Find whether there is path between two cells in matrix
Last Updated :
22 Nov, 2023
Given N X N matrix filled with 1, 0, 2, 3. Find whether there is a path possible from source to destination, traversing through blank cells only. You can traverse up, down, right, and left.
- A value of cell 1 means Source.
- A value of cell 2 means Destination.
- A value of cell 3 means Blank cell.
- A value of cell 0 means Blank Wall.
Note: there are an only a single source and single destination(sink).
Examples:
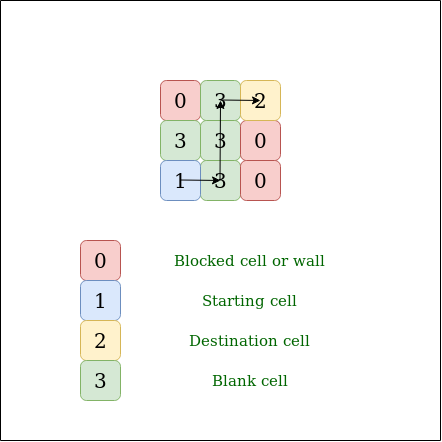
Input:
M[3][3] = {{ 0, 3, 2 },
{ 3, 3, 0 },
{ 1, 3, 0 }};
Output : Yes
Explanation:
Input:
M[4][4] = {{ 0, 3, 1, 0 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 0, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 }};
Output: Yes
Explanation:

Find whether there is path between two cells in matrix using Recursion:
The idea is to find the source index of the cell in each matrix and then recursively find a path from the source index to the destination in the matrix. The algorithm involves recursively finding all the paths until a final path is found to the destination.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Traverse the matrix and find the starting index of the matrix.
- Create a recursive function that takes the index and visited matrix.
- Mark the current cell and check if the current cell is a destination or not. If the current cell is the destination, return true.
- Call the recursion function for all adjacent empty and unvisited cells.
- If any of the recursive functions returns true then unmark the cell and return true else unmark the cell and return false.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
bool isSafe(int i, int j, int matrix[][N])
{
if (i >= 0 && i < N && j >= 0 && j < N)
return true;
return false;
}
bool isaPath(int matrix[][N], int i, int j,
bool visited[][N])
{
if (isSafe(i, j, matrix) && matrix[i][j] != 0
&& !visited[i][j]) {
visited[i][j] = true;
if (matrix[i][j] == 2)
return true;
bool up = isaPath(matrix, i - 1, j, visited);
if (up)
return true;
bool left = isaPath(matrix, i, j - 1, visited);
if (left)
return true;
bool down = isaPath(matrix, i + 1, j, visited);
if (down)
return true;
bool right = isaPath(matrix, i, j + 1, visited);
if (right)
return true;
}
return false;
}
void isPath(int matrix[][N])
{
bool visited[N][N];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j])
if (isaPath(matrix, i, j, visited)) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag)
cout << "YES";
else
cout << "NO";
}
int main()
{
int matrix[N][N] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
isPath(matrix);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class Path {
public static void isPath(int matrix[][], int n)
{
boolean visited[][] = new boolean[n][n];
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j])
if (isPath(matrix, i, j, visited)) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag)
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
}
public static boolean isSafe(int i, int j,
int matrix[][])
{
if (i >= 0 && i < matrix.length && j >= 0
&& j < matrix[0].length)
return true;
return false;
}
public static boolean isPath(int matrix[][], int i,
int j, boolean visited[][])
{
if (isSafe(i, j, matrix) && matrix[i][j] != 0
&& !visited[i][j]) {
visited[i][j] = true;
if (matrix[i][j] == 2)
return true;
boolean up = isPath(matrix, i - 1, j, visited);
if (up)
return true;
boolean left
= isPath(matrix, i, j - 1, visited);
if (left)
return true;
boolean down
= isPath(matrix, i + 1, j, visited);
if (down)
return true;
boolean right
= isPath(matrix, i, j + 1, visited);
if (right)
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int matrix[][] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
isPath(matrix, 4);
}
}
|
Python3
def isPath(matrix, n):
visited = [[False for x in range(n)]
for y in range(n)]
flag = False
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if (matrix[i][j] == 1 and not
visited[i][j]):
if (checkPath(matrix, i,
j, visited)):
flag = True
break
if (flag):
print("YES")
else:
print("NO")
def isSafe(i, j, matrix):
if (i >= 0 and i < len(matrix) and
j >= 0 and j < len(matrix[0])):
return True
return False
def checkPath(matrix, i, j,
visited):
if (isSafe(i, j, matrix) and
matrix[i][j] != 0 and not
visited[i][j]):
visited[i][j] = True
if (matrix[i][j] == 2):
return True
up = checkPath(matrix, i - 1,
j, visited)
if (up):
return True
left = checkPath(matrix, i,
j - 1, visited)
if (left):
return True
down = checkPath(matrix, i + 1,
j, visited)
if (down):
return True
right = checkPath(matrix, i,
j + 1, visited)
if (right):
return True
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
matrix = [[0, 3, 0, 1],
[3, 0, 3, 3],
[2, 3, 3, 3],
[0, 3, 3, 3]]
isPath(matrix, 4)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void isPath(int[, ] matrix, int n)
{
bool[, ] visited = new bool[n, n];
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[i, j] == 1 && !visited[i, j])
if (isPath(matrix, i, j, visited)) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag)
Console.WriteLine("YES");
else
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
public static bool isSafe(int i, int j, int[, ] matrix)
{
if (i >= 0 && i < matrix.GetLength(0) && j >= 0
&& j < matrix.GetLength(1))
return true;
return false;
}
public static bool isPath(int[, ] matrix, int i, int j,
bool[, ] visited)
{
if (isSafe(i, j, matrix) && matrix[i, j] != 0
&& !visited[i, j]) {
visited[i, j] = true;
if (matrix[i, j] == 2)
return true;
bool up = isPath(matrix, i - 1, j, visited);
if (up)
return true;
bool left = isPath(matrix, i, j - 1, visited);
if (left)
return true;
bool down = isPath(matrix, i + 1, j, visited);
if (down)
return true;
bool right = isPath(matrix, i, j + 1, visited);
if (right)
return true;
}
return false;
}
static void Main()
{
int[, ] matrix = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
isPath(matrix, 4);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function isPath(matrix,n)
{
let visited = new Array(n);
for(let i=0;i<n;i++)
{
visited[i]=new Array(n);
for(let j=0;j<n;j++)
{
visited[i][j]=false;
}
}
let flag = false;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (
matrix[i][j] == 1
&& !visited[i][j])
if (checkPath(
matrix, i, j, visited)) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag)
document.write("YES<br>");
else
document.write("NO<br>");
}
function isSafe(i,j,matrix)
{
if (
i >= 0 && i < matrix.length
&& j >= 0
&& j < matrix[0].length)
return true;
return false;
}
function checkPath(matrix,i,j,visited)
{
if (
isSafe(i, j, matrix)
&& matrix[i][j] != 0
&& !visited[i][j]) {
visited[i][j] = true;
if (matrix[i][j] == 2)
return true;
let up = checkPath(
matrix, i - 1,
j, visited);
if (up)
return true;
let left
= checkPath(
matrix, i, j - 1, visited);
if (left)
return true;
let down = checkPath(
matrix, i + 1, j, visited);
if (down)
return true;
let right
= checkPath(
matrix, i, j + 1,
visited);
if (right)
return true;
}
return false;
}
let matrix= [[ 0, 3, 0, 1 ],
[ 3, 0, 3, 3 ],
[ 2, 3, 3, 3 ],
[ 0, 3, 3, 3 ]];
isPath(matrix, 4);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N*M), In the worst case, we have to visit each cell only one time because we keep the visited array for not visiting the already visited cell.
Auxiliary Space: O(N*M), Space is required to store the visited array.
Find whether there is path between two cells in matrix using Breadth First Search:
The idea is to use Breadth-First Search. Consider each cell as a node and each boundary between any two adjacent cells be an edge. so the total number of Node is N * N. So the idea is to do a breadth-first search from the starting cell till the ending cell is found.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create an empty Graph having N*N node(Vertex), push all nodes into a graph, and note down the source and sink vertex.
- Now apply BFS on the graph, create a queue and insert the source node in the queue
- Run a loop till the size of the queue is greater than 0
- Remove the front node of the queue and check if the node is the destination if the destination returns true. mark the node
- Check all adjacent cells if unvisited and blank insert them in the queue.
- If the destination is reached return true.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
class Graph {
int V;
list<int>* adj;
public:
Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
void addEdge(int s, int d);
bool BFS(int s, int d);
};
void Graph::addEdge(int s, int d) { adj[s].push_back(d); }
bool Graph::BFS(int s, int d)
{
if (s == d)
return true;
bool* visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
list<int> queue;
visited[s] = true;
queue.push_back(s);
list<int>::iterator i;
while (!queue.empty()) {
s = queue.front();
queue.pop_front();
for (i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i) {
if (*i == d)
return true;
if (!visited[*i]) {
visited[*i] = true;
queue.push_back(*i);
}
}
}
return false;
}
bool isSafe(int i, int j, int M[][N])
{
if ((i < 0 || i >= N) || (j < 0 || j >= N)
|| M[i][j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
bool findPath(int M[][N])
{
int s, d;
int V = N * N + 2;
Graph g(V);
int k = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (M[i][j] != 0) {
if (isSafe(i, j + 1, M))
g.addEdge(k, k + 1);
if (isSafe(i, j - 1, M))
g.addEdge(k, k - 1);
if (i < N - 1 && isSafe(i + 1, j, M))
g.addEdge(k, k + N);
if (i > 0 && isSafe(i - 1, j, M))
g.addEdge(k, k - N);
}
if (M[i][j] == 1)
s = k;
if (M[i][j] == 2)
d = k;
k++;
}
}
return g.BFS(s, d);
}
int main()
{
int M[N][N] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
(findPath(M) == true) ? cout << "Yes"
: cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class Graph {
int V;
List<List<Integer> > adj;
Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList<>(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj.add(i, new ArrayList<>());
}
}
void addEdge(int s, int d) { adj.get(s).add(d); }
boolean BFS(int s, int d)
{
if (s == d)
return true;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited[s] = true;
queue.offer(s);
List<Integer> edges;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
s = queue.poll();
edges = adj.get(s);
for (int curr : edges) {
if (curr == d)
return true;
if (!visited[curr]) {
visited[curr] = true;
queue.offer(curr);
}
}
}
return false;
}
static boolean isSafe(int i, int j, int[][] M)
{
int N = M.length;
if ((i < 0 || i >= N) || (j < 0 || j >= N)
|| M[i][j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
static boolean findPath(int[][] M)
{
int s = -1, d = -1;
int N = M.length;
int V = N * N + 2;
Graph g = new Graph(V);
int k = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (M[i][j] != 0) {
if (isSafe(i, j + 1, M))
g.addEdge(k, k + 1);
if (isSafe(i, j - 1, M))
g.addEdge(k, k - 1);
if (i < N - 1 && isSafe(i + 1, j, M))
g.addEdge(k, k + N);
if (i > 0 && isSafe(i - 1, j, M))
g.addEdge(k, k - N);
}
if (M[i][j] == 1)
s = k;
if (M[i][j] == 2)
d = k;
k++;
}
}
return g.BFS(s, d);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
int[][] M = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
System.out.println(((findPath(M)) ? "Yes" : "No"));
}
}
|
Python3
from collections import defaultdict
class Graph:
def __init__(self):
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
def BFS(self, s, d):
if s == d:
return True
visited = [False]*(len(self.graph) + 1)
queue = []
queue.append(s)
visited[s] = True
while(queue):
s = queue.pop(0)
for i in self.graph[s]:
if i == d:
return True
if visited[i] == False:
queue.append(i)
visited[i] = True
return False
def isSafe(i, j, matrix):
if i >= 0 and i <= len(matrix) and j >= 0 and j <= len(matrix[0]):
return True
else:
return False
def findPath(M):
s, d = None, None
N = len(M)
g = Graph()
k = 1
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if (M[i][j] != 0):
if (isSafe(i, j + 1, M)):
g.addEdge(k, k + 1)
if (isSafe(i, j - 1, M)):
g.addEdge(k, k - 1)
if (isSafe(i + 1, j, M)):
g.addEdge(k, k + N)
if (isSafe(i - 1, j, M)):
g.addEdge(k, k - N)
if (M[i][j] == 1):
s = k
if (M[i][j] == 2):
d = k
k += 1
return g.BFS(s, d)
if __name__ == '__main__':
M = [[0, 3, 0, 1], [3, 0, 3, 3], [2, 3, 3, 3], [0, 3, 3, 3]]
if findPath(M):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Graph {
public int V;
public List<List<int> > adj;
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new List<List<int>>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
}
public void AddEdge(int s, int d) { adj[s].Add(d); }
public bool BFS(int s, int d)
{
if (s == d)
return true;
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
List<int> queue = new List<int>();
visited[s] = true;
queue.Add(s);
List<int> edges = new List<int>();
while (queue.Count != 0 ) {
s = queue[0];
queue.RemoveAt(0);
edges = adj[s];
foreach (int curr in edges) {
if (curr == d)
return true;
if (!visited[curr]) {
visited[curr] = true;
queue.Add(curr);
}
}
}
return false;
}
static bool isSafe(int i, int j, int[, ] M)
{
if ((i < 0 || i >= M.GetLength(0)) || (j < 0 || j >= M.GetLength(1))
|| M[i, j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
static bool findPath(int[, ] M)
{
int s = -1, d = -1;
int N = M.GetLength(0);
int V = N * N + 2;
Graph g = new Graph(V);
int k = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (M[i, j] != 0) {
if (isSafe(i, j + 1, M))
g.AddEdge(k, k + 1);
if (isSafe(i, j - 1, M))
g.AddEdge(k, k - 1);
if (i < N - 1 && isSafe(i + 1, j, M))
g.AddEdge(k, k + N);
if (i > 0 && isSafe(i - 1, j, M))
g.AddEdge(k, k - N);
}
if (M[i, j] == 1)
s = k;
if (M[i, j] == 2)
d = k;
k++;
}
}
return g.BFS(s, d);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[, ] M = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
Console.WriteLine(((findPath(M)) ? "Yes" : "No"));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let V;
let adj=[];
function Graph(v)
{
V=v;
for (let i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj.push([]);
}
}
function addEdge(s,d)
{
adj[s].push(d);
}
function BFS(s,d)
{
if (s == d)
return true;
let visited = new Array(V);
for(let i=0;i<V;i++)
{
visited[i]=false;
}
let queue=[];
visited[s] = true;
queue.push(s);
let edges;
while (queue.length!=0) {
s = queue.shift();
edges = adj[s];
for (let curr=0;curr< edges.length;curr++) {
if (edges[curr] == d)
return true;
if (!visited[edges[curr]]) {
visited[edges[curr]] = true;
queue.push(edges[curr]);
}
}
}
return false;
}
function isSafe(i,j,M)
{
let N = M.length;
if (
(i < 0 || i >= N)
|| (j < 0 || j >= N)
|| M[i][j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
function findPath(M)
{
let s = -1, d = -1;
let N = M.length;
let V = N * N + 2;
Graph(V);
let k = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (M[i][j] != 0) {
if (isSafe(i, j + 1, M))
addEdge(k, k + 1);
if (isSafe(i, j - 1, M))
addEdge(k, k - 1);
if (i < N - 1
&& isSafe(i + 1, j, M))
addEdge(k, k + N);
if (i > 0 && isSafe(i - 1, j, M))
addEdge(k, k - N);
}
if (M[i][j] == 1)
s = k;
if (M[i][j] == 2)
d = k;
k++;
}
}
return BFS(s, d);
}
let M = [[ 0, 3, 0, 1 ],
[ 3, 0, 3, 3 ],
[ 2, 3, 3, 3 ],
[ 0, 3, 3, 3 ]];
document.write(((findPath(M)) ? "Yes" : "No"));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N*M), Every cell of the matrix is visited only once so the time complexity is O(N*M).
Auxiliary Space: O(N*M), Space is required to store the visited array and to create the queue.
Find whether there is path between two cells in matrix using Breadth First Search (On matrix):
The idea is to use Breadth-First Search on the matrix itself. Consider a cell=(i,j) as a vertex v in the BFS queue. A new vertex u is placed in the BFS queue if u=(i+1,j) or u=(i-1,j) or u=(i,j+1) or u=(i,j-1). Starting the BFS algorithm from cell=(i,j) such that M[i][j] is 1 and stopping either if there was a reachable vertex u=(i,j) such that M[i][j] is 2 and returning true or every cell was covered and there was no such a cell and returning false.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create BFS queue q
- scan the matrix, if there exists a cell in the matrix such that its value is 1 then push it to q
- Run BFS algorithm with q, skipping cells that are not valid. i.e: they are walls (value is 0) or outside the matrix bounds and marking them as walls upon successful visitation.
- If in the BFS algorithm process there was a vertex x=(i,j) such that M[i][j] is 2 stop and return true.
- BFS algorithm terminated without returning true then there was no element M[i][j] which is 2, then return false
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define R 4
#define C 4
typedef struct BFSElement {
BFSElement(int i, int j)
{
this->i = i;
this->j = j;
}
int i;
int j;
} BFSElement;
bool findPath(int M[R][C])
{
queue<BFSElement> q;
for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j) {
if (M[i][j] == 1) {
q.push(BFSElement(i, j));
break;
}
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
BFSElement x = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = x.i;
int j = x.j;
if (i >= 0 && i < R && j >= 0 && j < C)
{
if (M[i][j] == 0)
continue;
if (M[i][j] == 2)
return true;
M[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = -1; k <= 1; k += 2) {
q.push(BFSElement(i + k, j));
q.push(BFSElement(i, j + k));
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int M[R][C] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
(findPath(M) == true) ? cout << "Yes"
: cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class BFSElement {
int i, j;
BFSElement(int i, int j)
{
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
}
}
class GFG {
static int R = 4, C = 4;
BFSElement b;
static boolean findPath(int M[][])
{
Queue<BFSElement> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j) {
if (M[i][j] == 1) {
q.add(new BFSElement(i, j));
break;
}
}
}
while (q.size() != 0) {
BFSElement x = q.peek();
q.remove();
int i = x.i;
int j = x.j;
if (i < 0 || i >= R || j < 0 || j >= C)
continue;
if (M[i][j] == 0)
continue;
if (M[i][j] == 2)
return true;
M[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = -1; k <= 1; k += 2) {
q.add(new BFSElement(i + k, j));
q.add(new BFSElement(i, j + k));
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int M[][] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
if (findPath(M) == true)
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
|
Python3
class BFSElement:
def __init__(self, i, j):
self.i = i
self.j = j
R, C = 4, 4
def findPath(M):
q = []
for i in range(R):
for j in range(C):
if (M[i][j] == 1):
q.append(BFSElement(i, j))
break
while (len(q) != 0):
x = q[0]
q = q[1:]
i = x.i
j = x.j
if (i < 0 or i >= R or j < 0 or j >= C):
continue
if (M[i][j] == 0):
continue
if (M[i][j] == 2):
return True
M[i][j] = 0
for k in range(-1, 2, 2):
q.append(BFSElement(i + k, j))
q.append(BFSElement(i, j + k))
return False
M = [[0, 3, 0, 1],
[3, 0, 3, 3],
[2, 3, 3, 3],
[0, 3, 3, 3]]
if(findPath(M) == True):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class BFSElement {
public int i, j;
public BFSElement(int i, int j)
{
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
}
}
public class GFG {
static int R = 4, C = 4;
static bool findPath(int[, ] M)
{
Queue<BFSElement> q = new Queue<BFSElement>();
for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j) {
if (M[i, j] == 1) {
q.Enqueue(new BFSElement(i, j));
break;
}
}
}
while (q.Count != 0) {
BFSElement x = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
int i = x.i;
int j = x.j;
if (i < 0 || i >= R || j < 0 || j >= C)
continue;
if (M[i, j] == 0)
continue;
if (M[i, j] == 2)
return true;
M[i, j] = 0;
for (int k = -1; k <= 1; k += 2) {
q.Enqueue(new BFSElement(i + k, j));
q.Enqueue(new BFSElement(i, j + k));
}
}
return false;
}
static public void Main()
{
int[, ] M = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
if (findPath(M) == true)
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class BFSElement
{
constructor(i,j)
{
this.i=i;
this.j=j;
}
}
let R = 4, C = 4;
let b;
function findPath(M)
{
let q = [];
for (let i = 0; i < R; ++i)
{
for (let j = 0; j < C; ++j)
{
if (M[i][j] == 1) {
q.push(new BFSElement(i, j));
break;
}
}
}
while (q.length != 0)
{
let x = q.shift();
let i = x.i;
let j = x.j;
if (i < 0 || i >= R || j < 0 || j >= C)
continue;
if (M[i][j] == 0)
continue;
if (M[i][j] == 2)
return true;
M[i][j] = 0;
for (let k = -1; k <= 1; k += 2)
{
q.push(new BFSElement(i + k, j));
q.push(new BFSElement(i, j + k));
}
}
return false;
}
let M=[[ 0, 3, 0, 1 ],
[ 3, 0, 3, 3 ],
[ 2, 3, 3, 3 ],
[ 0, 3, 3, 3 ]];
if(findPath(M) == true)
document.write("Yes");
else
document.write("No");
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N*M), Every cell of the matrix is visited only once so the time complexity is O(N*M).
Auxiliary Space: O(N*M), Space is required to store the visited array and to create the queue.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...