Financial Market : Meaning, Functions, and Classification
Last Updated :
28 Jul, 2023
What is Financial Market?
A market that serves as a link between the savers and borrowers, by transferring the capital or money from those who have a surplus amount of money to those who are in need of money or investment, is known as Financial Market. Simply put, Financial Market is a market that creates and exchanges financial assets. In general, the investors are known as the surplus units and business enterprises are known as the deficit units. Hence, a financial market acts as a link between surplus units and deficit units and brings the borrowers and lenders together. One can allocate funds with the help of the following two main ways:
- Through Banks
- Through Financial Markets

The households (who are the surplus units) may keep their savings in banks or they may use that amount for buying securities from the capital market. The financial market and banks then lend the funds to the business firms (who are the deficit units). The banks and financial market compete with each other. Financial Markets are classified into two broad categories; namely, Capital Market(Primary Market and Secondary Market) and Money Market.
Functions of Financial Markets

The important functions performed by Financial Markets are as follows:
1. Facilitation of Price Discovery
The price of anything depends upon two factors: its demand and supply in the market. Hence, the demand and supply of financial securities and assets help decide the price of different financial securities.
2. Mobilisation of Savings and Channelising the Savings into the most Productive Uses
As the financial markets act as a link between the savers and investors, it transfers savers’ savings to the most productive and appropriate investment opportunities.
3. Providing Liquidity to Financial Assets
Financial Markets provides the savers and investors with a platform to convert the securities into cash, as they easily sell and buy the financial securities in this market.
4. Reduction of the Cost of Transaction
Investors and companies have to collect information regarding financial securities before investing in them, which can be very time-consuming. The financial markets help these investors and companies by providing them with all information regarding financial securities including its price, availability, and cost.
Classification of Financial Market
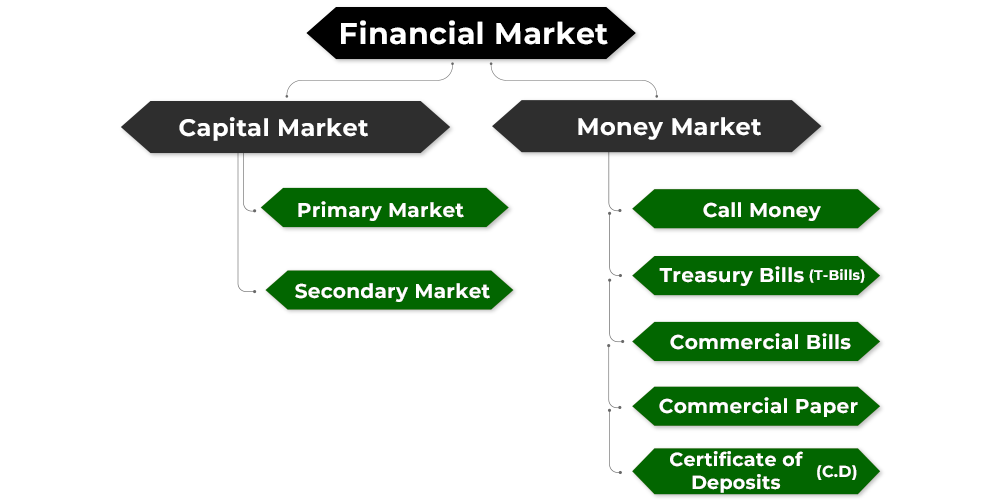
The Financial Market is divided into two broad categories; viz., Capital Market and Money Market.
Capital Market
A marketer including all institutions, organisations, and instruments providing medium and long-term funds is known as a Capital Market. A capital market does not include institutions and instruments providing finance for a short term, i.e., up to one year. Some of the common instruments of a capital market are debentures, shares, bonds, public deposits, mutual funds, etc. An ideal capital market is one which allocates capital productively, provides sufficient information to the investors, facilitates economic growth, where finance is available to the traders at a reasonable cost, and where the market operations are fair, free, competitive, and transparent.
A capital market is of two types, namely, Primary Market and Secondary Market.
- Primary Market: A market in which the securities are sold for the first time is known as a Primary Market. It means that under the primary market, new securities are issued from the company. Another name for the primary market is New Issue Market. This market contributes directly to the capital formation of a company, as the company directly goes to investors and uses the funds for investment in machines, land, building, equipment, etc.
- Secondary Market: A market in which the sale and purchase of newly issued securities and second-hand securities are made is known as a Secondary Market. In this market, a company does not directly issue its securities to the investors. Instead, the existing investors of the company sell the securities to other investors. The investor who wants to sell the securities and the one who wants to purchase meet each other in the secondary market, and exchange the securities for cash takes place with the help of an intermediary called a broker.
Money Market
A market for short-term funds that are meant to use for a period of up to one year is known as Money Market. In the general case, the money market is the source of funds or finance for working capital. The transactions held in the money market involve lending and borrowing of cash for a short term and also consist of the sale and purchase of securities with one year term or securities which get paid back (redeemed) within one year. Some of the common instruments of the money market are Call Money, Commercial Bills, T. Bills, Commercial Paper, Certificates of Deposits, etc.
Some of the features of a Money Market are as follows:
1. It is a market for the short term.
2. There is no fixed geographical location of a money market.
3. Some of the common instruments of the money market are Call Money, Commercial Bills, Certificates of Deposits, etc.
4. Some of the major institutions involved in the money market are LIC, GIC, RBI, Commercial Banks, etc.
Some of the Instruments of Money Market are as follows:
1. Call Money: The money borrowed or lent on demand for a short period of time (generally one day) is known as Call Money. The term of the call money does not include Sundays and other holidays. It is used mostly by banks. It means that when one bank faces a temporary shortage of cash then the bank with surplus cash lends the former bank with money for one or two days. It is also known as Interbank Call Money Market.
2. Treasury Bills (T. Bills): On behalf of the Government of India, Treasury Bills are issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). With the help of T. Bills, the Government of India can get short-term borrowings as they are sold to the general public and banks. The Treasury Bills are freely transferable and negotiable instruments and are issued at a discount. As Treasury Bills are issued by the Reserve Bank of India, they are considered the safest investments. The maturity period of the Treasury Bills varies from 14 days to 364 days.
3. Commercial Bills: Commercial Bills also known as Trade Bills or Accommodation Bills are the bills drawn by one organisation on another. Commercial Bills are the common instruments of the money market which are used in credit sales and purchases. The maturity period of commercial bills is for short-term, generally of 90 days. However, one can get the commercial bills discounted with the bank before the maturity period. The Trade Bills are negotiable and easily transferable instruments.
4. Commercial Paper: An unsecured promissory note issued by private or public sector companies with a fixed maturity period varying from 15 days to one year, is known as a Commercial Paper. It was for the first time introduced in India in 1990. As this instrument is unsecured, it can be issued by companies with creditworthiness and good reputation. The main investors of commercial papers are commercial banks and mutual funds.
5. Certificate of Deposits: A time or deposit that can be sold in the secondary market is known as a Certificate of Deposits (C.D.). It can be issued by a bank only and is a bearer certificate or document of title. A Certificate of Deposits is a negotiable and easily transferable instrument. The banks issue the Certificate of Deposits against the deposit kept by the institutions and companies. The time period of a Certificate of Deposits ranges from 91 days to one year. The C.D.’s can be issued to companies, corporations, and individuals during a period of tight liquidity. It is that time when the bank’s deposit growth is slow, but the credit demand is high.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...