Haversine formula to find distance between two points on a sphere
Last Updated :
05 Sep, 2022
The Haversine formula calculates the shortest distance between two points on a sphere using their latitudes and longitudes measured along the surface. It is important for use in navigation. The haversine can be expressed in trigonometric function as:
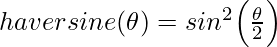
The haversine of the central angle (which is d/r) is calculated by the following formula:
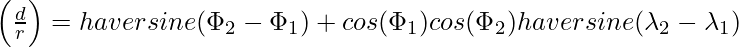
where r is the radius of the earth(6371 km), d is the distance between two points, 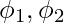 is the latitude of the two points, and
is the latitude of the two points, and 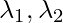 is the longitude of the two points respectively.
is the longitude of the two points respectively.
Solving d by applying the inverse haversine or by using the inverse sine function, we get:
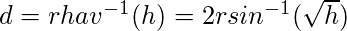
or
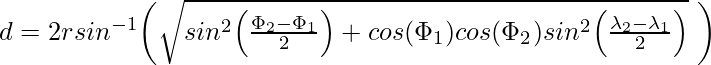
The distance between Big Ben in London (51.5007° N, 0.1246° W) and The Statue of Liberty in
New York (40.6892° N, 74.0445° W) is 5574.8 km. This is not the exact measurement because the
formula assumes that the Earth is a perfect sphere when in fact it is an oblate spheroid.
Below is the implementation of the above formulae:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
static double haversine(double lat1, double lon1,
double lat2, double lon2)
{
double dLat = (lat2 - lat1) *
M_PI / 180.0;
double dLon = (lon2 - lon1) *
M_PI / 180.0;
lat1 = (lat1) * M_PI / 180.0;
lat2 = (lat2) * M_PI / 180.0;
double a = pow(sin(dLat / 2), 2) +
pow(sin(dLon / 2), 2) *
cos(lat1) * cos(lat2);
double rad = 6371;
double c = 2 * asin(sqrt(a));
return rad * c;
}
int main()
{
double lat1 = 51.5007;
double lon1 = 0.1246;
double lat2 = 40.6892;
double lon2 = 74.0445;
cout << haversine(lat1, lon1,
lat2, lon2) << " K.M.";
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class Haversine {
static double haversine(double lat1, double lon1,
double lat2, double lon2)
{
double dLat = Math.toRadians(lat2 - lat1);
double dLon = Math.toRadians(lon2 - lon1);
lat1 = Math.toRadians(lat1);
lat2 = Math.toRadians(lat2);
double a = Math.pow(Math.sin(dLat / 2), 2) +
Math.pow(Math.sin(dLon / 2), 2) *
Math.cos(lat1) *
Math.cos(lat2);
double rad = 6371;
double c = 2 * Math.asin(Math.sqrt(a));
return rad * c;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double lat1 = 51.5007;
double lon1 = 0.1246;
double lat2 = 40.6892;
double lon2 = 74.0445;
System.out.println(haversine(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2) + " K.M.");
}
}
|
Python 3
import math
def haversine(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2):
dLat = (lat2 - lat1) * math.pi / 180.0
dLon = (lon2 - lon1) * math.pi / 180.0
lat1 = (lat1) * math.pi / 180.0
lat2 = (lat2) * math.pi / 180.0
a = (pow(math.sin(dLat / 2), 2) +
pow(math.sin(dLon / 2), 2) *
math.cos(lat1) * math.cos(lat2));
rad = 6371
c = 2 * math.asin(math.sqrt(a))
return rad * c
if __name__ == "__main__":
lat1 = 51.5007
lon1 = 0.1246
lat2 = 40.6892
lon2 = 74.0445
print(haversine(lat1, lon1,lat2, lon2), "K.M.")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static double haversine(double lat1, double lon1,
double lat2, double lon2)
{
double dLat = (Math.PI / 180) * (lat2 - lat1);
double dLon = (Math.PI / 180) * (lon2 - lon1);
lat1 = (Math.PI / 180) * (lat1);
lat2 = (Math.PI / 180) * (lat2);
double a = Math.Pow(Math.Sin(dLat / 2), 2) +
Math.Pow(Math.Sin(dLon / 2), 2) *
Math.Cos(lat1) * Math.Cos(lat2);
double rad = 6371;
double c = 2 * Math.Asin(Math.Sqrt(a));
return rad * c;
}
public static void Main()
{
double lat1 = 51.5007;
double lon1 = 0.1246;
double lat2 = 40.6892;
double lon2 = 74.0445;
Console.WriteLine(haversine(lat1, lon1,
lat2, lon2) + " K.M.");
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function haversine($lat1, $lon1,
$lat2, $lon2)
{
$dLat = ($lat2 - $lat1) *
M_PI / 180.0;
$dLon = ($lon2 - $lon1) *
M_PI / 180.0;
$lat1 = ($lat1) * M_PI / 180.0;
$lat2 = ($lat2) * M_PI / 180.0;
$a = pow(sin($dLat / 2), 2) +
pow(sin($dLon / 2), 2) *
cos($lat1) * cos($lat2);
$rad = 6371;
$c = 2 * asin(sqrt($a));
return $rad * $c;
}
$lat1 = 51.5007;
$lon1 = 0.1246;
$lat2 = 40.6892;
$lon2 = 74.0445;
echo haversine($lat1, $lon1,
$lat2, $lon2) .
" K.M.";
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function haversine(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2)
{
let dLat = (lat2 - lat1) * Math.PI / 180.0;
let dLon = (lon2 - lon1) * Math.PI / 180.0;
lat1 = (lat1) * Math.PI / 180.0;
lat2 = (lat2) * Math.PI / 180.0;
let a = Math.pow(Math.sin(dLat / 2), 2) +
Math.pow(Math.sin(dLon / 2), 2) *
Math.cos(lat1) *
Math.cos(lat2);
let rad = 6371;
let c = 2 * Math.asin(Math.sqrt(a));
return rad * c;
}
let lat1 = 51.5007;
let lon1 = 0.1246;
let lat2 = 40.6892;
let lon2 = 74.0445;
document.write(haversine(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2) + " K.M.");
</script>
|
Output: 5574.840456848555 K.M.
Time Complexity: O(logn) as inbuilt sqrt function is used
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...