How to Define an Auto Increment Primary Key in PostgreSQL using Python?
Last Updated :
06 Jan, 2023
Prerequisite: PostgreSQL
Python has various database drivers for PostgreSQL. Currently, most used version is psycopg2 because it fully implements the Python DB-API 2.0 specification. The psycopg2 provides many useful features such as client-side and server-side cursors, asynchronous notification and communication, COPY command support, etc.
Installation
psycopg2 can be downloaded like any other module using the following command:
pip install psycopg2
Approach
PostgreSQL’s way of creating Primary key with auto increment feature :
A column has to be defined with SERIAL PRIMARY KEY. Here SERIAL is not a true data type, but is simply shorthand notation that tells Postgres to create an auto incremented, unique identifier for the specified column. By simply setting a column as SERIAL with PRIMARY KEY attached, Postgres will handle all the complicated behind-the-scenes work and automatically increment our the specified column with a unique, primary key value for every INSERT.
Database Information
Database name: testdb
Table name: EMPLOYEE
In the EMPLOYEE TABLE, column named EMPLOYEE_ID will be implemented as an auto-incremented Primary key column.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE <table_name>(
<column1_name> SERIAL NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
.
.
);
The implementation of creating a table with such specification is given below:
Python3
import psycopg2
def create_table():
conn = None
try:
conn = psycopg2.connect(database="testdb", user="postgres",
password="password", host="127.0.0.1", port="5432")
print("Opened database successfully")
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EMPLOYEE")
sql =
cursor.execute(sql)
print("Table created successfully........")
cursor.close()
conn.commit()
except (Exception, psycopg2.DatabaseError) as error:
print(error)
finally:
if conn is not None:
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
create_table()
|
We can see the table created using pgadmin tool
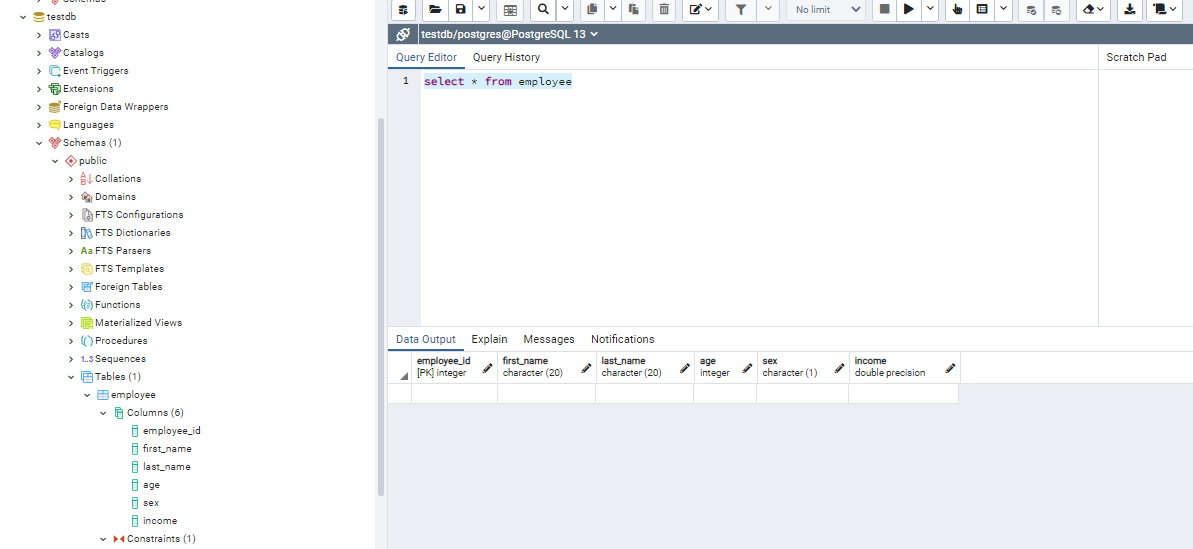
Now, Insertion needs to done to see if our auto-increment feature works or not. This can be done either directly through pgadmin or using python code.
pgadmin way :
Below is the screenshot that shows execution of insert queries and resultant result-set.

Explanation of auto increment primary key
Using python code:
Python3
import psycopg2
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(user="postgres",
password="password",
host="127.0.0.1",
port="5432",
database="testdb")
cursor = connection.cursor()
postgres_insert_query =
record_to_insert = ('asd', 'wer', 19, 'f', 5000)
cursor.execute(postgres_insert_query, record_to_insert)
connection.commit()
count = cursor.rowcount
print(count, "Record inserted successfully into Employee table")
except (Exception, psycopg2.Error) as error:
if(connection):
print("Failed to insert record into Employee table", error)
finally:
if(connection):
cursor.close()
connection.close()
print("PostgreSQL connection is closed")
|
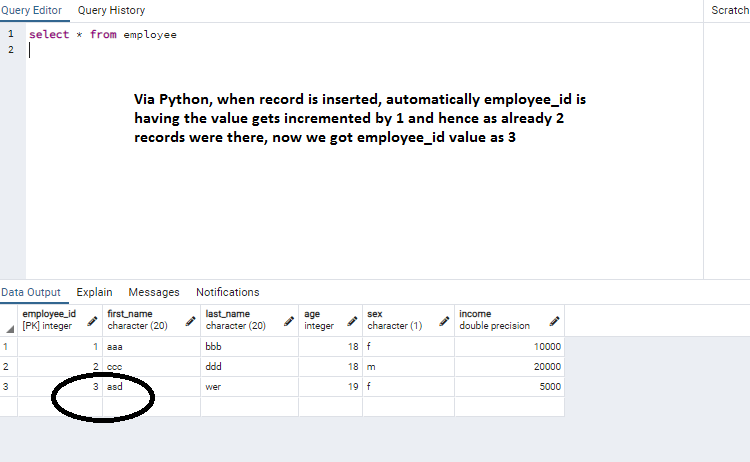
Output of employee table after executing above program :
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...