Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (GPON) Fundamentals
Last Updated :
17 Oct, 2020
GPON is abbreviation for Gigabit Passive Optical Networks which is defined series G.984.1 through G.984.6 by ITU-T recommendation. Gigabit Passive Optical Networks can be transported ATM, TDM (PSTN, ISDN, E1, and E3) traffic and by Ethernet. The network architecture of GBON various FTTx architecture is given below as follows.

GBON
Figure 1 shown above shows a single fiber from OLT runs to a passive Optical Splitter. Its location is near user’s point. Passive word in passive optical splitter means that it does not require any power to operate. Optical splitter does work to divides optical power into N separate paths to users. It varies between range of 2 to 128. In the part from Optical Splitter, a single-mode (SM) fiber strand runs towards each user.
Typical GBON Architecture is described below :
This figure 2 shows two multiplexing mechanisms as following.
- In downstream direction :
It states the multiplexing mechanism from OLT to users. It implies that data is transferred in a broadcast manner. It enables encryption (AES) which is used to prevent eavesdropping.
- In upstream direction :
It states the multiplexing mechanism from users to OLT. It enables data packets are transmitted in a TDMA manner.

GBON ARCHITECTURE
GPON key technologies :
- ONU Identifier (ONU-ID) :
ONU Identifier is defined as 8-bit identifier. Its main purpose is to assign 8-bit number by OLT to ONU during ONU activation via PLOAM messages. ONU id remains unique ONU is powered off or deactivated by the OLT.
- Allocation Identifier (ALLOC_ID) :
ONU Identifier is defined as 12-bit identifier. It assigns 12-bit number to ONU. It is used to identify traffic-bearing entity which is also called T-CONT.
- Transmission Containers (T-CONT) :
A Transmission Container (T-CONT) is an Optical Network Unit which is used to t represent group of logical connections that appear as a single entity. The purpose behind representation is to upstream bandwidth assignment on PON. For instance, in given Optical Network Unit, number of supported T-CONTs is fixed.
To active T-CONT instance, OLT has to establish mapping between T-CONT via PLOAM messages.
Five types of T-CONTs which can be allocated to the user are as follows :
- Type 1 –
It is used in high proxy like VOIP. It has high-frequency bandwidth which is used for services sensitive to delay.
- Type 2 and Type 3 –
Its main usage is in video services and data services of higher priorities.
- Type 4 –
This is defined as best-effort time and it is put into use of data services such as Internet and services.
- Type 5 –
It is defined as mixed type as it is mixture of all bandwidth types and all bearing services.
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) :
The major responsibility of Optical Network Unit (ONU) is allocating upstream bandwidth to ONUs. It may also collide if they were transmitted at random times. Distance location of ONUs can be at varying distances therefore, transmission delay from each ONU is unique. To measure interval of time for upstream transmission, grant is permission is used.
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) is methodology that allows users to quickly for bandwidth allocation based on current traffic requirements. It is capable of managing bursty upstream traffic. Furthermore, DBA upstream timeslots to shrink and grow based on the upstream traffic loads.
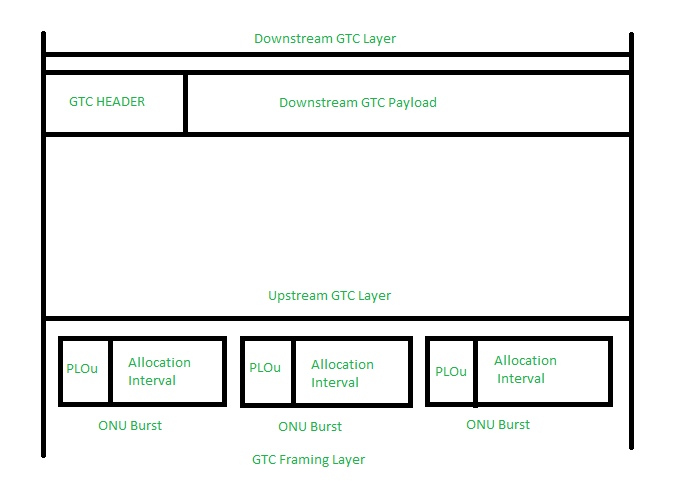
GPON Transmission Convergence (TC) Layer :
GPON Transmission Convergence (TC) layer is used to specify media access control protocol, OAM processes, and information encryption method. Figure 3 shows below describes GTC frame structures for downstream and upstream directions. It also consists of physical control block downstream (PCB) and GTC payload section.
In GPON Transmission Convergence (TC) Layer downstream GTC frame for PON provides the common time reference. It also provides common control signaling for upstream.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...