Find the Factorial of a large number
Last Updated :
17 Nov, 2023
Find the factorial of a large number.
What is Factorial of a number?
Factorial of a non-negative integer, is the multiplication of all integers smaller than or equal to n.

Factorial of a number
Examples:
Input: 100
Output: 933262154439441526816992388562667004-
907159682643816214685929638952175999-
932299156089414639761565182862536979-
208272237582511852109168640000000000-
00000000000000
Input: 50
Output: 3041409320171337804361260816606476884-
4377641568960512000000000000
We have discussed a simple program for factorial.
Why conventional way of computing factorial fails for large numbers?
A factorial of 100 has 158 digits. It is not possible to store these many digits even if we use long int.
The idea is to use basic mathematics for multiplication.
Illustration:
Example to show working of multiply(res[], x)
- A number 5189 is stored in res[] as following: res[] = {9, 8, 1, 5}
- let x = 10
Initialize carry = 0
- At i = 0, prod = res[0]*x + carry = 9*10 + 0 = 90.
res[0] = 0, carry = 9
- At i = 1, prod = res[1]*x + carry = 8*10 + 9 = 89
res[1] = 9, carry = 8
- At i = 2, prod = res[2]*x + carry = 1*10 + 8 = 18
res[2] = 8, carry = 1
- At i = 3, prod = res[3]*x + carry = 5*10 + 1 = 51
res[3] = 1, carry = 5

- res[4] = carry = 5
res[] = {0, 9, 8, 1, 5}

Follow the steps below to solve the given problem:
- Create an array res[] of MAX size where MAX is a number of maximum digits in output.
- Initialize value stored in res[] as 1 and initialize res_size (size of ‘res[]’) as 1.
- Multiply x with res[] and update res[] and res_size to store the multiplication result for all the numbers from x = 2 to n.
- To multiply a number x with the number stored in res[], one by one multiply x with every digit of res[].
- To implement multiply function perform the following steps:
- Initialize carry as 0.
- Do following for i = 0 to res_size – 1
- Find value of res[i] * x + carry. Let this value be prod.
- Update res[i] by storing the last digit of prod in it.
- Update carry by storing the remaining digits in carry.
- Put all digits of carry in res[] and increase res_size by the number of digits in carry.
Below is the implementation of the above algorithm.
NOTE: In the below implementation, the maximum digits in the output are assumed as 500. To find a factorial of a much larger number ( > 254), increase the size of an array or increase the value of MAX. This can also be solved using Linked List instead of using res[] array which will not waste extra space.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 500
int multiply(int x, int res[], int res_size);
void factorial(int n)
{
int res[MAX];
res[0] = 1;
int res_size = 1;
for (int x = 2; x <= n; x++)
res_size = multiply(x, res, res_size);
cout << "Factorial of given number is \n";
for (int i = res_size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
cout << res[i];
}
int multiply(int x, int res[], int res_size)
{
int carry = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < res_size; i++) {
int prod = res[i] * x + carry;
res[i] = prod % 10;
carry = prod / 10;
}
while (carry) {
res[res_size] = carry % 10;
carry = carry / 10;
res_size++;
}
return res_size;
}
int main()
{
factorial(100);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static void factorial(int n)
{
int res[] = new int[500];
res[0] = 1;
int res_size = 1;
for (int x = 2; x <= n; x++)
res_size = multiply(x, res, res_size);
System.out.println("Factorial of given number is ");
for (int i = res_size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
System.out.print(res[i]);
}
static int multiply(int x, int res[], int res_size)
{
int carry = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < res_size; i++) {
int prod = res[i] * x + carry;
res[i] = prod % 10;
carry = prod / 10;
}
while (carry != 0) {
res[res_size] = carry % 10;
carry = carry / 10;
res_size++;
}
return res_size;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
factorial(100);
}
}
|
Python3
import sys
def factorial(n):
res = [None]*500
res[0] = 1
res_size = 1
x = 2
while x <= n:
res_size = multiply(x, res, res_size)
x = x + 1
print("Factorial of given number is")
i = res_size-1
while i >= 0:
sys.stdout.write(str(res[i]))
sys.stdout.flush()
i = i - 1
def multiply(x, res, res_size):
carry = 0
i = 0
while i < res_size:
prod = res[i] * x + carry
res[i] = prod % 10
carry = prod//10
i = i + 1
while (carry):
res[res_size] = carry % 10
carry = carry // 10
res_size = res_size + 1
return res_size
factorial(100)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void factorial(int n)
{
int[] res = new int[500];
res[0] = 1;
int res_size = 1;
for (int x = 2; x <= n; x++)
res_size = multiply(x, res, res_size);
Console.WriteLine("Factorial of "
+ "given number is ");
for (int i = res_size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
Console.Write(res[i]);
}
static int multiply(int x, int[] res, int res_size)
{
int carry = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < res_size; i++) {
int prod = res[i] * x + carry;
res[i] = prod % 10;
carry = prod / 10;
}
while (carry != 0) {
res[res_size] = carry % 10;
carry = carry / 10;
res_size++;
}
return res_size;
}
static public void Main() { factorial(100); }
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function factorial(n)
{
let res = new Array(500);
res[0] = 1;
let res_size = 1;
for (let x=2; x<=n; x++)
res_size = multiply(x, res, res_size);
document.write("Factorial of given number is " + "<br>");
for (let i=res_size-1; i>=0; i--)
document.write(res[i]);
}
function multiply(x, res, res_size)
{
let carry = 0;
for (let i=0; i<res_size; i++)
{
let prod = res[i] * x + carry;
res[i] = prod % 10;
carry = Math.floor(prod/10);
}
while (carry)
{
res[res_size] = carry%10;
carry = Math.floor(carry/10);
res_size++;
}
return res_size;
}
factorial(100);
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
$MAX = 500;
function factorial($n)
{
global $MAX;
$res = array_fill(0, $MAX, 0);
$res[0] = 1;
$res_size = 1;
for ($x = 2; $x <= $n; $x++)
$res_size = multiply($x, $res, $res_size);
echo "Factorial of given number is \n";
for ($i = $res_size - 1; $i >= 0; $i--)
echo $res[$i];
}
function multiply($x, &$res, $res_size)
{
$carry = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $res_size; $i++)
{
$prod = $res[$i] * $x + $carry;
$res[$i] = $prod % 10;
$carry = (int)($prod / 10);
}
while ($carry)
{
$res[$res_size] = $carry % 10;
$carry = (int)($carry / 10);
$res_size++;
}
return $res_size;
}
factorial(100);
?>
|
Output
Factorial of given number is
93326215443944152681699238856266700490715968264381621468592963895217599993229915608941463976156518286253697920827223758251185210916864000000000000000000000000
Time Complexity: O(N log (N!)), where O(N) is for loop and O(log N!) is for nested while loop
Auxiliary Space: O(max(digits in factorial))
Find the Factorial of a large number using Basic BigInteger
This problem can be solved using the below idea:
Big Integer can also be used to calculate the factorial of large numbers.
Illustration:
N = 5
ans = 1
At i = 2: ans = ans x i = 1 x 2 = 2
At i = 3: ans = ans x i = 2 x 3 = 6
At i = 4: ans = ans x i = 6 x 4 = 24
At i = 5: ans = ans x i = 24 x 5 = 120
Hence factorial of N is 120
Follow the steps below to solve the given problem:
- Declare a BigInteger f with 1 and perform the conventional way of calculating factorial
- Traverse a loop from x = 2 to N and multiply x with f and store the resultant value in f
Below is the implementation of the above idea :
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ull unsigned long long
ull factorial(int N)
{
ull f = 1;
for (ull i = 2; i <= N; i++)
f *= i;
return f;
}
int main()
{
int N = 20;
cout << factorial(N) << endl;
}
|
Java
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example {
static BigInteger factorial(int N)
{
BigInteger f
= new BigInteger("1");
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
f = f.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i));
return f;
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
int N = 20;
System.out.println(factorial(N));
}
}
|
Python3
def factorial(N):
f = 1
for i in range(2, N + 1):
f *= i
return f;
N = 20;
print(factorial(N));
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Numerics;
public class Example {
static BigInteger factorial(int N)
{
BigInteger f
= new BigInteger(1);
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
f = BigInteger.Multiply(f, new BigInteger(i));
return f;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int N = 20;
Console.WriteLine(factorial(N));
}
}
|
Javascript
function factorial(N)
{
let f = BigInt(1);
for (var i = 2; i <= N; i++)
f *= BigInt(i);
return f;
}
let N = 20;
console.log(factorial(N));
|
Output
2432902008176640000
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Find Factorial of a number using Linked List :-
So the basic idea is to multiply the next number ranging between 2 to N with the data stored in the current Node and also maintain a carry just like the array approach. And then move on to the next node.
Let’s break it down into following steps :
- Initially we’ll create 1 single node containing 1 in it.
- Then initialized i of a for loop with 2.
- And for each value of i up till N, we’ll call a function multiply which takes 2 parameter, head of the list and value of i.
- And perform the below operation (See the image)
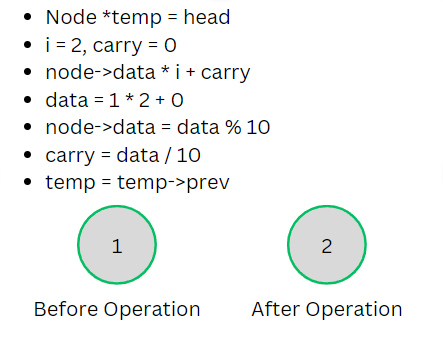
Operation
The above operation will be carried out till our temp pointer becomes NULL.
Now there are further 2 cases , The multiplication of i with the node’s data :
- Doesn’t exceed 1 digit
- Exceeds 1 digit
If the multiplication of current node’s data with i – Exceeds 1 digit, then we won’t be storing it into a single node. Rather, we’ll be storing each digit into a single node. And if it doesn’t then we’ll simply replace current node’s data with it.
So, by above explanation we can conclude and form the following steps to solve this problem :
Algorithm:
- Find value of : node’s data * i + carry. Store it in a variable ‘prod’.
- Initialize 2 pointers let’s say prev and temp on the current node and Update the current node’s value by storing the last digit of the ‘prod’
- Update carry by storing the remaining digits in carry (excluding the last digit)
- Now, bring prev ptr on temp and move temp to the next node (if any) and then again perform, the previous steps until the carry becomes 0 or the temp ptr becomes NULL.
- Once the temp pointer reaches the NULL there is a possibility that carry is still not 0. So, until carry becomes 0 we have to again perform the same steps by creating a new node for every remaining digit.
See the image below for the Dry run of above steps :
(i) Node’s data = 1, i = 2, carry = 0.
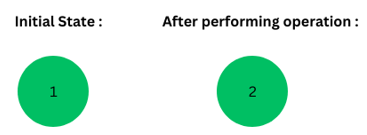
(ii) Node’s Data : 2, i = 3, carry = 0
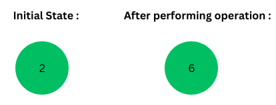
(iii) Node’s Data : 6, i = 4, carry = 2 (6*4 = 24, 24 % 10 = 4, 24/10 = 2)
X = NULL in the below image :
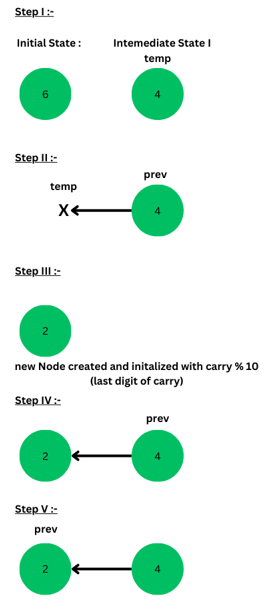
6 × 4 = 24
Just like this, we’ll do for the remaining digits, and each of the digit will be stored in a single node.
Code :
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* prev;
Node(int n)
{
data = n;
prev = NULL;
}
};
void Multiply(Node* head, int i)
{
Node *temp = head,
*prevPtr = head;
int carry = 0;
while (temp != NULL) {
int prod = temp->data * i + carry;
temp->data = prod % 10;
carry = prod / 10;
prevPtr = temp;
temp = temp->prev;
}
while (carry != 0) {
prevPtr->prev = new Node((int)(carry % 10));
carry /= 10;
prevPtr = prevPtr->prev;
}
}
void print(Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return;
print(head->prev);
cout << head->data;
}
int main()
{
int n = 100;
Node *head = new Node(1);
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
Multiply(head, i);
cout << "Factorial of " << n << " is : \n";
print(head);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
public int data;
public Node prev;
public Node(int n) {
data = n;
prev = null;
}
}
class Main {
public static void Multiply(Node head, int i) {
Node temp = head;
Node prevPtr = head;
int carry = 0;
while (temp != null) {
int prod = temp.data * i + carry;
temp.data = prod % 10;
carry = prod / 10;
prevPtr = temp;
temp = temp.prev;
}
while (carry != 0) {
prevPtr.prev = new Node((int) (carry % 10));
carry /= 10;
prevPtr = prevPtr.prev;
}
}
public static void print(Node head) {
if (head == null)
return;
print(head.prev);
System.out.print(head.data);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 100;
Node head = new Node(1);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
Multiply(head, i);
System.out.println("Factorial of " + n + " is : ");
print(head);
System.out.println();
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, n):
self.data = n
self.prev = None
def Multiply(head, i):
temp = head
prevPtr = head
carry = 0
while temp is not None:
prod = temp.data * i + carry
temp.data = prod % 10
carry = prod // 10
prevPtr = temp
temp = temp.prev
while carry != 0:
prevPtr.prev = Node(carry % 10)
carry = carry // 10
prevPtr = prevPtr.prev
def print_list(head):
if head is None:
return
print_list(head.prev)
print(head.data, end="")
def main():
n = 100
head = Node(1)
for i in range(2, n+1):
Multiply(head, i)
print("Factorial of", n, "is : ")
print_list(head)
print()
main()
|
C#
using System;
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node prev;
public Node(int n)
{
data = n;
prev = null;
}
}
public class Program
{
public static void Multiply(Node head, int i)
{
Node temp = head;
Node prevPtr = head;
int carry = 0;
while (temp != null)
{
int prod = temp.data * i + carry;
temp.data = prod % 10;
carry = prod / 10;
prevPtr = temp;
temp = temp.prev;
}
while (carry != 0)
{
prevPtr.prev = new Node((int)(carry % 10));
carry /= 10;
prevPtr = prevPtr.prev;
}
}
public static void Print(Node head)
{
if (head == null)
return;
Print(head.prev);
Console.Write(head.data);
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 100;
Node head = new Node(1);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
Multiply(head, i);
Console.WriteLine("Factorial of " + n + " is : ");
Print(head);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(n) {
this.data = n;
this.prev = null;
}
}
function Multiply(head, i) {
let temp = head;
let prevPtr = head;
let carry = 0;
while (temp !== null) {
let prod = temp.data * i + carry;
temp.data = prod % 10;
carry = Math.floor(prod / 10);
prevPtr = temp;
temp = temp.prev;
}
while (carry !== 0) {
prevPtr.prev = new Node(carry % 10);
carry = Math.floor(carry / 10);
prevPtr = prevPtr.prev;
}
}
function print(head) {
if (head === null)
return;
print(head.prev);
process.stdout.write(head.data.toString());
}
function main() {
const n = 100;
const head = new Node(1);
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++)
Multiply(head, i);
console.log("Factorial of " + n + " is : ");
print(head);
console.log();
}
main();
|
Output
Factorial of 100 is :
93326215443944152681699238856266700490715968264381621468592963895217599993229915608941463976156518286253697920827223758251185210916864000000000000000000000000
Time Complexity : O(N²)
Space Complexity : O(digits in factorial)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...