final variables in Java
Last Updated :
23 Feb, 2024
In Java, we can use final keyword with variables, methods, and classes. When the final keyword is used with a variable of primitive data types such as int, float, etc), the value of the variable cannot be changed.
Example 1: Usage of final with primitive datatype
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
final int i = 10;
i = 30;
}
}
|
Output:
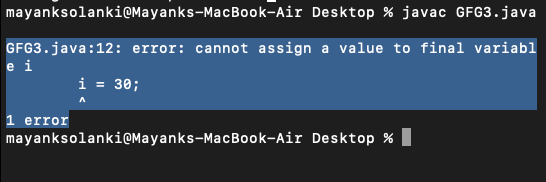
Now you must be wondering what if we do use final keyword non-primitive variables, let us explore the same as we did above with the help of an example.
Note: Non-primitive variables are always references to objects in Java, the members of the referred object can be changed. final for non-primitive variables just means that they cannot be changed to refer to any other object.
Example 2: Usage of final with primitive datatype
Java
class Helper {
int i = 10;
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
final Helper t1 = new Helper();
t1.i = 30;
System.out.print("Successfully executed");
}
}
|
Output
Successfully executed
Note: A final variable can’t be declared inside a function, this is so because scope of local variables of a function are limited to scope of function and declaring it their will be against the principle of immutability. If program demands a constant value then the final variable should be declared at class level and may be used in function.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...