false command in Linux with examples
Last Updated :
05 Mar, 2019
false command is used to return an exit status code (“1” by default) that indicates failure. It is useful when the user wants a conditional expression or an argument to always be unsuccessful. When no argument is passed to the false command, it fails with no output and exit status as 1.
Syntax:
false [argument]
Example:

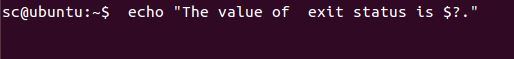
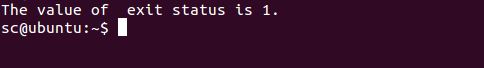
We can see that no output is returned but we can check the exit status value by checking the value of the special shell variable i.e. ?, that contain the exit status of the false command. Since ? is a variable, we need to prefix it with $ for the reference.
Syntax:
"$?"
Example: To print the exit status of the previous command.
Options:
- –help : It is used to show this help information and exit.
- –version: It gives the version information and exit.
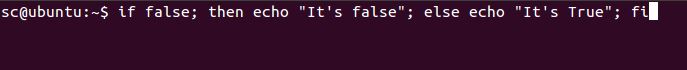
Implementing false command in an if statement: We can use the false command in if statement when we want to execute a statement/command if the condition becomes false.
Syntax:
if false; then [Executable statements]; else [Executable statement]; fi
Example:
if false; then echo "It's false"; else echo "It's True"; fi

Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...