GSM in Wireless Communication
Last Updated :
23 Mar, 2023
GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communication. GSM is an open and digital cellular technology used for mobile communication. It uses 4 different frequency bands of 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz and 1900 MHz . It uses the combination of FDMA and TDMA. This article includes all the concepts of GSM architecture and how it works.
GSM is having 4 different sizes of cells are used in GSM :
- Macro : In this size of cell, Base Station antenna is installed.
- Micro : In this size of cell, antenna height is less than the average roof level.
- Pico : Small cells’ diameter of few meters.
- Umbrella : It covers the shadowed (Fill the gaps between cells) regions.
Features of GSM are :
- Supports international roaming
- Clear voice clarity
- Ability to support multiple handheld devices.
- Spectral / frequency efficiency
- Low powered handheld devices.
- Ease of accessing network
- International ISDN compatibility.
- Low service cost.
- New features and services.
GSM is nothing but a larger system which is divided into further 3 subsystems.
- BSS : BSS stands for Base Station Subsystem. BSS handles traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. BSS having two components BTS and BSC.
- NSS : NSS stands for Network and Switching Subsystem. NSS is the core network of GSM. That carried out call and mobility management functions for mobile phone present in network. NSS have different components like VLR, HLR and EIR.
- OSS : OSS stands for Operating Subsystem. OSS is a functional entity which the network operator monitor and control the system. OMC is the part of OSS. Purpose of OSS is to offer the customer cost-effective support for all GSM related maintenance services.
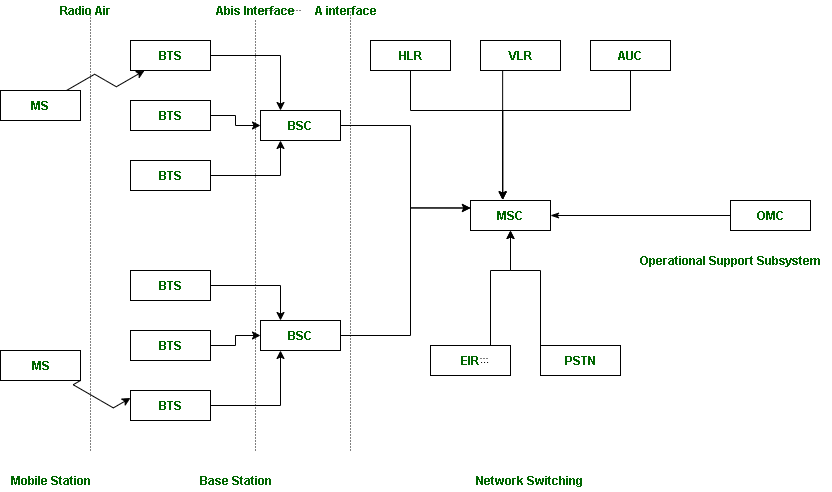
Suppose there are 3 Mobile stations which are connected with the tower and that tower is connected to BTS through TRX, then further connected to BSC and MSC. Let’s understand the functionality of different components.
1. MS : MS stands for Mobile System. MS comprises user equipment and software needed for communication with a mobile network. Mobile Station (MS) = Mobile Equipment(ME) + Subscriber Identity Module (SIM). Now, these mobile stations are connected to tower and that tower connected with BTS through TRX. TRX is a transceiver which comprises transmitter and receiver. Transceiver has two performance of sending and receiving.
2. BTS : BTS stands for Base Transceiver Station which facilitates wireless communication between user equipment and a network. Every tower has BTS.
3. BSC : BSC stands for Base Station Controller. BSC has multiple BTS. You can consider the BSC as a local exchange of your area which has multiple towers and multiple towers have BTS.
4. MSC : MSC stands for Mobile Switching Center. MSC is associated with communication switching functions such as call setup, call release and routing. Call tracing, call forwarding all functions are performed at the MSC level. MSC is having further components like VLR, HLR, AUC, EIR and PSTN.
- VLR : VLR stands for Visitor Location Register. VLR is a database which contains the exact location of all mobile subscribers currently present in the service area of MSC. If you are going from one state to another state then your entry is marked into the database of VLR.
- HLR : HLR stands for Home Location Register. HLR is a database containing pertinent data regarding subscribers authorized to use a GSM network.. If you purchase SIM card from in the HLR. HLR is like a home which contains all data like your ID proof, which plan you are taking, which caller tune you are using etc.
- AUC : AUC stands for Authentication Center. AUC authenticates the mobile subscriber that wants to connect in the network.
- EIR : EIR stands for Equipment Identity Register. EIR is a database that keeps the record of all allowed or banned in the network. If you are banned in the network then you can’t enter the network, and you can’t make the calls.
- PSTN : PSTN stands for Public Switched Telephone Network. PSTN connects with MSC. PSTN originally a network of fixed line analog telephone systems. Now almost entirely digital in its core network and includes mobile and other networks as well as fixed telephones. The earlier landline phones which places at our home is nothing but PSTN.
5.OMC : OMC stands for Operation Maintenance Center. OMC monitor and maintain the performance of each MS, BSC and MSC within a GSM system.
Three subsystem BSS, NSS and OSS are connected with each other via some interfaces. Total three interfaces are there:
- Air Interface : Air interface is also known as UM interface. Interface between MS and BTS is called as UM interface because it is mobile analog to the U interface of ISDN.
- Abis Interface : It is a BSS internal interface linking with BTS and BSC.
- A interface : It provides communication between BSS and MSC.
Services of GSM:
- Bearer services/ data services:
GSM specifies different mechanism for data transmission, The original GSM allowing for data rates of up to 9600 bits/s.
Bearer services permit transparent or non transparent data transmission.
- Transparent bearer services:
Transparent bearer services only use the physical layer to transmit data. Data transmission has a constant delay at throughput if no transmission error occurs.
- Non-transparent bearer services:
Non-transparent bearer services use protocols of layer two and three two three to implement error correction and flow control.(data link layer and network layer).
2.Tele services:
Tele services are nothing but we use now as at also.
- Video calls.
- Video text and face emoji.
- short text message(SMS).
3.Supplementary services:
supplementary services it means advanced services.
- Conference calls.
- Call waiting.
- Call forwarding.
GSM security:
- GSM offers several security using confidential information stored in the AUC and in the individual SIM.
- The SIM stores personal secret data and is protected with a pin against unauthorized use.
Advantages:
Compatibility: GSM is widely used around the world, so it is compatible with many different networks and devices.
Security: GSM offers enhanced security features such as authentication, encryption and confidentiality, which helps to protect the user’s privacy and data.
Efficient use of bandwidth: GSM uses a time-division multiplexing (TDM) technique which enables many users to share the same frequency channel at different times, making it an efficient use of the available bandwidth.
Roaming: GSM allows users to roam internationally and use their mobile phones in other countries that use the same GSM standard.
Wide range of features: GSM supports a wide range of features, including call forwarding, call waiting, voicemail, conference calling, and more.
Disadvantages:
Limited coverage: GSM networks may have limited coverage in some remote areas, which can make it difficult for users to make calls or access the internet.
Network congestion: GSM networks may become congested during peak hours, which can lead to dropped calls or poor call quality.
Security vulnerabilities: Although GSM offers enhanced security features, it is still vulnerable to certain types of attacks, such as eavesdropping and spoofing.
Data transfer speed: GSM networks offer relatively slow data transfer speeds compared to newer technologies such as 3G and 4G.
Limited capacity: GSM networks have a limited capacity for handling large volumes of data, which can be a disadvantage for users who require high-speed internet access or other data-intensive applications.
Hence, this is the complete architecture and functionalities of GSM components.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...