Expressing factorial n as sum of consecutive numbers
Last Updated :
10 Jan, 2023
Given two numbers N and M. Find the number of ways in which factorial N can be expressed as a sum of two or more consecutive numbers. Print the result modulo M.
Examples:
Input : N = 3, M = 7
Output : 1
Explanation: 3! can be expressed
in one way, i.e. 1 + 2 + 3 = 6.
Hence 1 % 7 = 1
Input : N = 4, M = 7
Output : 1
Explanation: 4! can be expressed
in one way, i.e. 7 + 8 + 9 = 24
Hence 1 % 7 = 1
A simple solution is to first compute factorial, then count number of ways to represent factorial as sum of consecutive numbers using Count ways to express a number as sum of consecutive numbers. This solution causes overflow.
Below is a better solution to avoid overflow.
Let us consider that sum of r consecutive numbers be expressed as:
(a + 1) + (a + 2) + (a + 3) + … + (a + r), which simplifies as (r * (r + 2*a + 1)) / 2
Hence, (a + 1) + (a + 2) + (a + 3) + … + (a + r) = (r * (r + 2*a + 1)) / 2. Since the above expression is equal to factorial N, we write it as
2 * N! = r * (r + 2*a + 1)
Instead of counting all the pairs (r, a), we will count all pairs (r, r + 2*a + 1). Now, we are just counting all ordered pairs (X, Y) with XY = 2 * N! where X < Y and X, Y have different parity, that means if (r) is even, (r + 2*a + 1) is odd or if (r) is odd then (r + 2*a + 1) is even. This is equivalent to finding the odd divisors of 2 * N! which will be same as odd divisors of N!.
For counting the number of divisors in N!, we calculate the power of primes in factorization and total count of divisors become (p1 + 1) * (p2 + 1) * … * (pn + 1). To calculate the largest power of a prime in N!, we will use legendre’s formula.
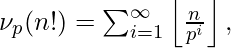
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 50002
vector<int> primes;
void sieve()
{
bool isPrime[MAX];
memset(isPrime, true, sizeof(isPrime));
for (int p = 2; p * p < MAX; p++) {
if (isPrime[p] == true) {
for (int i = p * 2; i < MAX; i += p)
isPrime[i] = false;
}
}
for (int p = 2; p < MAX; p++)
if (isPrime[p])
primes.push_back(p);
}
long long int power(long long int x,
long long int y)
{
long long int count = 0;
long long int z = y;
while (x >= z) {
count += (x / z);
z *= y;
}
return count;
}
long long int modMult(long long int a,
long long int b,
long long int mod)
{
long long int res = 0;
a = a % mod;
while (b > 0) {
if (b % 2 == 1)
res = (res + a) % mod;
a = (a * 2) % mod;
b /= 2;
}
return res % mod;
}
long long int countWays(long long int n,
long long int m)
{
long long int ans = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < primes.size(); i++) {
long long int powers = power(n, primes[i]);
if (powers == 0)
break;
ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1, m) % m;
}
if (((ans - 1) % m) < 0)
return (ans - 1 + m) % m;
else
return (ans - 1) % m;
}
int main()
{
sieve();
long long int n = 4, m = 7;
cout << countWays(n, m);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int MAX = 50002;
static ArrayList<Integer> primes
= new ArrayList<Integer>();
public static void sieve()
{
boolean isPrime[] = new boolean[MAX];
for(int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
isPrime[i] = true;
for (int p = 2; p * p < MAX; p++) {
if (isPrime[p] == true) {
for (int i = p * 2; i < MAX; i += p)
isPrime[i] = false;
}
}
for (int p = 2; p < MAX; p++)
if (isPrime[p] == true)
primes.add(p);
}
public static int power(int x, int y)
{
int count = 0;
int z = y;
while (x >= z) {
count += (x / z);
z *= y;
}
return count;
}
public static int modMult(int a, int b, int mod)
{
int res = 0;
a = a % mod;
while (b > 0) {
if (b % 2 == 1)
res = (res + a) % mod;
a = (a * 2) % mod;
b /= 2;
}
return res % mod;
}
public static int countWays(int n, int m)
{
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < primes.size(); i++) {
int powers = power(n, primes.get(i));
if (powers == 0)
break;
ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1, m) % m;
}
if (((ans - 1) % m) < 0)
return (ans - 1 + m) % m;
else
return (ans - 1) % m;
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
sieve();
int n = 4, m = 7;
System.out.println(countWays(n,m));
}
}
|
Python 3
MAX = 50002;
primes = []
def sieve():
isPrime = [True]*(MAX)
p = 2
while p * p < MAX :
if (isPrime[p] == True):
for i in range( p * 2,MAX, p):
isPrime[i] = False
p+=1
for p in range( 2,MAX):
if (isPrime[p]):
primes.append(p)
def power( x, y):
count = 0
z = y
while (x >= z):
count += (x // z)
z *= y
return count
def modMult(a, b,mod):
res = 0
a = a % mod
while (b > 0):
if (b % 2 == 1):
res = (res + a) % mod
a = (a * 2) % mod
b //= 2
return res % mod
def countWays(n,m):
ans = 1
for i in range(1,len(primes)):
powers = power(n, primes[i])
if (powers == 0):
break
ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1, m) % m
if (((ans - 1) % m) < 0):
return (ans - 1 + m) % m
else:
return (ans - 1) % m
if __name__ == "__main__":
sieve()
n = 4
m = 7
print(countWays(n, m))
|
C#
using System ;
using System.Collections;
class GFG {
static int MAX = 50002;
static ArrayList primes = new ArrayList ();
public static void sieve()
{
bool []isPrime = new bool[MAX];
for(int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
isPrime[i] = true;
for (int p = 2; p * p < MAX; p++) {
if (isPrime[p] == true) {
for (int i = p * 2; i < MAX; i += p)
isPrime[i] = false;
}
}
for (int p = 2; p < MAX; p++)
if (isPrime[p] == true)
primes.Add(p);
}
public static int power_prime(int x, int y)
{
int count = 0;
int z = y;
while (x >= z) {
count += (x / z);
z *= y;
}
return count;
}
public static int modMult(int a, int b, int mod)
{
int res = 0;
a = a % mod;
while (b > 0) {
if (b % 2 == 1)
res = (res + a) % mod;
a = (a * 2) % mod;
b /= 2;
}
return res % mod;
}
public static int countWays(int n, int m)
{
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < primes.Count; i++) {
int powers = power_prime(n, Convert.ToInt32(primes[i]));
if (powers == 0)
break;
ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1, m) % m;
}
if (((ans - 1) % m) < 0)
return (ans - 1 + m) % m;
else
return (ans - 1) % m;
}
public static void Main () {
sieve();
int n = 4, m = 7;
Console.WriteLine(countWays(n,m));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let MAX = 50002;
let primes = [];
function sieve()
{
let isPrime = new Array(MAX);
for(let i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
isPrime[i] = true;
for (let p = 2; p * p < MAX; p++)
{
if (isPrime[p] == true)
{
for (let i = p * 2; i < MAX; i += p)
isPrime[i] = false;
}
}
for (let p = 2; p < MAX; p++)
if (isPrime[p] == true)
primes.push(p);
}
function power(x,y)
{
let count = 0;
let z = y;
while (x >= z) {
count += Math.floor(x / z);
z *= y;
}
return count;
}
function modMult(a,b,mod)
{
let res = 0;
a = a % mod;
while (b > 0) {
if (b % 2 == 1)
res = (res + a) % mod;
a = (a * 2) % mod;
b = Math.floor(b/2);
}
return res % mod;
}
function countWays(n,m)
{
let ans = 1;
for (let i = 1; i < primes.length; i++) {
let powers = power(n, primes[i]);
if (powers == 0)
break;
ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1, m) % m;
}
if (((ans - 1) % m) < 0)
return (ans - 1 + m) % m;
else
return (ans - 1) % m;
}
sieve();
let n = 4, m = 7;
document.write(countWays(n,m));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(MAX*log(log(MAX))+M*log(K)) where MAX=5002, M is the number of primes less than MAX(i.e 5002), and K is the greatest prime number less than MAX.
Auxiliary Space: O(MAX)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...