Find the node whose absolute difference with X gives maximum value
Last Updated :
12 Apr, 2021
Given a tree, and the weights of all the nodes and an integer x, the task is to find a node i such that |weight[i] – x| is maximum.
Examples:
Input:
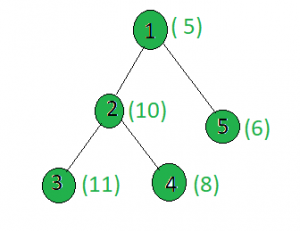
x = 15
Output: 1
Node 1: |5 – 15| = 10
Node 2: |10 – 15| = 5
Node 3: |11 -15| = 4
Node 4: |8 – 15| = 7
Node 5: |6 -15| = 9
Approach: Perform dfs on the tree and keep track of the node whose weighted absolute difference with x gives the maximum value.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maximum = INT_MIN, x, ans;
vector<int> graph[100];
vector<int> weight(100);
void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
if (maximum < abs(weight[node] - x)) {
maximum = abs(weight[node] - x);
ans = node;
}
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
int main()
{
x = 15;
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(4);
graph[1].push_back(5);
dfs(1, 1);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int maximum = Integer.MIN_VALUE, x, ans;
static Vector<Vector<Integer>> graph=new Vector<Vector<Integer>>();
static Vector<Integer> weight=new Vector<Integer>();
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
if (maximum < Math.abs(weight.get(node) - x))
{
maximum = Math.abs(weight.get(node) - x);
ans = node;
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(node).size(); i++)
{
if (graph.get(node).get(i) == parent)
continue;
dfs(graph.get(node).get(i), node);
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
x = 15;
weight.add(0);
weight.add(5);
weight.add(10);;
weight.add(11);;
weight.add(8);
weight.add(6);
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
graph.add(new Vector<Integer>());
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(2).add(3);
graph.get(2).add(4);
graph.get(1).add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
System.out.println( ans);
}
}
|
Python3
from sys import maxsize
def dfs(node, parent):
global minimum, graph, weight, x, ans
if minimum < abs(weight[node] - x):
minimum = abs(weight[node] - x)
ans = node
for to in graph[node]:
if to == parent:
continue
dfs(to, node)
if __name__ == "__main__":
minimum = -maxsize
graph = [[] for i in range(100)]
weight = [0] * 100
x = 15
ans = 0
weight[1] = 5
weight[2] = 10
weight[3] = 11
weight[4] = 8
weight[5] = 6
graph[1].append(2)
graph[2].append(3)
graph[2].append(4)
graph[1].append(5)
dfs(1, 1)
print(ans)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int maximum = int.MinValue, x, ans;
static List<List<int>> graph = new List<List<int>>();
static List<int> weight = new List<int>();
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
if (maximum < Math.Abs(weight[node] - x))
{
maximum = Math.Abs(weight[node] - x);
ans = node;
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph[node].Count; i++)
{
if (graph[node][i] == parent)
continue;
dfs(graph[node][i], node);
}
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
x = 15;
weight.Add(0);
weight.Add(5);
weight.Add(10);;
weight.Add(11);;
weight.Add(8);
weight.Add(6);
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
graph.Add(new List<int>());
graph[1].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(3);
graph[2].Add(4);
graph[1].Add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
Console.WriteLine( ans);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let maximum = Number.MIN_VALUE, x, ans;
let graph= [];
let weight=[];
function dfs(node,parent)
{
if (maximum < Math.abs(weight[node] - x))
{
maximum = Math.abs(weight[node] - x);
ans = node;
}
for (let i = 0; i < graph[node].length; i++)
{
if (graph[node][i] == parent)
continue;
dfs(graph[node][i], node);
}
}
x = 15;
weight.push(0);
weight.push(5);
weight.push(10);;
weight.push(11);;
weight.push(8);
weight.push(6);
for(let i = 0; i < 100; i++)
graph.push([]);
graph[1].push(2);
graph[2].push(3);
graph[2].push(4);
graph[1].push(5);
dfs(1, 1);
document.write( ans);
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity : O(N).
In dfs, every node of the tree is processed once and hence the complexity due to the dfs is O(N) if there are total N nodes in the tree. Therefore, the time complexity is O(N).
- Auxiliary Space : O(1).
Any extra space is not required, so the space complexity is constant.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...