Find temperature of missing days using given sum and average
Last Updated :
25 Apr, 2023
Given integers x and y which denotes the average temperature of the week except for days Day1 and Day2 respectively, and the sum of the temperature of Day1 and Day2 as S, the task is to find the temperature of the days Day1 and Day2.
Examples:
Input: x = 15, y = 10, S = 50
Output: Day1 = 10, Day2 = 40
Explanation:
The average of week excluding Day1 is 15, the average of week excluding Day2 is 10 and the sum of temperature of Day1 and Day2 is 50. Individual temperature of the two days are 10 and 40 respectively.
Input: x = 5, y = 10, s = 40
Output: Day1 = 35, Day2 = 5
Explanation:
The average of week excluding Day1 is 5, the average of week excluding Day2 is 10 and the sum of temperature of Day1 and Day2 is 40. Individual temperature of the two days are 35 and 5 respectively.
Approach: We know that Average = sum of all observation / total number of observation. Hence, the sum of observation = Average * number of observation i.e., S = A * n
So after excluding Day1 or Day2 we are left with only 6 days
so N = 6 and the equations are:
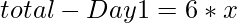
and
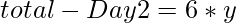
on subtracting the above two equations we get,
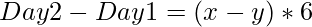
(Equation 1)
and it is given in the problem statement that
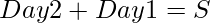
(Equation 2)
Solving the above two equations, the value of Day1 and Day2 is given by:
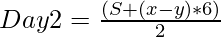 [Tex]Day1 = S – Day2 [/Tex]
[Tex]Day1 = S – Day2 [/Tex]
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void findTemperature(int x, int y, int s)
{
double Day1, Day2;
double diff = (x - y) * 6;
Day2 = (diff + s) / 2;
Day1 = s - Day2;
cout << "Day1 : " << Day1 << endl;
cout << "Day2 : " << Day2 << endl;
}
int main()
{
int x = 5, y = 10, s = 40;
findTemperature(x, y, s);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG{
static void findTemperature(int x, int y, int s)
{
double Day1, Day2;
double diff = (x - y) * 6;
Day2 = (diff + s) / 2;
Day1 = s - Day2;
System.out.println( "Day1 : " + Day1);
System.out.println( "Day2 : " + Day2);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 5, y = 10, s = 40;
findTemperature(x, y, s);
}
}
|
Python
def findTemperature(x, y, s):
diff = (x - y) * 6
Day2 = (diff + s) // 2
Day1 = s - Day2
print("Day1 : ", Day1)
print("Day2 : ", Day2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = 5
y = 10
s = 40
findTemperature(x, y, s)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static void findTemperature(int x, int y, int s)
{
double Day1, Day2;
double diff = (x - y) * 6;
Day2 = (diff + s) / 2;
Day1 = s - Day2;
Console.Write( "Day1 : " + Day1 + '\n');
Console.WriteLine( "Day2 : " + Day2 + '\n');
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 5, y = 10, s = 40;
findTemperature(x, y, s);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function findTemperature(x, y, s)
{
let Day1, Day2;
let diff = (x - y) * 6;
Day2 = (diff + s) / 2;
Day1 = s - Day2;
document.write("Day1 : " + Day1 + "</br>");
document.write("Day2 : " + Day2 + "</br>");
}
let x = 5, y = 10, s = 40;
findTemperature(x, y, s);
</script>
|
Output: Day1 : 35
Day2 : 5
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...