Factorial of a number using JavaScript
Last Updated :
04 Dec, 2023
Given a positive integer n and the task is to find the factorial of that number using JavaScript code.
For any positive integer ‘n’, the factorial of n is the product of all the values from 1 to n. In mathematics, the factorial of n is represented by n!. a factorial of 0 is 1.
Note: Factorials of negative numbers are not defined as only positive numbers including 0 are defined in the domain of factorials.
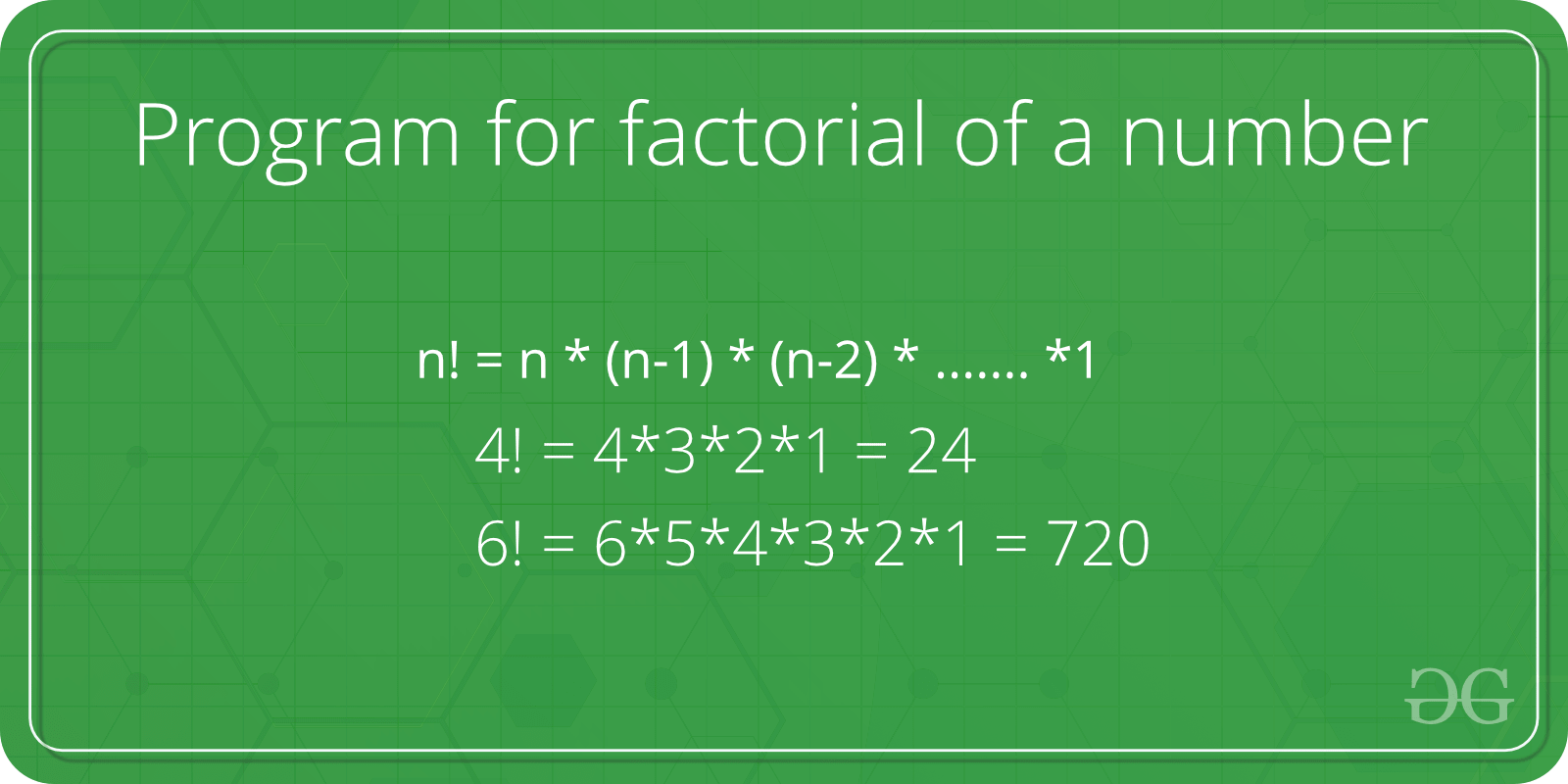
JavaScript Program for Factorial
Examples:
Input : 4
Output : 24
Input : 5
Output : 120
Approach 1: Iterative Method
- Declare a variable with a value of the number whose factorial you have to find.
- Declare a function factorial taking the value as a parameter.
- In the function definition, initialize variable ans to 1.
- Loop in the range of [2, n].
- Multiply ans by the value of i in each iteration.
- Return the value of ans.
Example: In this example, we a following iterative method.
Javascript
let n = 5;
function factorial(n) {
let ans = 1;
if(n === 0)
return 1;
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++)
ans = ans * i;
return ans;
}
console.log(factorial(n));
|
Time Complexity: O(n) Since the code is running for all the values of n
Space Complexity: O(1) As we are not allocating any extra space for a variable.
Approach 2: Recursive Method
- Declare a variable with a value of the number whose factorial you have to find.
- Declare a recursive function factorial taking the value as a parameter.
- The function returns 1 if the value is 0 else the return calls the function for value – 1.
- After recursion is over the value returned is the factorial.
Example: In this example, we are following Recursive method
Javascript
let n = 5;
function factorial(n) {
if (n === 0) {
return 1;
}
else {
return n * factorial( n - 1 );
}
}
console.log(factorial(n));
|
Time Complexity: O(n) Since the code is running for all the values of n
Space Complexity: O(n) As the stack is being created for each function call
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...