Find the last digit of given series
Last Updated :
22 Jul, 2022
Given an integer n, find the last digit of this sequence,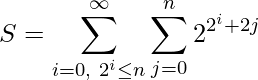 i.e. Summation of F(n) from i = 0 to 2i ? n, where F(n) is the summation of 22i+2j Where j varies from 0 to n. n can varies from 0 to 1017 Examples:
i.e. Summation of F(n) from i = 0 to 2i ? n, where F(n) is the summation of 22i+2j Where j varies from 0 to n. n can varies from 0 to 1017 Examples:
Input: 2
Output: 6
Explanation:
After computing the above expression, the value
obtained is 216. Hence the last digit is 6.
Input: 3
Output: 0
A Naive approach is to run two loops, one for ‘i’ and other for ‘j’ and compute the value after taking (modulo 10) with every calculated value. But this approach will definitely time out for large value of n. An efficient approach is to expand the above expression in a general form that can easily be calculated. 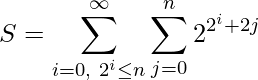 [Tex]\implies \displaystyle \sum_{i=0,\ 2^i\le n}^\infty \sum_{j=0}^n 2^{2^i}\cdot 2^{2j} [/Tex]
[Tex]\implies \displaystyle \sum_{i=0,\ 2^i\le n}^\infty \sum_{j=0}^n 2^{2^i}\cdot 2^{2j} [/Tex]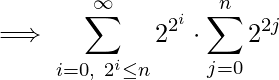 [Tex]\implies\displaystyle\sum_{i=0,\ 2^i\le n}^\infty 2^{2^i} \cdot \sum_{j=0}^n 4^j [/Tex]
[Tex]\implies\displaystyle\sum_{i=0,\ 2^i\le n}^\infty 2^{2^i} \cdot \sum_{j=0}^n 4^j [/Tex]
- First expression
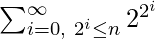 can be calculated directly by iterating a loop for all values of ‘i’ till 2i ? n.
can be calculated directly by iterating a loop for all values of ‘i’ till 2i ? n. - Second expression
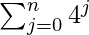 can be calculated easily by using Geometric series formula i.e.,
can be calculated easily by using Geometric series formula i.e., 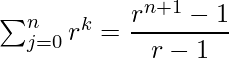
- Final answer will be the product of both these calculated result in both the steps. But after performing any calculation part of these expression, we have to take modulo with 10 to avoid overflow.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long powermod(long long x, long long y, long long p)
{
long long res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0) {
if (y & 1LL)
res = (res * x) % p;
y = y >> 1LL;
x = (x * x) % p;
}
return res;
}
long long modInverse(long long a, long long m)
{
long long m0 = m, t, q;
long long x0 = 0, x1 = 1;
if (m == 1)
return 0;
while (a > 1) {
q = a / m;
t = m;
m = a % m, a = t;
t = x0;
x0 = x1 - q * x0;
x1 = t;
}
if (x1 < 0)
x1 += m0;
return x1;
}
long long evaluteExpression(long long& n)
{
long long firstsum = 0, mod = 10;
for (long long i = 2, j = 0; (1LL << j) <= n; i *= i, ++j)
firstsum = (firstsum + i) % mod;
long long secondsum = (powermod(4LL, n + 1, mod) - 1) *
modInverse(3LL, mod);
return (firstsum * secondsum) % mod;
}
int main()
{
long long n = 3;
cout << evaluteExpression(n) << endl;
n = 10;
cout << evaluteExpression(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG{
static long powermod(long x, long y, long p)
{
long res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0) {
if ((y & 1L)>0)
res = (res * x) % p;
y = y >> 1L;
x = (x * x) % p;
}
return res;
}
static long modInverse(long a, long m)
{
long m0 = m, t, q;
long x0 = 0, x1 = 1;
if (m == 1)
return 0;
while (a > 1) {
q = a / m;
t = m;
m = a % m;
a = t;
t = x0;
x0 = x1 - q * x0;
x1 = t;
}
if (x1 < 0)
x1 += m0;
return x1;
}
static long evaluteExpression(long n)
{
long firstsum = 0, mod = 10;
for (long i = 2, j = 0; (1L << j) <= n; i *= i, ++j)
firstsum = (firstsum + i) % mod;
long secondsum = (powermod(4L, n + 1, mod) - 1) *
modInverse(3L, mod);
return (firstsum * secondsum) % mod;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long n = 3;
System.out.println(evaluteExpression(n));
n = 10;
System.out.println(evaluteExpression(n));
}
}
|
Python3
def powermod(x, y, p):
res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0):
if ((y & 1)>0):
res = (res * x) % p;
y = y >> 1;
x = (x * x) % p;
return res;
def modInverse(a, m):
m0 = m;
x0 = 0;
x1 = 1;
if (m == 1):
return 0;
while (a > 1):
q = int(a / m);
t = m;
m = a % m;
a = t;
t = x0;
x0 = x1 - q * x0;
x1 = t;
if (x1 < 0):
x1 += m0;
return x1;
def evaluteExpression(n):
firstsum = 0;
mod = 10;
i=2;
j=0;
while ((1 << j) <= n):
firstsum = (firstsum + i) % mod;
i *= i;
j+=1;
secondsum = (powermod(4, n + 1, mod) - 1) * modInverse(3, mod);
return (firstsum * secondsum) % mod;
n = 3;
print(evaluteExpression(n));
n = 10;
print(evaluteExpression(n));
|
C#
class GFG{
static long powermod(long x, long y, long p)
{
long res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0) {
if ((y & 1)>0)
res = (res * x) % p;
y = y >> 1;
x = (x * x) % p;
}
return res;
}
static long modInverse(long a, long m)
{
long m0 = m, t, q;
long x0 = 0, x1 = 1;
if (m == 1)
return 0;
while (a > 1) {
q = a / m;
t = m;
m = a % m;
a = t;
t = x0;
x0 = x1 - q * x0;
x1 = t;
}
if (x1 < 0)
x1 += m0;
return x1;
}
static long evaluteExpression(long n)
{
long firstsum = 0, mod = 10;
for (int i = 2, j = 0; (1 << j) <= n; i *= i, ++j)
firstsum = (firstsum + i) % mod;
long secondsum = (powermod(4L, n + 1, mod) - 1) *
modInverse(3L, mod);
return (firstsum * secondsum) % mod;
}
public static void Main()
{
long n = 3;
System.Console.WriteLine(evaluteExpression(n));
n = 10;
System.Console.WriteLine(evaluteExpression(n));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function powermod($x, $y, $p)
{
$res = 1;
$x = $x % $p;
while ($y > 0)
{
if (($y & 1) > 0)
$res = ($res * $x) % $p;
$y = $y >> 1;
$x = ($x * $x) % $p;
}
return $res;
}
function modInverse($a, $m)
{
$m0 = $m;
$x0 = 0;
$x1 = 1;
if ($m == 1)
return 0;
while ($a > 1)
{
$q = (int)($a / $m);
$t = $m;
$m = $a % $m;
$a = $t;
$t = $x0;
$x0 = $x1 - $q * $x0;
$x1 = $t;
}
if ($x1 < 0)
$x1 += $m0;
return $x1;
}
function evaluteExpression($n)
{
$firstsum = 0;
$mod = 10;
for ($i = 2, $j = 0; (1 << $j) <= $n;
$i *= $i, ++$j)
$firstsum = ($firstsum + $i) % $mod;
$secondsum = (powermod(4, $n + 1, $mod) - 1) *
modInverse(3, $mod);
return ($firstsum * $secondsum) % $mod;
}
$n = 3;
echo evaluteExpression($n) . "\n";
$n = 10;
echo evaluteExpression($n);
?>
|
Javascript
function powermod(x, y, p)
{
let res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0) {
if ((y & 1)>0)
res = (res * x) % p;
y = y >> 1;
x = (x * x) % p;
}
return res;
}
function modInverse(a, m)
{
let m0 = m, t, q;
let x0 = 0, x1 = 1;
if (m == 1)
return 0;
while (a > 1) {
q = Math.floor(a / m);
t = m;
m = a % m;
a = t;
t = x0;
x0 = x1 - q * x0;
x1 = t;
}
if (x1 < 0)
x1 += m0;
return x1;
}
function evaluteExpression(n)
{
let firstsum = 0, mod = 10;
for (var i = 2, j = 0; (1 << j) <= n; i *= i, ++j)
firstsum = (firstsum + i) % mod;
let secondsum = (powermod(4, n + 1, mod) - 1) *
modInverse(3, mod);
return (firstsum * secondsum) % mod;
}
let n = 3;
console.log(evaluteExpression(n));
n = 10;
console.log(evaluteExpression(n));
|
Output:
0
8
Time complexity: O(log(n))
Auxiliary space: O(1)
Note: Asked in TCS Code vita contest.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...