The mean or average of the given data distribution is the calculated central value. It is used to determine the average of the given data. It gives a measure of the central tendency of the data. The central tendency of data distribution is the statistical measure that represents and identifies the entire data distribution using a single value. It acts as an exact descriptor of the data represented.
In statistics, the mean of the data can also be defined as the sum of all observations to the total number of observations. The mean of data distribution is also known as the arithmetic mean or average. It is denoted by x̄.
⇒ Given a data set with total n values,
X = x1, x2,…, xn, the mean x̄ is the mean of the n values x1, x2,…, xn.
Mean Formula
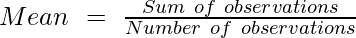
Mean Formula For Ungrouped Data
The formula to compute the mean in case of ungrouped data:
Let us assume, x1, x2, x3,……, xn be n observations of a data set.
Then we have,
The mean of these values is:
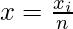
Here, we have,
xi = ith observation, 1 ≤ i ≤ n
∑xi = Sum of observations
n = Number of observations
Mean Formula For Grouped Data
The mean of the data is dependent on the computation of mean in the case of grouped data :
- Direct Method
- Assumed Mean Method
- Step-deviation Method
Calculating Mean Using Direct Method
The direct method is one of the easiest and simplest methods used to compute the mean of the grouped data. The following steps can be used to compute the mean of the given data distribution:
Step 1: Create a table having four columns as computed below,
Column 1- Class interval.
Column 2- Class marks, denoted by xi.
Column 3- Corresponding Frequencies (fi)
Column 4- xifi, which is the product of column 2 and column 3.
Step 2: Computing Mean by the Formula Mean, we have = 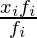
Calculating Mean Using Assumed Mean Method
The direct method used for the computation of the mean is a tedious method. The assumed mean method can be used in order to compute the mean of a set of grouped data. The following steps can be used to compute the mean of the given data distribution:
Step 1: Create a table having five columns as computed below,
Column 1- Class interval.
Column 2- Classmarks, denoted by xi. The central value of this column is taken as the Assumed Mean. This is denoted by A.
Column 3- Corresponding deviations are then computed. The column values are computed as follows, i.e. di = xi – A
Column 4- Corresponding Frequencies (fi)
Column 5- Mean of di values of Column 3 is computed using formula. Therefore, mean of di = 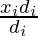
Step 2: At last, compute the mean of the given data distribution by performing the summation of the data to find the assumed mean to the mean of the di.
Calculating Mean Using Step Deviation Method
Also known as the shift of origin and scale method, the step deviation method is used to eliminate performing tedious calculations for computation of grouped data mean. The following steps can be used to compute the mean of the given data distribution:
Step 1: Create a table containing five columns as given below,
Column 1- Class interval.
Column 2- Classmarks, denoted by xi. The central value of this column is taken as the Assumed Mean. This is denoted by A.
Column 3- Corresponding deviations are then computed. The column values are computed as follows, di = xi – A
Column 4- Calculate the values of ui using the formula, ui= 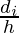 , where h is the class width.
, where h is the class width.
Column 5- Corresponding Frequencies (fi)
Step 2: Therefore, the Mean of ui = 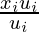
Step 3: At last, compute the mean of the given data distribution by calculating the Mean by performing the summation of the assumed mean A to the product of class width(h) with mean of ui.
Sample Questions
Question 1. Calculate the mean of the following data.
5, 10, 4, 20, 25, 18, 11, 13, 19, 22
Solution:
Here we have been given,
xi = 5, 10, 4, 20, 25, 18, 11, 13, 19, 22
n = 10
Mean x̄ = 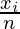
= 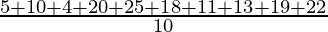
= 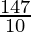
= 14.7
Hence,
The mean of this data is 14.7.
Question 2. Calculate the mean of the data for the distribution below of marks obtained by students in exams?
| Marks | 50 | 86 | 76 | 84 | 66 | 56 | 58 | 40 |
| Number of students | 40 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 30 | 48 | 56 | 12 |
Solution:
Finding the sum:
| Marks (xi) | Number of students (fi) | fixi |
| 50 | 40 | 1000 |
| 86 | 2 | 86 |
| 76 | 8 | 304 |
| 84 | 4 | 168 |
| 66 | 30 | 990 |
| 56 | 48 | 1344 |
| 58 | 56 | 1624 |
| 40 | 12 | 240 |
| Sum | 200 | 5756 |
Mean = 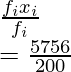
= 28.78
Therefore,
The mean of the following distribution is 28.78.
Question 3. Assume if in a class the height of 5 girls is 140 cm, 152 cm, 150 cm, 153 cm, and 154 cm. Then find the mean of the height of the girls?
Solution:
Here we are given height of girls
140 cm, 152 cm, 150 cm, 153 cm, and 154 cm
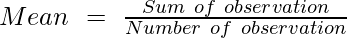
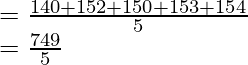
= 149.8
Therefore,
Mean, x̄ =149.8 cm.
Question 4. Find the mean of the first five natural numbers?
Solution:
First five natural are 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Further,
Mean of the first five natural numbers = 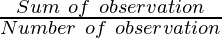
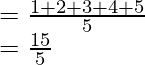
= 3
Thus,
The mean of first five natural numbers is 3.
Question 5. Find the mean of the first 10 prime numbers?
Solution:
The first 10 prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29.
Further,
Mean of the first five natural numbers = 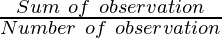
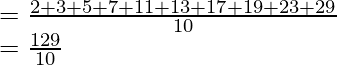
= 12.9
Thus,
The mean of first 10 prime numbers is 12.9.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...