Find the node whose sum with X has minimum set bits
Last Updated :
12 Jun, 2021
Given a tree, and the weights of all the nodes and an integer x, the task is to find a node i such that weight[i] + x gives the minimum setbits, If two or more nodes have the same count of set bits when added with x then find the one with the minimum value.
Examples:
Input:
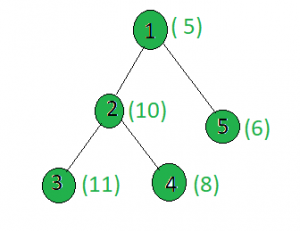
x = 15
Output: 1
Node 1: setbits(5 + 15) = 2
Node 2: setbits(10 + 15) = 3
Node 3: setbits(11 + 15) = 3
Node 4: setbits(8 + 15) = 4
Node 5: setbits(6 + 15) = 3
Approach: Perform dfs on the tree and keep track of the node whose sum with x has minimum set bits. If two or more nodes have an equal count of set bits then choose the one with the minimum number.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int minimum = INT_MAX, x, ans = INT_MAX;
vector<int> graph[100];
vector<int> weight(100);
void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
int a = __builtin_popcount(weight[node] + x);
if (minimum > a) {
minimum = a;
ans = node;
}
else if (minimum == a)
ans = min(ans, node);
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
int main()
{
x = 15;
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(4);
graph[1].push_back(5);
dfs(1, 1);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int minimum = Integer.MAX_VALUE,
x, ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static Vector<Integer> []graph =
new Vector[100];
static int []weight = new int[100];
static void dfs(int node,
int parent)
{
int a = Integer.bitCount(weight[node] + x);
if (minimum > a)
{
minimum = a;
ans = node;
}
else if (minimum == a)
ans = Math.min(ans, node);
for (int to : graph[node])
{
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
x = 15;
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++)
graph[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
graph[1].add(2);
graph[2].add(3);
graph[2].add(4);
graph[1].add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
System.out.print(ans);
}
}
|
Python3
from sys import maxsize
minimum, x, ans = maxsize, None, maxsize
graph = [[] for i in range(100)]
weight = [0] * 100
def dfs(node, parent):
global x, ans, graph, weight, minimum
a = bin(weight[node] + x).count('1')
if minimum > a:
minimum = a
ans = node
elif minimum == a:
ans = min(ans, node)
for to in graph[node]:
if to == parent:
continue
dfs(to, node)
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = 15
weight[1] = 5
weight[2] = 10
weight[3] = 11
weight[4] = 8
weight[5] = 6
graph[1].append(2)
graph[2].append(3)
graph[2].append(4)
graph[1].append(5)
dfs(1, 1)
print(ans)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
class GFG{
static int minimum = int.MaxValue, x,
ans = int.MaxValue;
static ArrayList[] graph = new ArrayList[100];
static int[] weight = new int[100];
static int PopCount(int n)
{
int count = 0;
while (n > 0)
{
count += n & 1;
n >>= 1;
}
return count;
}
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
int a = PopCount(weight[node] + x);
if (minimum > a)
{
minimum = a;
ans = node;
}
else if (minimum == a)
ans = Math.Min(ans, node);
foreach(int to in graph[node])
{
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
x = 15;
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
graph[i] = new ArrayList();
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
graph[1].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(3);
graph[2].Add(4);
graph[1].Add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let minimum = Number.MAX_VALUE;
let x;
let ans = Number.MAX_VALUE;
let graph = new Array(100);
let weight = new Array(100);
for(let i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
graph[i] = [];
weight[i] = 0;
}
function dfs(node, parent)
{
let a = (weight[node] + x).toString(2).split('').filter(
y => y == '1').length;
if (minimum > a)
{
minimum = a;
ans = node;
}
else if (minimum == a)
ans = Math.min(ans, node);
for(let to = 0; to < graph[node].length; to++)
{
if (graph[node][to] == parent)
continue
dfs(graph[node][to], node);
}
}
x = 15;
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
graph[1].push(2);
graph[2].push(3);
graph[2].push(4);
graph[1].push(5);
dfs(1, 1);
document.write(ans);
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(N).
In dfs, every node of the tree is processed once, and hence the complexity due to the dfs is O(N) if there are total N nodes in the tree. Also, for processing each node the builtin_popcount() function is used which has a complexity of O(c) where c is a constant, and since this complexity is constant, it doesn’t affect the overall time complexity. Therefore, the time complexity is O(N).
- Auxiliary Space: O(1).
Any extra space is not required, so the space complexity is constant.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...