Hashtable keys() Method in Java
Last Updated :
09 Oct, 2021
As we all know enumeration defines java class type so do enumerations can have constructors, methods, and instance variables. The java.util.Hashtable.keys() method of Hashtable class in Java is used to get the enumeration of the keys present in the hashtable.
Illustration:
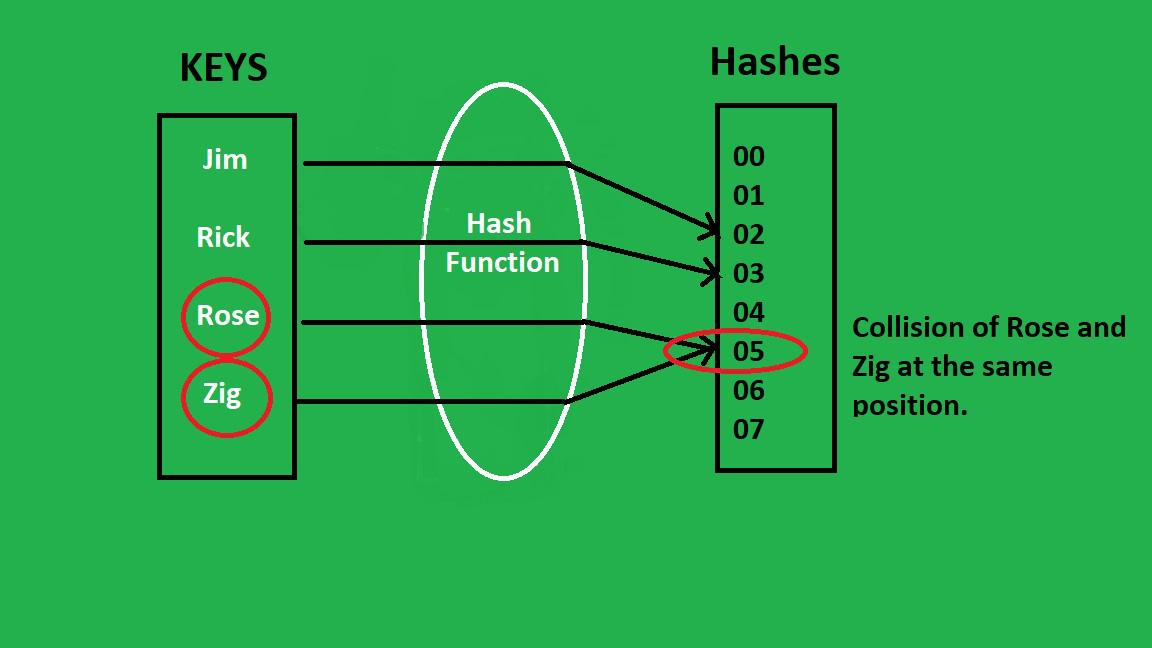
Syntax:
public Enumeration<K> keys()
Enumeration enu = Hash_table.keys();
Return value: An enumeration of the keys of the Hashtable.
Example 1:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Hashtable<Integer, String> hash_table
= new Hashtable<Integer, String>();
hash_table.put(10, "Geeks");
hash_table.put(15, "4");
hash_table.put(20, "Geeks");
hash_table.put(25, "Welcomes");
hash_table.put(30, "You");
System.out.println("The Table is: " + hash_table);
Enumeration enu = hash_table.keys();
System.out.println("The enumeration of keys are:");
while (enu.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println(enu.nextElement());
}
}
}
|
Output:
The Table is: {10=Geeks, 20=Geeks, 30=You, 15=4, 25=Welcomes}
The enumeration of keys are:
10
20
30
15
25
Example 2:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Hashtable<String, Integer> hash_table
= new Hashtable<String, Integer>();
hash_table.put("Geeks", 10);
hash_table.put("4", 15);
hash_table.put("Geeks", 20);
hash_table.put("Welcomes", 25);
hash_table.put("You", 30);
System.out.println("The Table is: " + hash_table);
Enumeration enu = hash_table.keys();
System.out.println("The enumeration of keys are:");
while (enu.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println(enu.nextElement());
}
}
}
|
Output:
The Table is: {You=30, Welcomes=25, 4=15, Geeks=20}
The enumeration of keys are:
You
Welcomes
4
Geeks
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...