example is :
create table fossil_fuels_c02(year int, country varchar,total int,solidfuel int, liquidfuel int,gasfuel int,cement int,gasflaring int,percapita int,bunkerfuels int);
Code:
Python3
import psycopg2
import numpy as np
import psycopg2.extras as extras
import pandas as pd
def execute_values(conn, df, table):
tuples = [tuple(x) for x in df.to_numpy()]
cols = ','.join(list(df.columns))
query = "INSERT INTO %s(%s) VALUES %%s" % (table, cols)
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
extras.execute_values(cursor, query, tuples)
conn.commit()
except (Exception, psycopg2.DatabaseError) as error:
print("Error: %s" % error)
conn.rollback()
cursor.close()
return 1
print("the dataframe is inserted")
cursor.close()
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="ENVIRONMENT_DATABASE", user='postgres', password='pass', host='127.0.0.1', port='5432'
)
df = pd.read_csv('fossilfuels.csv')
execute_values(conn, df, 'fossil_fuels_c02')
|
Output:
the dataframe is inserted
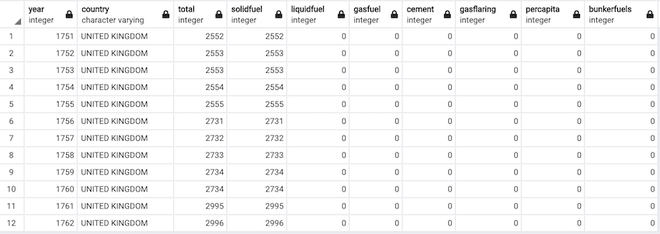
after inserting the dataFrame
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...