How does fileless malware make its way to Computer
Last Updated :
09 Jun, 2022
In early 2018, there was a shift from using malicious.exe for PDF and DOC attachments via emails to fileless techniques to deploy malware in the systems. Fileless malware is also known as an invisible threat. It is hard to detect as it resides in system memory and Windows tools are hijacked to perform these attacks. So there is no interference of victim in these kinds of attacks.
Using tools already installed on PC or by running simple scripts and shell-code in memory via Windows Power Shell the malware can be deployed on the victims machine. The malicious scripts are also frequently hidden in the windows registry and Windows Management System (WMS). This technique is also called “Living Off the Land”.
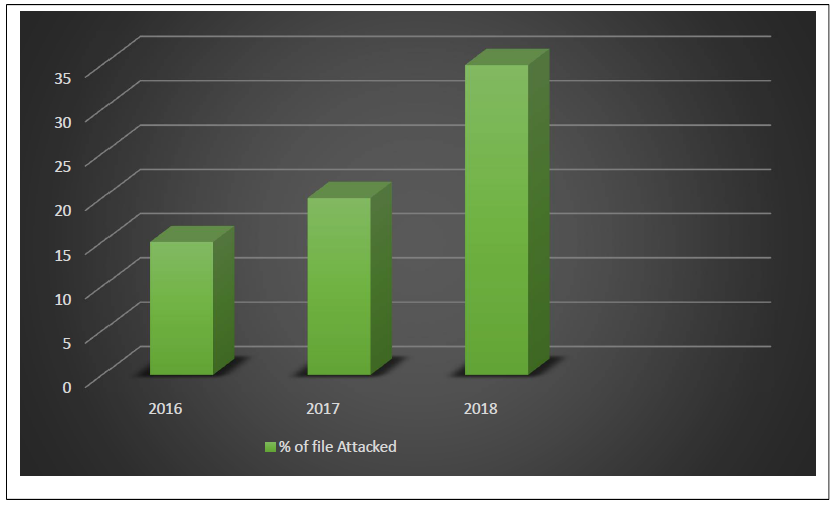
Fileless attacks were at its highest peak in 2017 and early 2018 as fileless malware is so powerful that security products cannot just block the systems or software that are utilizing RAM and Windows tools and it does not have any executable file (Malicious files) on disk to detect. Fileless malware does not leave any traces behind. Some of fileless attacks are Kovter, Hancitor, Sorebrect ransomware.
Fileless attacks mostly uses below techniques:
- Windows registry manipulation
- Memory code injection
- Powershell, Wscript or Cscript based
It is estimated that in 2018 almost 35 percent of cyber attacks are comprised because of fileless technique.
Exploits: Exploits are programs or code that take the advantage of any system vulnerability (flaws) to perform an attack on a system or use for gaining privileged access and thereby control the system. Exploit attacks are considered powerful as they do not require interaction with victims.
In the year 2018, research revealed that nearly every computer chip manufactured in the last 20 years contains two major vulnerabilities known as spectre (cve-2017-5753) and meltdown(cve-2017-5715). Microsoft has released its patches to fix this but still, its traces remain and they are trying to completely eliminate it. Some zero-day exploits including flash (cve-2018-4878) and internet explorer (cve-2018-8174). In addition to this, adobe reader zero-day (cve-2018-4990) and flash player vulnerability (cve-2018-5002) which allows a maliciously crafted flash object to execute code on victims computer were fixed by Adobe but it was largely hampered in middle east countries.
There are basically two types of exploits: Known and Unknown. Known Exploits are those which take the advantage of a known vulnerability in software and systems. Developers have already created patches for the same but it is not easy to maintain for every piece of software. Unknown exploits or Zero-Day are those which are not yet been in Public. This can be due to Cybercriminals have spotted it before the developers and uses it as an opportunity to carry out exploit attack.
How can attacks be avoided?
- There are not full-fledged detection provided by security antivirus for these attacks. But take some preventive measures to avoid these attack.
- Keep Windows, software’s (Adobe, MS-Office etc) up-to-date.
- Regularly scan PC for infections, vulnerabilities and keep antivirus updated.
- Install browser protection on PC and disable direct plugins download of software like Adobe.
- Disable Power shell and WMI if not using.
- Security is getting more expensive and difficult to manage so little awareness can secure business.
- Install an advanced internet security software like REVE Antivirus capable of detecting and blocking malicious documents, spam and exploits that are designed to take advantage of installed software’s, browsers and system vulnerabilities.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...