How to Get the Body of Request in Spring Boot?
Last Updated :
29 Feb, 2024
Java language is one of the most popular languages among all programming languages. There are several advantages of using the Java programming language, whether for security purposes or building large distribution projects. One of the advantages of using Java is that Java tries to connect every concept in the language to the real world with the help of the concepts of classes, inheritance, polymorphism, etc.
There are several other concepts present in Java that increase the user-friendly interaction between the Java code and the programmer such as generic, Access specifiers, Annotations, etc. These features add an extra property to the class as well as the method of the Java program. In this article, we will discuss how to get the body of the incoming request in the spring boot.
@RequestBody: Annotation is used to get the request body in the incoming request.
Spring Initializr is a web-based tool using which we can easily generate the structure of the Spring Boot project. It also provides various features for the projects expressed in a metadata model. This model allows us to configure the list of dependencies that are supported by JVM. Here, we will create the structure of an application using a spring initializer and then use an IDE to create a sample GET route. Therefore, to do this, the following steps are followed sequentially as follows:
Step 1: Go to Spring Initializr
Fill in the details as per the requirements. For this application:
Project: Maven
Language: Java
Spring Boot: 2.2.8
Packaging: JAR
Java: 8
Dependencies: Spring Web
Step 2: Click on Generate which will download the starter project.
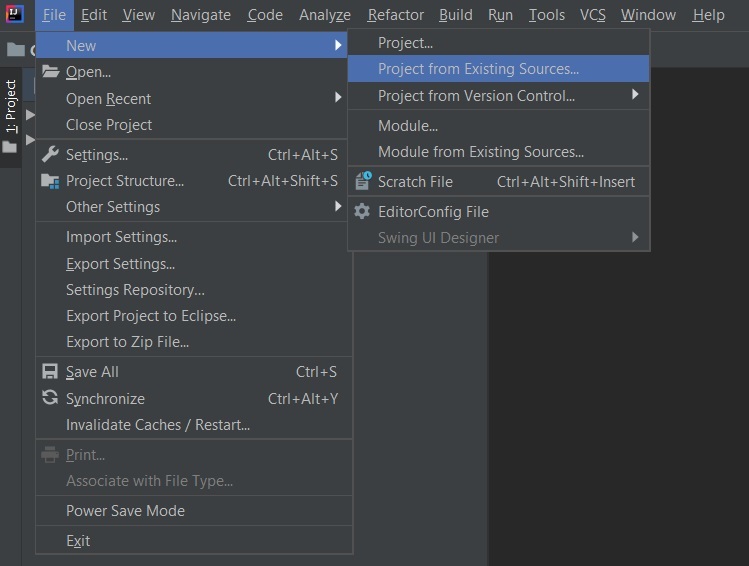
Step 3: Extract the zip file. Now open a suitable IDE and then go to File->New->Project from existing sources->Spring-boot-app and select pom.xml. Click on import changes on prompt and wait for the project to sync.
Note: In the Import Project for Maven window, make sure you choose the same version of JDK which you selected while creating the project.
Step 4: Go to src -> main -> java -> com.gfg.Spring.boot.app and create a Java class with the name Controller and add the annotation @RestController. Now create a GET API as shown below as follows:
Example:
Person.java
Java
public class Person {
int id;
String name;
int age;
public Person(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return id + " " + name + " " + age;
}
|
Controller.java
Java
@RestController
public class Controller {
@GetMapping("/Get")
public void getBody() {
Person ob = createPerson();
System.out.println(ob);
}
private Person createPerson() {
return new Person(1, "Aayush", 32);
}
}
|
This application is now ready to run. Run the Main class and wait for the Tomcat server to start.
Note: Here we have not used @RequestBody annotation as it is used to handle POST requests; since we are not sending any data in the request body so, there is no need for @RequestBody annotation here.
If we want to add @RequestBody annotation to handle GET request, we should use a different HTTP method i.e. @PostMapping instead of @GetMapping. Below is the code implementation for the same.
Java
@RestController
public class Controller
{
@PostMapping("/Get")
public void getBody(@RequestBody Person ob)
{
System.out.println(ob);
}
}
|
We do not have to create Person object because the ob parameter will be automatically related with the data from the request body when a request is made to the /Get endpoint.
Note: The creation of the Person object will be handled by the Spring framework based on the JSON data in the request body.
Step 5: Now go to the Postman and add URL address and make get request.

Note: The default port of the Tomcat server is 8080 and can be changed in the application.properties file.
Output: Lastly output will be generated on terminal/CMD below as follows:
1 Aayush 32
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...