Find the root of given non decreasing function between A and B
Last Updated :
07 May, 2021
Given three numbers a, b, and c that forms a monotonically increasing function 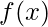 of the form a*x2 + b*x + c and two number A and B, the task is to find the root of the function i.e., find the value of x such that
of the form a*x2 + b*x + c and two number A and B, the task is to find the root of the function i.e., find the value of x such that 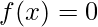 where A ? x ? B.
where A ? x ? B.
Examples:
Input: a = 2, b = -3, c = -2, A = 0, B = 3
Output: 2.0000
Explanation:
f(x) = 2x^2 – 3x – 2 putting the value of x = 2.000
We get f(2.000) = 2(2.000)^2 – 3(2.000) – 2 = 0
Input: a = 2, b = -3, c = -2, A = -2, B = 1
Output: No solution
Approach: Below is the graphical representation of any function :
:

From the above graph, we have,
- Whenever f(A)*f(B) ? 0, it means that the graph of the function will cut the x-axis somewhere within that range and signifies that somewhere there is a point which makes the value of the function as 0 and then the graph proceeds to be negative y-axis.
- If f(A)*f(B) > 0, it means that in this range [A, B] the y values of f(A) and f(B) both remain positive throughout, so they never cut x-axis.
Therefore, from the above observation, the idea is to use Binary Search to solve this problem. Using the given range of [A, B] as lower and upper bound for the root of the equation, x can be found out by applying binary search on this range. Below are the steps:
- Find the middle(say mid) of the range [A, B].
- If f(mid)*f(A) ? 0 is true then search space is reduced to [A, mid], because the cut at x-axis has been occurred in this segment.
- Else search space is reduced to [mid, B]
- The minimum possible value for root is when the high value becomes just smaller than EPS(the smallest value ~10-6) + lower bound value i.e., fabs(high – low) > EPS.
- Print the value of the root.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define eps 1e-6
double func(double a, double b,
double c, double x)
{
return a * x * x + b * x + c;
}
double findRoot(double a, double b,
double c, double low,
double high)
{
double x;
while (fabs(high - low) > eps) {
x = (low + high) / 2;
if (func(a, b, c, low)
* func(a, b, c, x)
<= 0) {
high = x;
}
else {
low = x;
}
}
return x;
}
void solve(double a, double b, double c,
double A, double B)
{
if (func(a, b, c, A)
* func(a, b, c, B)
> 0) {
cout << "No solution";
}
else {
cout << fixed
<< setprecision(4)
<< findRoot(a, b, c,
A, B);
}
}
int main()
{
double a = 2, b = -3, c = -2,
A = 0, B = 3;
solve(a, b, c, A, B);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG{
static final double eps = 1e-6;
static double func(double a, double b,
double c, double x)
{
return a * x * x + b * x + c;
}
static double findRoot(double a, double b,
double c, double low,
double high)
{
double x = -1;
while (Math.abs(high - low) > eps)
{
x = (low + high) / 2;
if (func(a, b, c, low) *
func(a, b, c, x) <= 0)
{
high = x;
}
else
{
low = x;
}
}
return x;
}
static void solve(double a, double b, double c,
double A, double B)
{
if (func(a, b, c, A) * func(a, b, c, B) > 0)
{
System.out.println("No solution");
}
else
{
System.out.format("%.4f", findRoot(
a, b, c, A, B));
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
double a = 2, b = -3, c = -2,
A = 0, B = 3;
solve(a, b, c, A, B);
}
}
|
Python3
import math
eps = 1e-6
def func(a ,b , c , x):
return a * x * x + b * x + c
def findRoot( a, b, c, low, high):
x = -1
while abs(high - low) > eps:
x = (low + high) / 2
if (func(a, b, c, low) *
func(a, b, c, x) <= 0):
high = x
else:
low = x
return x
def solve(a, b, c, A, B):
if (func(a, b, c, A) *
func(a, b, c, B) > 0):
print("No solution")
else:
print("{:.4f}".format(findRoot(
a, b, c, A, B)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = 2
b = -3
c = -2
A = 0
B = 3
solve(a, b, c, A, B)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static readonly double eps = 1e-6;
static double func(double a, double b,
double c, double x)
{
return a * x * x + b * x + c;
}
static double findRoot(double a, double b,
double c, double low,
double high)
{
double x = -1;
while (Math.Abs(high - low) > eps)
{
x = (low + high) / 2;
if (func(a, b, c, low) *
func(a, b, c, x) <= 0)
{
high = x;
}
else
{
low = x;
}
}
return x;
}
static void solve(double a, double b, double c,
double A, double B)
{
if (func(a, b, c, A) * func(a, b, c, B) > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("No solution");
}
else
{
Console.Write("{0:F4}", findRoot(
a, b, c, A, B));
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
double a = 2, b = -3, c = -2,
A = 0, B = 3;
solve(a, b, c, A, B);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let eps = 1e-6;
function func(a, b,
c, x)
{
return a * x * x + b * x + c;
}
function findRoot(a, b,
c, low,
high)
{
let x = -1;
while (Math.abs(high - low) > eps)
{
x = (low + high) / 2;
if (func(a, b, c, low) *
func(a, b, c, x) <= 0)
{
high = x;
}
else
{
low = x;
}
}
return x;
}
function solve(a, b, c, A, B)
{
if (func(a, b, c, A) * func(a, b, c, B) > 0)
{
document.write("No solution");
}
else
{
document.write(findRoot(
a, b, c, A, B));
}
}
let a = 2, b = -3, c = -2,
A = 0, B = 3;
solve(a, b, c, A, B);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(log(B – A))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...