Fabaceae – Overview, Characteristics, Classification, Importance
Last Updated :
25 Jul, 2022
Morphology is the study of phenotypes character or the exterior character with respect to other parts. Morphology of plants deals with the morphology of plants and we study different parts of plants. Fabaceae (pea family) is a huge group of angiosperms. It is otherwise called Leguminosae and the plants are generally known as vegetables. It is generally conveyed everywhere. It incorporates numerous significant heartbeats like peas, soybean, chickpeas, and so forth.
Classification
Kingdom – Plantae
Subkingdom– Tracheobionta
Class – Dicotyledons
Subclass – Polypetalous
Order – Leguminales
Family – Fabaceae
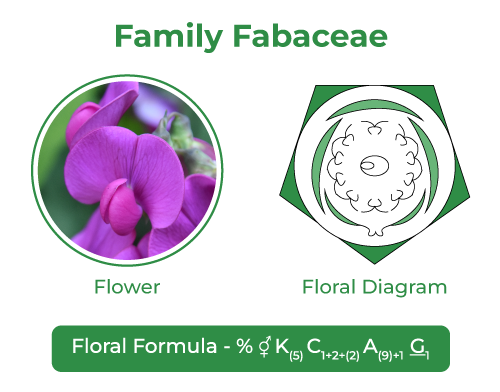
Floral Formula
Peas
% ⚥ K(5) C1+2+(2) A(9)+1 G1
| % |
Zygomorphic (two-sided evenness) |
| ⚥ |
Bisexual |
| K(5) |
Calyx – 5 sepals, gamosepalous (joined together) |
| C1+2+(2) |
Corolla – 5 petals, polypetalous |
| A(9)+1 |
Androecium – 10 stamens, diadelphous |
| G1 |
Gynoecium – monocarpellary, predominant ovary |
Characteristics of Fabaceae Family
- Plants of this family are spices, bushes, plants, or moving by twining or ringlets.
- The root contains root knobs that have nitrogen-fixing microscopic organisms (rhizobium) and regularly non protein amino acids are found.
- Leaves are generally pinnatus and are spirally organized, pulvinus of leaf and individual pamphlets are advanced.
- Blossoms are normally sexually unbiased, petals are standard or unpredictable cup molded hypanthium. Petals are by and large five in number.
- This is imbricate or basally connate, standard, and normally valvate.
- The androecium is with one to various stamens however typically ten, concealed by perianth to long-applied and in some cases gaudy fibers particular or connate.
- On the off chance that connate is monodelphous or diadelphous , dust grains are tricolporate, tricolpate or triporate.
- Gynoecium of one carpel, particularly, is normally prolonged and with a short gynophore.
- The ovary is prevalent with parietal (peripheral) placentation.
- Ovules are anatropous to campylotropous.
- Natural products are normally vegetables.
- Seeds are hard external, incipient organisms directly bent with no or less endosperm.
Normal names – peas, legumes
This family was before called Papilionoideae, a subfamily of the Leguminosae family.
Vegetative Characters
Trees, bushes, herbs root with root nodulesStem: erect or climber leaves: substitute, pinnately compound or straightforward; leaf base, pulvinate; specify; venation reticulate.
- Floral characters-Inflorescence racemose
- Flower: sexually open, zygomorphic
- Calyx: sepals five, gamosepalous; imbricate aestivation
- Corolla: petals five, polypetalous, papilionaceous, comprising of a back norm, two sidelong wings, two foremost ones framing a fall (encasing stamens and pistil), vexillary aestivation
- Androecium: ten, diadelphous, anther dithecous
- Gynoecium: ovary predominant, mono carpellary, unilocular with numerous ovules, style single
- Fruit: vegetable; seed: one to many, non-Economic significance: Many plants having a place with the family are wellsprings of heartbeats like gram, arhar; edible oil like soybean, groundnut; color like Indigofera; fiber like sun hemp; grain like Sesbania, Trifolium, ornamentals like lupin, sweet pea; medication like muliathi.
Examples:- groundnut, soybean
Economic importance
- Lumber yielding plant – Indian blackwood, Sheesham, Ironwood, Siris, Australian blackwood.
- Oil yielding plant – Soybean oil, ground however oil is separated from certain plants of the family.
- Color yielding plant – Dyes like indigo and hematoxylin are additionally gotten from the plants.
- Beats yielding: Lentil, Masur, green gram, pea, chickpea, dark gram, urad, mung, pigeon pea, arhar, and so forth are gotten from the plants which have a place with this family.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: Fabaceae was before known as?
Answer:
Fabaceae was prior known as Papilionoideae. They are for the most part far-reaching all through the world and are a sub-group of the family Leguminosae. They are found for the most part as climbers yet some of the time can be even erect.
Question2: The gynoecium consists of many free pistils in flowers?
Answer:
If more than one carpel is present in gynoecium this condition is called polycarpellary. If all the carpels in gynoecium are free, then this condition is called apocarpous. For example, Michelia.
Question 3: Vexillary aestivation is characteristic of the family?
Answer:
The petals are overlapping (imbricate) in the bud with the posterior petal (called the banner or flag) outermost (i.e., exterior) in position. The two lowermost petals are joined together called the keel petals. The lateral petals are often called the wings. This arrangement of floral whorls is called vexillary aestivation. So, the correct answer is ‘Fabaceae‘.
Question 4: Phyllode is present in?
Answer:
Phyllode is present in Australian Acacia. It is a modification of the leaf in which lamina is absent and the petiole becomes flattened and performs the function of food synthesis.
Question 5: Zygomorphic symmetry seen in?
Answer:
When a flower can be divided into two similar halves only in one particular vertical plane, it is zygomorphic, e.g. pea, Gulmohar, bean, etc.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...