ER diagram of Bank Management System
Last Updated :
20 Sep, 2021
ER diagram is known as Entity-Relationship diagram. It is used to analyze to structure of the Database. It shows relationships between entities and their attributes. An ER model provides a means of communication.
ER diagram of Bank has the following description :
- Bank have Customer.
- Banks are identified by a name, code, address of main office.
- Banks have branches.
- Branches are identified by a branch_no., branch_name, address.
- Customers are identified by name, cust-id, phone number, address.
- Customer can have one or more accounts.
- Accounts are identified by account_no., acc_type, balance.
- Customer can avail loans.
- Loans are identified by loan_id, loan_type and amount.
- Account and loans are related to bank’s branch.
ER Diagram of Bank Management System :
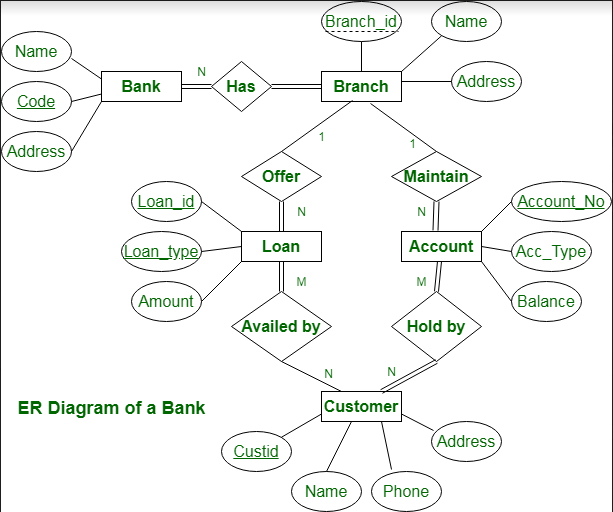
This bank ER diagram illustrates key information about bank, including entities such as branches, customers, accounts, and loans. It allows us to understand the relationships between entities.
Entities and their Attributes are :
- Bank Entity : Attributes of Bank Entity are Bank Name, Code and Address.
Code is Primary Key for Bank Entity.
- Customer Entity : Attributes of Customer Entity are Customer_id, Name, Phone Number and Address.
Customer_id is Primary Key for Customer Entity.
- Branch Entity : Attributes of Branch Entity are Branch_id, Name and Address.
Branch_id is Primary Key for Branch Entity.
- Account Entity : Attributes of Account Entity are Account_number, Account_Type and Balance.
Account_number is Primary Key for Account Entity.
- Loan Entity : Attributes of Loan Entity are Loan_id, Loan_Type and Amount.
Loan_id is Primary Key for Loan Entity.
Relationships are :
- Bank has Branches => 1 : N
One Bank can have many Branches but one Branch can not belong to many Banks, so the relationship between Bank and Branch is one to many relationship.
- Branch maintain Accounts => 1 : N
One Branch can have many Accounts but one Account can not belong to many Branches, so the relationship between Branch and Account is one to many relationship.
- Branch offer Loans => 1 : N
One Branch can have many Loans but one Loan can not belong to many Branches, so the relationship between Branch and Loan is one to many relationship.
- Account held by Customers => M : N
One Customer can have more than one Accounts and also One Account can be held by one or more Customers, so the relationship between Account and Customers is many to many relationship.
- Loan availed by Customer => M : N
(Assume loan can be jointly held by many Customers).
One Customer can have more than one Loans and also One Loan can be availed by one or more Customers, so the relationship between Loan and Customers is many to many relationship.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...