Execution Engine in Java
Last Updated :
17 May, 2020
Java virtual machine or JVM can be visualized as a virtual machine residing in the computer that provides an environment for the code to get executed. Java Runtime Environment or JRE is an implementation of the JVM. In order to execute the code, an execution engine is used. In this article, let’s understand the execution engine and different components in it.
The execution engine is the Central Component of the java virtual machine(JVM). It communicates with various memory areas of the JVM. Each thread of a running application is a distinct instance of the virtual machine’s execution engine. Execution engine executes the byte code which is assigned to the run time data areas in JVM via class loader. Java Class files are executed by the execution engine.
Execution Engine contains three main components for executing Java Classes. They are:
- Interpreter: It reads the byte code and interprets(convert) into the machine code(native code) and executes them in a sequential manner. This component runs the application from the command line by accepting a filename argument. The problem with the interpreter is that it interprets every time, even the same method multiple times, which reduces the performance of the system. To overcome this problem JIT Compilers is introduced in 1.1 version.
- JIT Compiler: JIT compiler counterbalances the interpreter’s disadvantage of slow execution and improves the performance.
- At run time, the JVM loads the class files, the semantic of each is determined and appropriate computations are performed. The additional processor and memory usage during interpretation makes a Java application perform slowly as compared to a native application.
- The JIT compiler aids in improving the performance of Java programs by compiling bytecode into native machine code at run time.
- The JIT compiler is enabled throughout, while it gets activated when a method is invoked. For a compiled method, the JVM directly calls the compiled code, instead of interpreting it. Theoretically speaking, If compiling did not require any processor time or memory usage, the speed of a native compiler and that of a Java compiler would have been same.
- JIT compilation requires processor time and memory usage. When the java virtual machine first starts up, thousands of methods are invoked. Compiling all these methods can significantly affect startup time, even if the end result is a very good performance optimization.
Profiler: This is a tool which is the part of JIT Compiler is responsible to monitor the java bytecode constructs and operations at the JVM level.
- Garbage Collector: This is a program in java that manages the memory automatically. It is a daemon thread which always runs in the background. This basically frees up the heap memory by destroying unreachable methods.
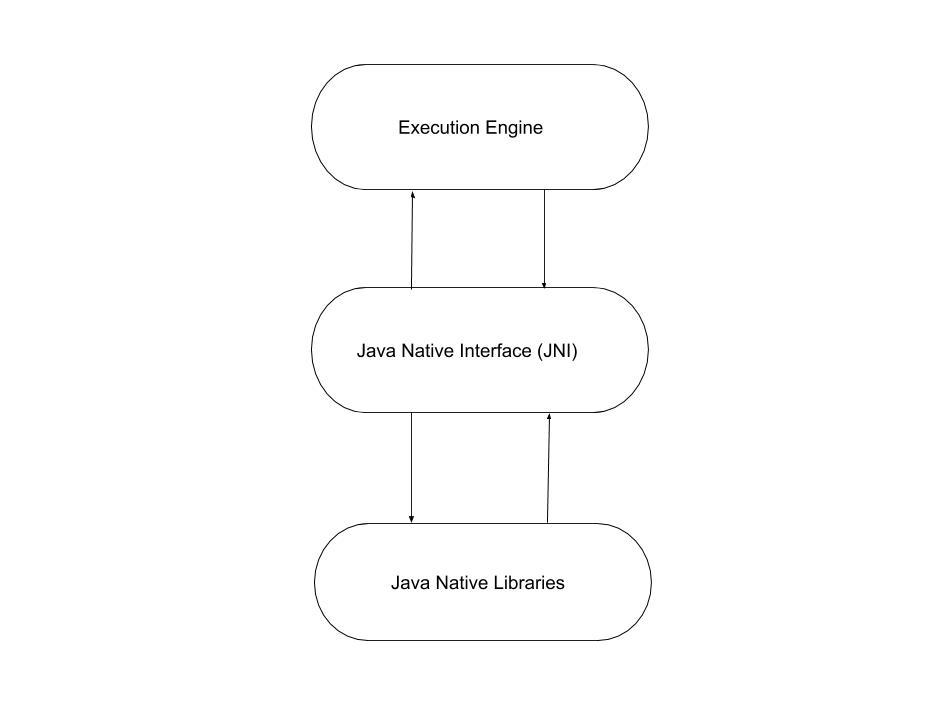
Java Native Interface(JNI): JNI acts as a bridge(mediator) between java method calls and corresponding native libraries. That is:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...