How to access variables from another file using JavaScript ?
Last Updated :
22 Dec, 2023
In JavaScript, variables can be accessed from another file using the <script> tags or the import or export statement. The script tag is mainly used when we want to access a variable of a JavaScript file in an HTML file. This works well for client-side scripting as well as for server-side scripting. The import or export statement however cannot be used for client-side scripting. The import or export statement works in Node.js during server-side scripting.
Below are the approaches for both server and client side:
Approach 1: client-side program
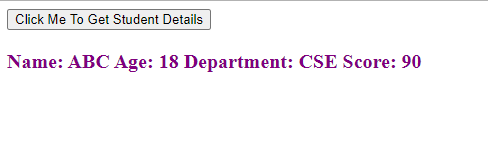
At first the “module1.js” file is created and a Student object with properties “name”, “age”, “dept” and “score” is defined. The module1.js JavaScript file is imported using the src attribute of the script tag within the “head” section of the HTML file. Since the JavaScript file is imported, the contents are accessible within the HTML file.
We create a button that when clicked triggers the JavaScript function. The Student object properties are accessed through the f() function and all the Student object properties are concatenated to a string variable. This string is placed within the <p> tag having ‘text’ id using the document.getElementById() and innerHTML property of HTML DOM.
Example: In this example, we are following the above approach.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript"
src="module1.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="f()">
Click Me To Get Student Details
</button>
<div>
<p id="text" style="color:purple;
font-weight:bold;font-size:20px;">
</p>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function f() {
let name = Student.name;
let age = Student.age;
let dept = Student.dept;
let score = Student.score;
let str = "Name:" + name + "\nAge: "
+ age + "\nDepartment:" + dept
+ "\nScore: " + score;
document.getElementById(
'text').innerHTML = str;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
module1.js This file is used in the above HTML code.
Javascript
let Student =
{
name : "ABC",
age : 18,
dept : "CSE",
score : 90
};
|
Output:
Approach 2: Server-side scripting
In this approach, we create a JavaScript file “module1.js” and define a Student object having properties “name”, “age”, “dept” and “score”. The Student object is exported using module.exports. In another JavaScript module file “module2.js“, we import “module1.js” using the import statement at the beginning of the file. The objects Hostel and Hostel_Allocation are defined in the “module2.js” file and the Student object is accessed in the Hostel_Allocation object.
An HTTP server is created and hosted at port no. 8080. The properties of Hostel_Allocation are concatenated in a string. This string is printed on the landing page of the web application whenever it is run.
Example: In this example, we are following the above approach.
module1.js
Javascript
let Student = {
name : "ABC",
age : 18,
dept : "CSE",
score : 90
};
module.exports = {Student};
|
module2.js
Javascript
let http = require('http');
const { Student } = require('./module1.js');
let Hostel = {
student_count: 500,
no_of_rooms: 250,
hostel_fees: 12000
}
let Hostel_Allocation = {
room_no: 151,
student_name: Student.name,
student_age: Student.age,
student_dept: Student.dept,
total_fees: 12000
}
let str = "Room No: " + Hostel_Allocation.room_no
+ "\nStudent Name: "
+ Hostel_Allocation.student_name
+ "\nTotal Fees: "
+ Hostel_Allocation.total_fees;
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
res.write(str);
res.end();
}).listen(8080);
|
Output:
Start the server
node module2.js
Run the application in the browser
localhost:8080

JavaScript is best known for web page development but it is also used in a variety of non-browser environments. You can learn JavaScript from the ground up by following this JavaScript Tutorial and JavaScript Examples.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...