Get Current directory in Python
Last Updated :
03 Feb, 2024
In this article, we will cover How to Get and Change the Working Directory in Python. While working with file handling you might have noticed that files are referenced only by their names, e.g. ‘GFG.txt’ and if the file is not located in the directory of the script, Python raises an error. The concept of the Current Working Directory (CWD) becomes important here. Consider the CWD as the folder, the Python is operating inside. Whenever the files are called only by their name, Python assumes that it starts in the CWD which means that a name-only reference will be successful only if the file is in Python’s CWD.
Note: The folder where the Python script is running is known as the Current Directory. This may not be the path where the Python script is located.
What is the Python os module?
Python provides an os module for interacting with the operating system. This module comes under Python’s standard utility module. All functions in the os module raise OSError in the case of invalid or inaccessible file names and paths, or other arguments that have the correct type but are not accepted by the operating system.
Python Find Current Directory
Get a Directory of the Current Python Script using sys.argv[0]
In this example, we have used sys.argv[0] to retrieve the path of the script file and os.path.dirname() extracts the current directory from the path.
Python3
import os
import sys
script_directory = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(sys.argv[0]))
print(script_directory)
|
Output :

Get a directory of the current Python script
Get the Directory of the Current Python Script using Inspect Module
In this example, we have used inspect.getfile(inspect.currentframe()) which returns the path of the current script file, and os.path.dirname() extracts the current directory from the path.
Python3
import inspect
import os
script_directory = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(
inspect.getfile(inspect.currentframe())))
print(script_directory)
|
Output :

Get directory of current Python script
Get the current working directory using os.getcwd()
In this example, we have used os.getcwd() to get current directory of Python script.
Python3
import os
print("File location using os.getcwd():", os.getcwd())
|
Output :
File location using os.getcwd(): /home/tuhingfg/Documents/Scripts
Note: Using os.getcwd() doesn’t work as expected when running the Python code from a different directory from the Python script.
Unexpected result when running Python script from a different directory other than script using os.getcwd()
The Python script is placed inside /home/tuhingfg/Documents/Scripts. When we run the script from inside the same folder, it gives the correct script location. But when we change our directory to some other place, it outputs the location of that directory. This is because os.getcwd() considers the directory from where we are executing the script. Based on this, the result of os.getcwd() also varies.
Python3
import os
print("File location using os.getcwd():", os.getcwd())
|
Output:
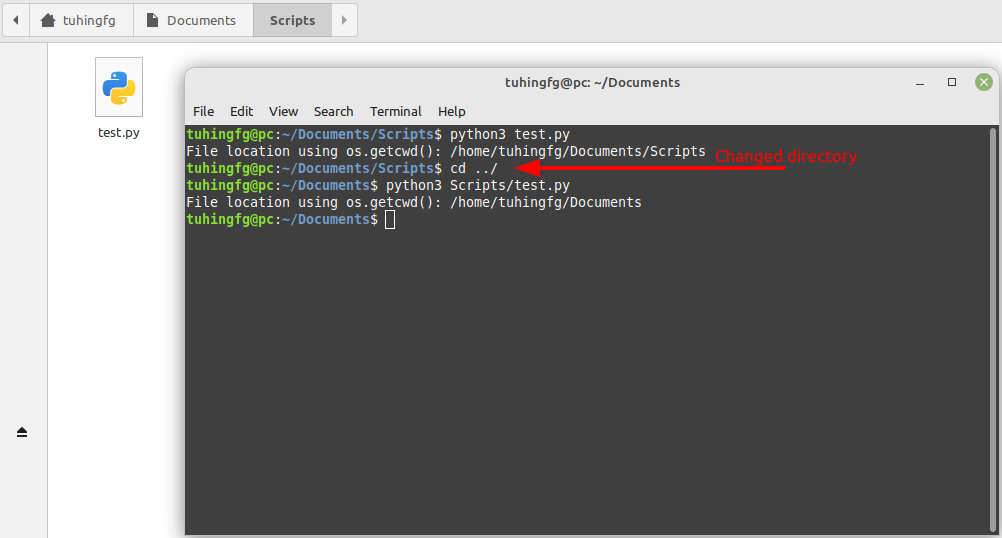
Get Script location using os.getcwd()
Get the Python Script location using os.path.realpath() Method
os.path.realpath() can be used to get the path of the current Python script. Actually, os.path.realpath() method in Python is used to get the canonical path of the specified filename by eliminating any symbolic links encountered in the path. A special variable __file__ is passed to the realpath() method to get the path of the Python script.
In this example, the os.getcwd() and __file__ provide two different results. Since we are executing the script from a different folder than the script, os.getcwd() output has changed according to the folder of execution of the script. But __file__ generates the constant result irrespective of the current working directory.
Python3
import os
print("File location using os.getcwd():",
os.getcwd())
print(f"File location using __file__ variable:"+
"{os.path.realpath(os.path.dirname(__file__))}")
|
Output:

Get a directory With Python
Note: __file__ is the pathname of the file from which the module was loaded if it was loaded from a file.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...