Find the sum of the series 2, 5, 13, 35, 97…
Last Updated :
23 Dec, 2022
Given a series and a number n, the task is to find the sum of its first n terms. Below is the series:
2, 5, 13, 35, 97, …
Examples:
Input: N = 2
Output: 7
The sum of first 2 terms of Series is
2 + 5 = 7
Input: N = 4
Output: 55
The sum of first 4 terms of Series is
2 + 5 + 13 + 35 = 55
Approach: From this given series we find it is the sum of the Two GP series with common ratios 2, 3.
Sn = 2 + 5 + 13 + 35 + 97 … + upto nth term
Sn = (2^0 + 3^ 0) + (2^1 + 3^1) + (2^2 + 3^2) + (2^3 + 3^3)+ (2^4 + 3^4) …… + upto nth term
Sn = (2^0 + 2^1 + 2^2 + 2^3 + 2^4 … + upto nth term) + ( 3^0 + 3^1 + 3^2 + 3^3 …… + unto nth term )
Since We know that the sum of n terms of the GP is given by the following formula:
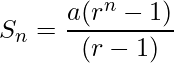
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int calculateSum(int n)
{
int r1 = 2, r2 = 3;
int a1 = 1, a2 = 1;
return a1 * (pow(r1, n) - 1) / (r1 - 1)
+ a2 * (pow(r2, n) - 1) / (r2 - 1);
}
int main()
{
int n = 4;
cout << "Sum = " << calculateSum(n)
<< endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class GFG {
static int calculateSum(int n)
{
int r1 = 2, r2 = 3;
int a1 = 1, a2 = 1;
return (int)(a1 * (Math.pow(r1, n) - 1) / (r1 - 1)
+ a2 * (Math.pow(r2, n) - 1) / (r2 - 1));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 4;
System.out.println("Sum = " +calculateSum(n));
}
}
|
Python 3
from math import *
def calculateSum(n) :
r1, r2 = 2, 3
a1, a2 = 1, 1
return (a1 * (pow(r1, n) - 1) // (r1 - 1)
+ a2 * (pow(r2, n) - 1) // (r2 - 1))
if __name__ == "__main__" :
n = 4
print("SUM = ",calculateSum(n))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int calculateSum(int n)
{
int r1 = 2, r2 = 3;
int a1 = 1, a2 = 1;
return (int)(a1 * (Math.Pow(r1, n) - 1) / (r1 - 1) +
a2 * (Math.Pow(r2, n) - 1) / (r2 - 1));
}
static public void Main ()
{
int n = 4;
Console.Write("Sum = " +
calculateSum(n));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function calculateSum($n)
{
$r1 = 2;
$r2 = 3;
$a1 = 1;
$a2 = 1;
return $a1 * (pow($r1, $n) - 1) /
($r1 - 1) + $a2 *
(pow($r2, $n) - 1) /
($r2 - 1);
}
$n = 4;
echo "Sum = ", calculateSum($n);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function calculateSum(n)
{
var r1 = 2, r2 = 3;
var a1 = 1, a2 = 1;
return parseInt((a1 * (Math.pow(r1, n) - 1) / (r1 - 1)
+ a2 * (Math.pow(r2, n) - 1) / (r2 - 1)));
}
var n = 4;
document.write("Sum = " +calculateSum(n));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(log n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1), As constant extra space is used.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...