Flip Binary Tree
Last Updated :
02 May, 2023
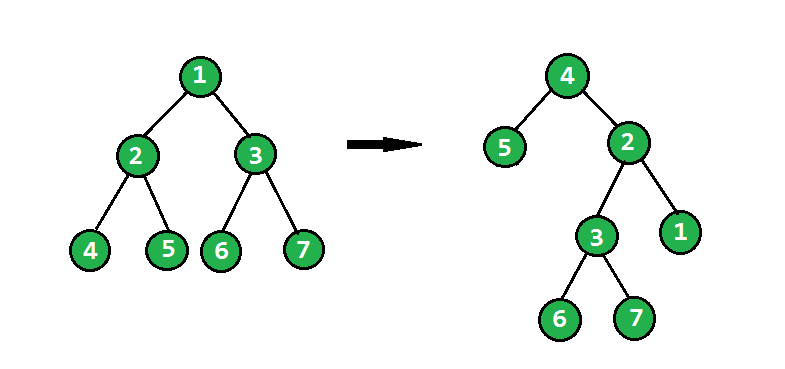
A Given a binary tree, the task is to flip the binary tree towards the right direction that is clockwise. See the below examples to see the transformation.
In the flip operation, the leftmost node becomes the root of the flipped tree and its parent becomes its right child and the right sibling becomes its left child and the same should be done for all left most nodes recursively.

Below is the main rotation code of a subtree
root->left->left = root->right;
root->left->right = root;
root->left = NULL;
root->right = NULL;
The above code can be understood by the following diagram –
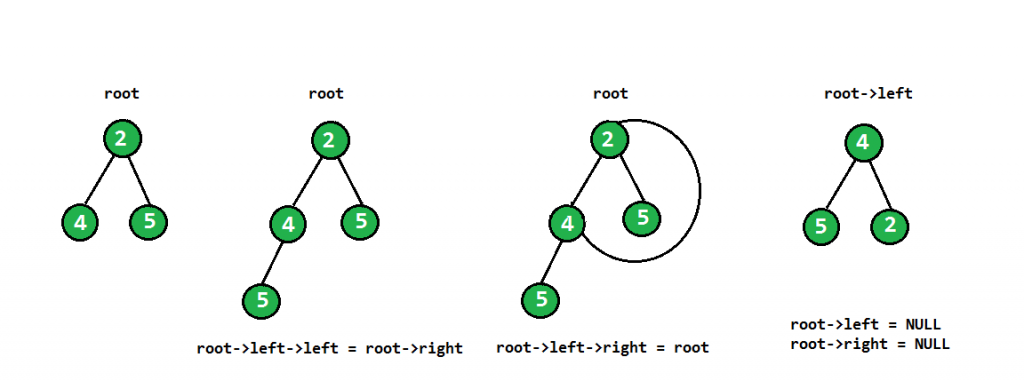
As we are storing root->left in the flipped root, flipped subtree gets stored in each recursive call.
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node *temp = new struct Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
Node* flipBinaryTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return root;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return root;
Node* flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root->left);
root->left->left = root->right;
root->left->right = root;
root->left = root->right = NULL;
return flippedRoot;
}
void printLevelOrder(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL) return;
queue<Node *> q;
q.push(root);
while (1)
{
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node *node = q.front();
cout << node->data << " ";
q.pop();
if (node->left != NULL)
q.push(node->left);
if (node->right != NULL)
q.push(node->right);
nodeCount--;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Level order traversal of given tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
cout << "\nLevel order traversal of the flipped"
" tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class FlipTree {
public static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return root;
if (root.left == null && root.right ==null)
return root;
Node flippedRoot=flipBinaryTree(root.left);
root.left.left=root.right;
root.left.right=root;
root.left=root.right=null;
return flippedRoot;
}
public static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
if(root==null)
return ;
Queue<Node> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while(true)
{
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.remove();
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
if (node.left != null)
q.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
q.add(node.right);
nodeCount--;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Node root=new Node(1);
root.left=new Node(2);
root.right=new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Level order traversal of given tree");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
System.out.println("Level order traversal of flipped tree");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int data)
{
this.data=data;
}
};
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.right = None
self.left = None
def flipBinaryTree(root):
if root is None:
return root
if (root.left is None and
root.right is None):
return root
flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left)
root.left.left = root.right
root.left.right = root
root.left = root.right = None
return flippedRoot
def printLevelOrder(root):
if root is None:
return
from Queue import Queue
q = Queue()
q.put(root)
while(True):
nodeCount = q.qsize()
if nodeCount == 0:
break
while nodeCount > 0:
node = q.get()
print(node.data, end=" ")
if node.left is not None:
q.put(node.left)
if node.right is not None:
q.put(node.right)
nodeCount -= 1
print
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(4)
root.right.right = Node(5)
print("Level order traversal of given tree")
printLevelOrder(root)
root = flipBinaryTree(root)
print("\nLevel order traversal of the flipped tree")
printLevelOrder(root)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class FlipTree
{
public static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return root;
if (root.left == null && root.right ==null)
return root;
Node flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left);
root.left.left = root.right;
root.left.right = root;
root.left = root.right = null;
return flippedRoot;
}
public static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
if(root == null)
return ;
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
q.Enqueue(root);
while(true)
{
int nodeCount = q.Count;
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.Dequeue();
Console.Write(node.data+" ");
if (node.left != null)
q.Enqueue(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
q.Enqueue(node.right);
nodeCount--;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Level order traversal of given tree");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
Console.WriteLine("Level order traversal of flipped tree");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
};
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node
{
constructor( data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left=this.right=null;
}
};
function flipBinaryTree(root)
{
if (root == null)
return root;
if (root.left == null && root.right ==null)
return root;
let flippedRoot=flipBinaryTree(root.left);
root.left.left=root.right;
root.left.right=root;
root.left=root.right=null;
return flippedRoot;
}
function printLevelOrder(root)
{
if(root==null)
return ;
let q=[];
q.push(root);
while(true)
{
let nodeCount = q.length;
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
let node = q.shift();
document.write(node.data+" ");
if (node.left != null)
q.push(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
q.push(node.right);
nodeCount--;
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
let root=new Node(1);
root.left=new Node(2);
root.right=new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
document.write("Level order traversal of given tree<br>");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
document.write("Level order traversal of flipped tree<br>");
printLevelOrder(root);
</script>
|
Output
Level order traversal of given tree
1
2 3
4 5
Level order traversal of the flipped tree
2
3 1
4 5
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the given binary tree.
Auxiliary Space: O(n), the size of the queue can grow up to n.
Iterative Approach: This approach is contributed by Pal13.
The iterative solution follows the same approach as the recursive one, the only thing we need to pay attention to is saving the node information that will be overwritten.
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node *temp = new struct Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
Node* flipBinaryTree(Node* root)
{
Node *curr = root;
Node *next = NULL;
Node *temp = NULL;
Node *prev = NULL;
while(curr)
{
next = curr->left;
curr->left = temp;
temp = curr->right;
curr->right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
void printLevelOrder(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL) return;
queue<Node *> q;
q.push(root);
while (1)
{
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node *node = q.front();
cout << node->data << " ";
q.pop();
if (node->left != NULL)
q.push(node->left);
if (node->right != NULL)
q.push(node->right);
nodeCount--;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Level order traversal of given tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
cout << "\nLevel order traversal of the flipped"
" tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
Node curr = root;
Node next = null;
Node temp = null;
Node prev = null;
while(curr != null)
{
next = curr.left;
curr.left = temp;
temp = curr.right;
curr.right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
if (root == null) return;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<Node>();
q.add(root);
while (true)
{
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.peek();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
q.remove();
if (node.left != null)
q.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
q.add(node.right);
nodeCount--;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
System.out.print("Level order traversal " +
"of given tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
System.out.print("\nLevel order traversal " +
"of the flipped tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
|
Python3
from collections import deque
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
def flipBinaryTree(root):
curr = root
next = None
temp = None
prev = None
while(curr):
next = curr.left
curr.left = temp
temp = curr.right
curr.right = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
return prev
def printLevelOrder(root):
if (root == None):
return
q = deque()
q.append(root)
while (1):
nodeCount = len(q)
if (nodeCount == 0):
break
while (nodeCount > 0):
node = q.popleft()
print(node.data, end = " ")
if (node.left != None):
q.append(node.left)
if (node.right != None):
q.append(node.right)
nodeCount -= 1
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(4)
root.right.right = Node(5)
print("Level order traversal of given tree")
printLevelOrder(root)
root = flipBinaryTree(root)
print("\nLevel order traversal of the flipped"
" tree")
printLevelOrder(root)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
}
public static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
public static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
Node curr = root;
Node next = null;
Node temp = null;
Node prev = null;
while (curr != null)
{
next = curr.left;
curr.left = temp;
temp = curr.right;
curr.right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
public static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
LinkedList<Node> q = new LinkedList<Node>();
q.AddLast(root);
while (true)
{
int nodeCount = q.Count;
if (nodeCount == 0)
{
break;
}
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.First.Value;
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
q.RemoveFirst();
if (node.left != null)
{
q.AddLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null)
{
q.AddLast(node.right);
}
nodeCount--;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
Console.Write("Level order traversal " +
"of given tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
Console.Write("\nLevel order traversal " +
"of the flipped tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node
{
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = data;
}
}
function newNode(data)
{
let temp = new Node(data);
return temp;
}
function flipBinaryTree(root)
{
let curr = root;
let next = null;
let temp = null;
let prev = null;
while(curr != null)
{
next = curr.left;
curr.left = temp;
temp = curr.right;
curr.right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
function printLevelOrder(root)
{
if (root == null) return;
let q = [];
q.push(root);
while (true)
{
let nodeCount = q.length;
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
let node = q[0];
document.write(node.data + " ");
q.shift();
if (node.left != null)
q.push(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
q.push(node.right);
nodeCount--;
}
document.write("</br>");
}
}
let root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
document.write("Level order traversal " +
"of given tree" + "</br>");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
document.write("</br>" + "Level order traversal " +
"of the flipped tree" + "</br>");
printLevelOrder(root);
</script>
|
Output
Level order traversal of given tree
1
2 3
4 5
Level order traversal of the flipped tree
2
3 1
4 5
Complexity Analysis:
- Time complexity: O(n) as in the worst case, depth of binary tree will be n.
- Auxiliary Space: O(1).
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...