Find bitwise OR of all possible sub-arrays
Last Updated :
01 May, 2023
Given an array A of size N where, 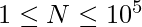 . The task is to find the OR of all possible sub-arrays of A and then the OR of all these results.
. The task is to find the OR of all possible sub-arrays of A and then the OR of all these results.
Examples:
Input : 1 4 6
Output : 7
All possible subarrays are
{1}, {1, 4}, {4, 6} and {1, 4, 6}
ORs of these subarrays are 1, 5, 6
and 7. OR of these ORs is 7.
Input : 10 100 1000
Output : 1006
Approach: In SET 1 we have seen how to find bitwise AND of all possible subarrays. A similar approach is also applicable here.
The Naive solution is to find the OR of all the sub-arrays and then output the OR of their results. This will lead to O(N2) solution.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int OR(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int curr = 0;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
curr |= arr[j];
res |= curr;
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
vector<int> arr1 = {1, 4, 6};
cout << OR(arr1) << endl;
vector<int> arr2 = {10, 100, 1000};
cout << OR(arr2) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int OR(List<Integer> arr) {
int n = arr.size();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int curr = 0;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
curr |= arr.get(j);
res |= curr;
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> arr1 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 4, 6));
System.out.println(OR(arr1));
List<Integer> arr2 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(10, 100, 1000));
System.out.println(OR(arr2));
}
}
|
Python3
def OR(arr):
n = len(arr)
res = 0
for i in range(n):
curr = 0
for j in range(i, n):
curr |= arr[j]
res |= curr
return res
arr1 = [1,4,6]
print(OR(arr1))
arr2 = [10,100,1000]
print(OR(arr2))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program {
static int OR(List<int> arr) {
int n = arr.Count;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int curr = 0;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
curr |= arr[j];
res |= curr;
}
}
return res;
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
List<int> arr1 = new List<int>{1, 4, 6};
Console.WriteLine(OR(arr1));
List<int> arr2 = new List<int>{10, 100, 1000};
Console.WriteLine(OR(arr2));
}
}
|
Javascript
function OR(arr) {
const n = arr.length;
let res = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let curr = 0;
for (let j = i; j < n; j++) {
curr |= arr[j];
res |= curr;
}
}
return res;
}
console.log(OR([1, 4,6]));
|
Efficient Solution: Using the property that 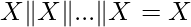 i:e it doesn’t matter how many times an element comes, it’s OR will be counted as one only. Thus our problem boils down to finding the OR of all the elements of the array.
i:e it doesn’t matter how many times an element comes, it’s OR will be counted as one only. Thus our problem boils down to finding the OR of all the elements of the array.
Implementation:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int OR(int a[], int n)
{
int ans = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
ans |= a[i];
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1, 4, 6 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
cout << OR(a, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static int OR(int a[],int n)
{
int ans = a[0];
int i;
for(i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
ans |= a[i];
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[] = { 1, 4, 6};
int n = a.length;
System.out.println(OR(a, n));
}
}
|
Python3
def OR(a, n):
ans = a[0]
for i in range(1,n):
ans |= a[i]
return ans
if __name__=='__main__':
a = [1, 4, 6]
n = len(a)
print(OR(a, n))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int OR(int[] a, int n)
{
int ans = a[0];
int i;
for(i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
ans |= a[i];
}
return ans;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] a = { 1, 4, 6};
int n = a.Length;
Console.Write(OR(a, n));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function O_R($a, $n)
{
$ans = $a[0];
for ($i = 1; $i < $n; ++$i)
$ans |= $a[$i];
return $ans;
}
$a = array( 1, 4, 6 );
$n = count($a);
echo O_R($a, $n);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function OR(a, n)
{
var ans = a[0];
for (var i = 1; i < n; ++i)
ans |= a[i];
return ans;
}
var a = [ 1, 4, 6 ];
var n = a.length;
document.write(OR(a, n));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Optimal Solution using Prefix Array for finding OR of all possible sub-arrays:-
Approach:-
- Create two arrays prefix_OR and suffix_OR, both of size N, to store the OR values of prefixes and suffixes respectively.
- Initialize the first element of prefix_OR with the first element of the input array, and the last element of suffix_OR with the last element of the input array.
- Traverse the input array from left to right, and fill prefix_OR using the formula prefix_OR[i] = prefix_OR[i-1] | arr[i].
- Traverse the input array from right to left, and fill suffix_OR using the formula suffix_OR[i] = suffix_OR[i+1] | arr[i].
- Initialize a variable res to 0, and traverse the input array. At each index i, calculate prefix_OR[i] | suffix_OR[i], and perform bitwise OR with res.
- Return the final value of res.
Here is the implementation of above approach:-
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int OR(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
vector<int> prefix_OR(n), suffix_OR(n);
prefix_OR[0] = arr[0];
suffix_OR[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
prefix_OR[i] = prefix_OR[i - 1] | arr[i];
}
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suffix_OR[i] = suffix_OR[i + 1] | arr[i];
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res |= prefix_OR[i] | suffix_OR[i];
}
return res;
}
int main() {
vector<int> arr = {1, 4, 6};
cout << OR(arr) << endl;
arr = {10, 100, 1000};
cout << OR(arr) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int OR(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
int[] prefix_OR = new int[n];
int[] suffix_OR = new int[n];
prefix_OR[0] = arr[0];
suffix_OR[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
prefix_OR[i] = prefix_OR[i - 1] | arr[i];
}
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suffix_OR[i] = suffix_OR[i + 1] | arr[i];
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res |= prefix_OR[i] | suffix_OR[i];
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 4, 6};
System.out.println(OR(arr));
arr = new int[]{10, 100, 1000};
System.out.println(OR(arr));
}
}
|
Python3
def OR(arr):
n = len(arr)
prefix_OR = [0] * n
suffix_OR = [0] * n
prefix_OR[0] = arr[0]
suffix_OR[n - 1] = arr[n - 1]
for i in range(1, n):
prefix_OR[i] = prefix_OR[i - 1] | arr[i]
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
suffix_OR[i] = suffix_OR[i + 1] | arr[i]
res = 0
for i in range(n):
res |= prefix_OR[i] | suffix_OR[i]
return res
if __name__=='__main__':
arr = [1, 4, 6]
print(OR(arr))
arr = [10, 100, 1000]
print(OR(arr))
|
C#
using System;
public class Program
{
public static int OR(int[] arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
int[] prefix_OR = new int[n];
int[] suffix_OR = new int[n];
prefix_OR[0] = arr[0];
suffix_OR[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
prefix_OR[i] = prefix_OR[i - 1] | arr[i];
}
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
suffix_OR[i] = suffix_OR[i + 1] | arr[i];
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
res |= prefix_OR[i] | suffix_OR[i];
}
return res;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr1 = { 1, 4, 6 };
Console.WriteLine(OR(arr1));
int[] arr2 = { 10, 100, 1000 };
Console.WriteLine(OR(arr2));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function OR($arr) {
$n = count($arr);
$prefix_OR = array();
$suffix_OR = array();
$prefix_OR[0] = $arr[0];
$suffix_OR[$n - 1] = $arr[$n - 1];
for ($i = 1; $i < $n; $i++) {
$prefix_OR[$i] = $prefix_OR[$i - 1] | $arr[$i];
}
for ($i = $n - 2; $i >= 0; $i--) {
$suffix_OR[$i] = $suffix_OR[$i + 1] | $arr[$i];
}
$res = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
$res |= $prefix_OR[$i] | $suffix_OR[$i];
}
return $res;
}
echo OR([1, 4, 6]);
?>
|
Javascript
function OR(arr) {
const n = arr.length;
const prefix_OR = new Array(n);
const suffix_OR = new Array(n);
prefix_OR[0] = arr[0];
suffix_OR[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
prefix_OR[i] = prefix_OR[i - 1] | arr[i];
}
for (let i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suffix_OR[i] = suffix_OR[i + 1] | arr[i];
}
let res = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res |= prefix_OR[i] | suffix_OR[i];
}
return res;
}
console.log(OR([1, 4, 6]));
console.log(OR([10, 100, 1000]));
|
Time Complexity:
The time complexity of this approach is O(N), where N is the size of the input array.
Space Complexity:
The space complexity of this approach is O(N), where N is the size of the input array, as we are using two extra arrays of size N to store the prefix and suffix OR values.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...