Filtration: Definition, Process, Diagram and Examples
Last Updated :
04 Apr, 2024
Filtration is a method to separate the components of a mixture where the solvent part is liquid and the solute is an insoluble solid. Let’s know more about Filtration Definition, Process, Application and examples in detail below.
In simple words, Filtration is the process in which solid particles in liquid or gases are removed by the filter that allow the passes of liquid but blocks the passage of solid. The mechanism of “filtration” can be mechanical, biological, or physical.
Filtration Definition
Filtration is defined as the process in which solid particles in liquid or gases are separated by the filter that only allow the liquid to pass through it but blocks the passage of solid.
This process is carried out using a filter medium, for instance, filter paper. The pores of the filter medium are bigger as compared to the solvent particle but are smaller compared to the solute particle, so they allow only solvent particles to pass through them the solute particle is left on the other side making the solution free from the insoluble solute.
The principle of filtration is based on the difference in sizes between the particles.
Filtration Process
The process of filtration uses the concept of difference in the particles. We have two types of mixtures
- Heterogenous Mixture
- Homogenous Mixture
We define a heterogeneous mixture as a mixture in which the solute particle is not evenly distributed in the solvent phase. Such as sand in the water is an example of a heterogeneous mixture.
On the other hand, a homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the solute particle is evenly distributed in the solvent phase. A brine solution is an example of a homogenous mixture. Homogenous mixtures are also called solutions. Various types of processes are used for the filtration.
In general, the filtration process uses the concept, we take a filtration membrane such that it allows only a specific size particle to move through it making the solution at one end free from the insoluble solute particle. We can understand this using the example, suppose we have to filter sand and water.
We use a muslin cloth at the mouth of the container containing the sand in water solution. After that, we allow the solution to pass through the muslin cloth which only allows water to pass through it separating the sand from the sand and water solution. We can also use filtration paper in place of muslin cloth as the filtration membrane.
Filtration Diagram
Below is the filtration diagram, which will we can understand the filtration process. In this process we allow the mixture to pass through the filter paper which separates the insoluble solid from the solution.
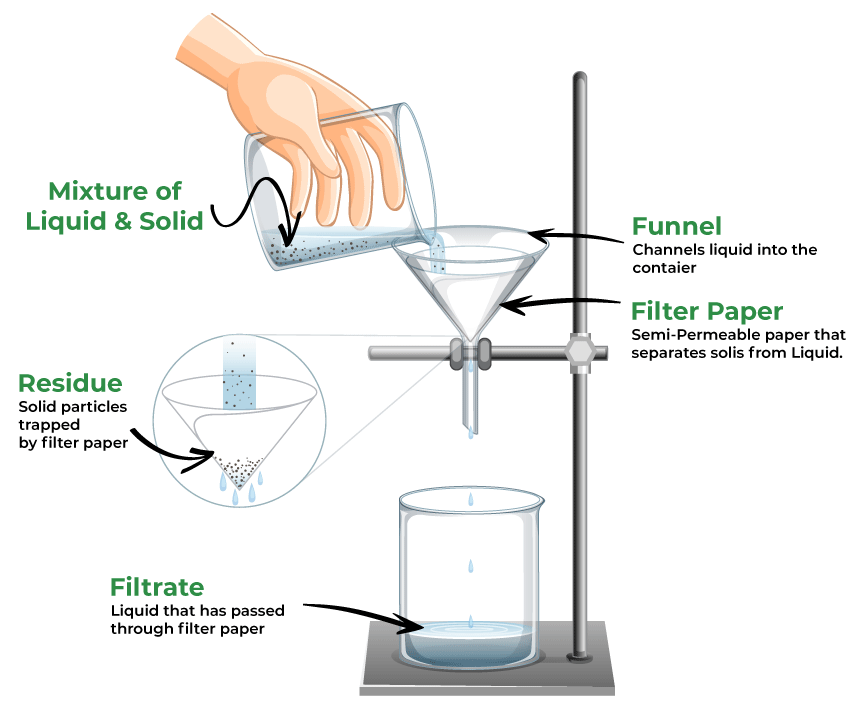
Here the filter paper allows the liquid to pass through it but stops the bigger solid particles which are then removed manually and the solution is filtered in this way.
We can easily filter any of the solutions, if we have
- Filter Medium (Filter Paper)
- Slurry or Residue (fluid with suspended solids)
- Filtration Driving Force (pressure, force, gravity, etc)
- Filtration Device that holds the filter medium and filtrate.
Filtration Examples
Filtration is one of the most important techniques for the Separation of Mixtures in a laboratory, it is also a common process happening in our everyday life like:
- When making coffee, hot water is filtered through the ground coffee and a coffee bean. The filtrate is the coffee in liquid form. Using a tea ball or a tea bag (paper filter) for brewing tea is very also an example of filtration example.
- A kidney is a biological filter that is used to filter the human blood.
- HEPA filters are used by various vacuum cleaners and air conditioners to filter out dust and pollen from the air.
- Filters with particulate-capturing fibres are commonly used in aquariums.
- During mining, belt filters extract precious metals.
- Sand and permeable rock in the ground filtered the water which is then stored in the aquifer and then used as groundwater.
Applications of Filtration
Some applications of separation by filtration method are mentioned below.
- Filtration of Tea or Coffee using a Sieve.
- Separation of chalk powder and water from their solution.
- Vacuum cleaners are fitted with filters in order to absorb dust particles.
- Filtration of sand particles from water or chalk powder.
- The wastewater treatment plant uses the filtration technique to filter the sewage.
- Filtration techniques are used in the metallurgical process to remove the slag.
- Air filters are used in automobiles and in factories to remove harmful particles from the smoke.
- The treatment of water uses filtration techniques.
- Blood filtering in kidneys is another application of the filtration technique.
Also Read
Filtration – FAQs
What is Filtration?
Filtration is a separation technique that uses a porous medium that retains the solid substance but allows the fluid to penetrate through it. It is the process of removing insoluble substances from the solution.
How to Filter Water at home?
We use various techniques to filter water at home. Some of the important methods used to filter water are,
- Use of Filtration Membrane (Muslin Cloth, etc)
- Bolling of Water.
- Use of Chemicals such as Chlorine, Bleaching Powder, etc.
- Use of RO (Reverse Osmosis) Filter
Which type of Mixture can be Separated by Filtration?
A mixture that contains a liquid and an insoluble solid can be Separated by Filtration.
What is the Principle of Filtration?
The size of the solute and the solvent particle differs a lot and this concept is used as the principle of filtration. That the difference in size allows only the smaller particles to move from the filtration membrane.
Who Filters the Blood in the Body?
The blood in the human body is filtered through the kidneys. The filtration unit of the kidney is called the nephron, which is responsible for the filtration of blood in the human body.
What is Filtration Membrane?
Filtration membranes are living or non-living membranes formed by either organic or inorganic materials that are used to separate dissolved materials or solutes from a true solution or from a colloidal solution.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...