Find the Nth term of the series 2, 15, 41, 80, 132…
Last Updated :
11 Aug, 2022
Given a number N, the task is to find the Nth term of the series 2, 15, 41, 80, 132….
Examples:
Input: N = 2
Output: 15
Input: N = 5
Output: 132
Approach: From the given series, the formula for Nth term can be found as:
1st term = 2
2nd term = 2 + 1 * 13 = 15
3rd term = 15 + 2 * 13 = 41
4th term = 41 + 3 * 13 = 80
.
.
Nth term = (N - 1)th term
+ (N - 1) * 13
Therefore, the Nth term of the series is given as
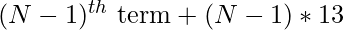
Below are the steps to find the Nth term using recursion:
Recursively iterate from value N:
- Base case: If the value called recursively is 1, then it is the first term of the series. Therefore return 2 from the function.
if(N == 1)
return 2;
- Recursive call: If the base case is not met, then recursively iterate from the function according to the Nth term of the series:
(N - 1) * 13 + func(N - 1);
- Return statement: At each recursive call(except the base case), return the recursive function for next iteration.
return ((13 * (N - 1))
+ func(N, i + 1));
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int nthTerm(int N)
{
if (N == 1) {
return 2;
}
return ((N - 1) * 13)
+ nthTerm(N - 1);
}
int main()
{
int N = 17;
cout << nthTerm(N) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG{
static int nthTerm(int N)
{
if (N == 1)
{
return 2;
}
return ((N - 1) * 13) +
nthTerm(N - 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 17;
System.out.print(nthTerm(N) + "\n");
}
}
|
Python 3
def nthTerm(N):
if (N == 1):
return 2
return ((N - 1) * 13) + nthTerm(N - 1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 17
print(nthTerm(N))
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG{
static public int nthTerm(int N)
{
if (N == 1)
{
return 2;
}
return ((N - 1) * 13) + nthTerm(N - 1);
}
static public void Main ()
{
int N = 17;
Console.WriteLine(nthTerm(N));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function nthTerm( N)
{
if (N == 1) {
return 2;
}
return ((N - 1) * 13)
+ nthTerm(N - 1);
}
let N = 17;
document.write( nthTerm(N) );
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N) for given input N
Auxiliary Space: O(N) for implicit call stack
Dynamic Programming (Top Down Using Memoization):
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int static dp[1001];
int nthTerm(int N)
{
if (N == 1) {
return 2;
}
if(dp[N] != -1) {
return dp[N];
}
dp[N] = ((N - 1) * 13) + nthTerm(N - 1);
return dp[N];
}
int main()
{
int N = 17;
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
cout << nthTerm(N) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG{
static int []dp = new int[1001];
static int nthTerm(int N)
{
if (N == 1) {
return 2;
}
if(dp[N] != -1) {
return dp[N];
}
dp[N] = ((N - 1) * 13) + nthTerm(N - 1);
return dp[N];
}
public static void main(String []args)
{
int N = 17;
for(int i = 0; i < 1001; i++) {
dp[i] = -1;
}
System.out.println(nthTerm(N));
}
}
|
Python
dp = [-1 for i in range(1001)]
def nthTerm(N):
if (N == 1):
return 2
if(dp[N] != -1):
return dp[N]
dp[N] = ((N - 1) * 13) + nthTerm(N - 1)
return dp[N]
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 17
print(nthTerm(N))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int []dp = new int[1001];
static int nthTerm(int N)
{
if (N == 1) {
return 2;
}
if(dp[N] != -1) {
return dp[N];
}
dp[N] = ((N - 1) * 13) + nthTerm(N - 1);
return dp[N];
}
public static void Main()
{
int N = 17;
for(int i = 0; i < 1001; i++) {
dp[i] = -1;
}
Console.Write(nthTerm(N));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let dp = [];
function nthTerm(N)
{
if (N == 1) {
return 2;
}
if(dp[N] != -1) {
return dp[N];
}
dp[N] = ((N - 1) * 13) + nthTerm(N - 1);
return dp[N];
}
let N = 17;
for(let i = 0; i < 1001; i++) {
dp[i] = -1;
}
document.write(nthTerm(N));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1001)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...