How to find the equation of an ellipse with foci and points?
Last Updated :
06 Mar, 2023
When a plane crosses a cone, conic sections, also known as conics, are created. The geometry of these sections is determined by the angle at which they cross. As a result, conic sections are divided into four categories: circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. Each of these forms has its own set of mathematical features and equations. The ellipse is discussed below.
Ellipse
As a conic section, an ellipse is a shape formed when a plane intersects a cone at an angle (β) less than the right angle but more than the angle formed at the vertex of a cone (α). In other words, an ellipse is formed when a plane cuts a cone at an angle β such that α<β<90o.

As shown in the figure above, a cone and a plane intersect at an angle β which is less than the right angle but more than α to form an ellipse due to the intersection.
Equation of an ellipse
- The standard equation of an ellipse centered at (h, k) with a major axis parallel to the x-axis is given by:
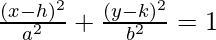 ,
,
where the coordinates of the vertex are (h±a, 0), coordinates of co-vertex are (h, k±b) and the coordinates of foci are (h±c, k), where c2 = a2 – b2.

Horizontal ellipse
- The standard equation of an ellipse centered at (h, k) with a major axis parallel to the y-axis is given by:
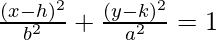 ,
,
where the coordinates of the vertex are (h, k±a), coordinates of co-vertex are (h±b, k) and the coordinates of foci are (h, k±c), where c2 = a2 – b2.

Vertical ellipse
How to find the equation of an ellipse with foci and points?
Solution:
To find the equation of an ellipse, we need the values a and b. Now, it is known that the sum of the distances of a point lying on an ellipse from its foci is equal to the length of its major axis, 2a. The value of a can be calculated by this property. To calculate b, use the formula c2 = a2 – b2. Substitute the obtained values of a and b in the standard form to get the required equation.
Let us understand this method in more detail through an example.
Example: Say, an ellipse passing through the origin with foci (±4, 0) and point (–4, 1.8).
Using the formula, we have
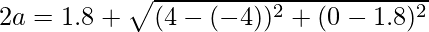
2a = 10
a = 5
Put a = 5 in c2 = a2 – b2 to find b.
b2 = 25 – 16
b2 = 9
As the ellipse lies on x-axis, the equation is of the form 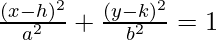 .
.
So, the equation is, 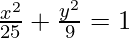 .
.
Similar Problems
Question 1. Find the equation of an ellipse passing through the origin with foci (±7, 0) and point (6, 2).
Solution:
Using the formula, we have
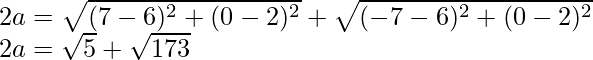
2a = 15.74
a = 7.87
Put a = 7.87 in c2 = a2 – b2 to find b.
b2 = 62 – 49
b2 = 13
As the ellipse lies on x-axis, the equation is of the form 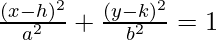 .
.
So, the equation is, 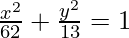 .
.
Question 2. Find the equation of an ellipse passing through the origin with foci (±5√3, 0) and point (6, 4).
Solution:
Using the formula, we have
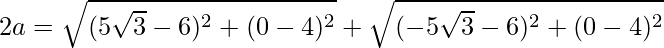
2a = 20
a = 10
Put a = 10 in c2 = a2 – b2 to find b.
b2 = 100 – 75
b2 = 25
As the ellipse lies on x-axis, the equation is of the form 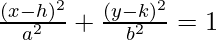 .
.
So, the equation is, 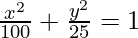 .
.
Question 3. Find the coordinates of the major axis of the ellipse with foci (0, ±5) and minor axis (12, 0).
Solution:
We have, c = 5 and b = 12.
Put these in c2 = a2 – b2 to find a.
a2 = 122 + 52
a2 = 169
a = 13
The coordinates of major axis are (0, ±13).
Question 4. Find the equation of the ellipse passing through the origin if a = 3, b = 5, and the major axis is parallel to the x-axis.
Solution:
The major axis is parallel to x-axis, so the ellipse lies on x-axis.
The equation is of the form 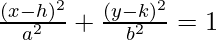 .
.
Here, a = 3, b = 5, h = 0 and k = 0.
So, the equation becomes,
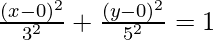
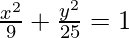
Question 5. Find the equation of the ellipse passing through the origin if a = 13, b = 5, and the minor axis is parallel to the x-axis.
Solution:
The major axis is parallel to x-axis, so the ellipse lies on x-axis.
The equation is of the form 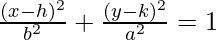 .
.
Here a = 13 and b = 5, h = 0 and k = 0.
So, the equation becomes,

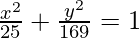
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...