Ember.js Route init() Method
Last Updated :
15 Dec, 2022
Ember.js is an open-source JavaScript framework used for developing large client-side web applications which is based on Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture. Ember.js is one of the most widely used front-end application frameworks. It is made to speed up development and increase productivity. Currently, it is utilized by a large number of websites, including Square, Discourse, Groupon, Linked In, Live Nation, Twitch, and Chipotle.
The init() method is called when objects are instantiated. By default, this method doesn’t have any use we have to override the method.
Syntax:
init(){ // method algo };
Steps to Install and Run Ember.js:
Step 1: To run the following examples you will need to have an ember project with you. To create one, you will need to install ember-cli first. Write the below code in the terminal:
npm install ember-cli
Step 2: Now you can create the project by typing in the following piece of code:
ember new <project-name> --lang en
To start the server, type:
ember serve
Example 1: Type the following code to generate the route for this example:
ember generate route init1
app/routes/init1.js
Javascript
import Route from '@ember/routing/route';
export default class StudentsRoute extends Route {
value = 'Oxygen';
init() {
this._super(...arguments);
this.addObserver('value', this, 'change');
alert('Route Init() is initiated');
}
change() {
console.log('Value changed ')
};
p1 = [
'Oxygen',
'Source Code',
'Infine',
'Tenet',
'SpiderHead',
'The Thing',
'A Quiet Place',
'The Invisible Man',
'Looper',
'Ad Astra',
];
model() {
return this.p1;
}
setupController(controller, model) {
super.setupController(controller, model);
controller.set('p1', this.p1);
controller.set('value', this.value);
}
}
|
app/controllers/init1.js
Javascript
import Ember from 'ember';
export default Ember.Controller.extend({
Change() {
console.log('value changed');
},
actions: {
remove(data) {
this.p1.set('[]', this.p1.without(data));
},
print() {
let ans = this.p1.get('[]');
alert(ans.join('\n'));
},
},
});
|
app/templates/init1.hbs
HTML
<ul>
<h3>List is : </h3>
{{#each this.p1 as |party|}}
<li>{{party}}</li>
{{/each}}
</ul>
<br />
{{input value=this.value}}
<br />
<input
type="button"
id="check-atIndex"
value="Remove"
{{action "remove" this.value}}
/>
<br /><br />
<input
type="button"
id="print-item"
value="Print All Items"
{{action "print"}}
/>
|
Output:

Ember.js Route init() Method
Example 2: Type the following code to generate the route for this example:
ember generate route init2
app/routes/init2.js
Javascript
import Route from '@ember/routing/route';
import EmberObject from '@ember/object';
const Fruit = EmberObject.extend({
init() {
alert(`Name is ${this.get('name')}`);
}
});
export default class FruitsRoute extends Route {
fruits = [Fruit.create({
'name': 'Lady Finger',
'isFruit': false,
'color': 'green'
}),
Fruit.create({
'name': 'Brinjal',
'isFruit': false,
'color': 'purple'
}),
Fruit.create({
'name': 'Apple',
'isFruit': true,
'color': 'red'
}),
Fruit.create({
'name': 'Grapes',
'isFruit': true,
'color': 'green'
})];
item2;
item3;
model() {
return this.fruits;
}
setupController(controller, model) {
super.setupController(controller, model);
controller.set('fruits', this.fruits);
controller.set('item1', this.item1);
controller.set('item2', this.item2);
controller.set('item3', this.item3);
}
}
|
app/controllers/init2.js
Javascript
import Ember from "ember";
import { addObject, isAny, isEvery } from "@ember/array";
import EmberObject from '@ember/object';
export default Ember.Controller.extend({
actions: {
print() {
let temp = '';
this.fruits.map((items) => temp +=
items.get('name') + '\n')
alert(temp);
}
},
});
|
app/templates/init2.hbs
HTML
{{page-title "Init"}}
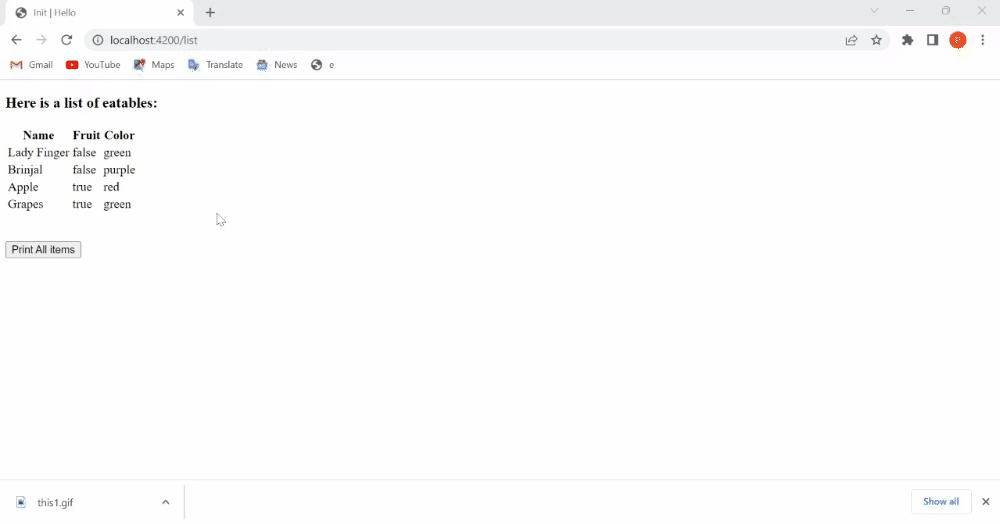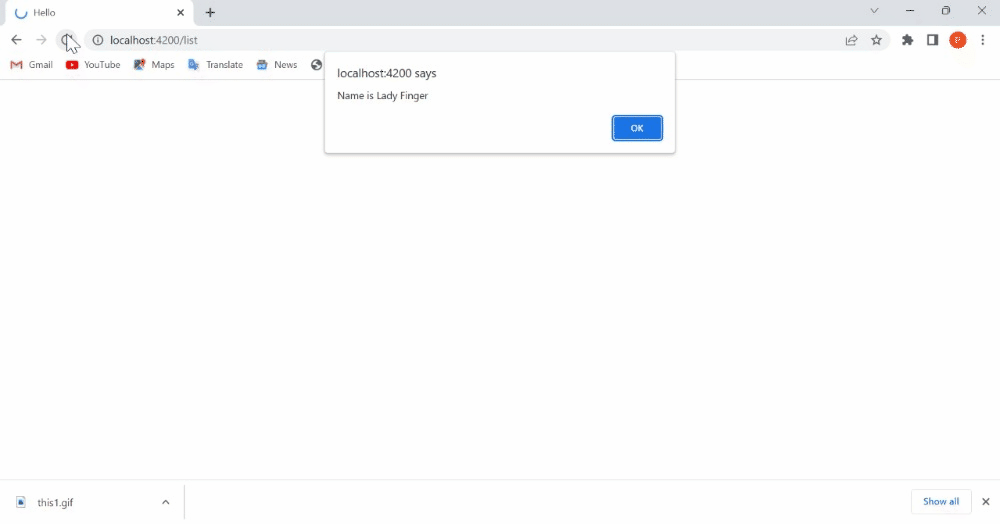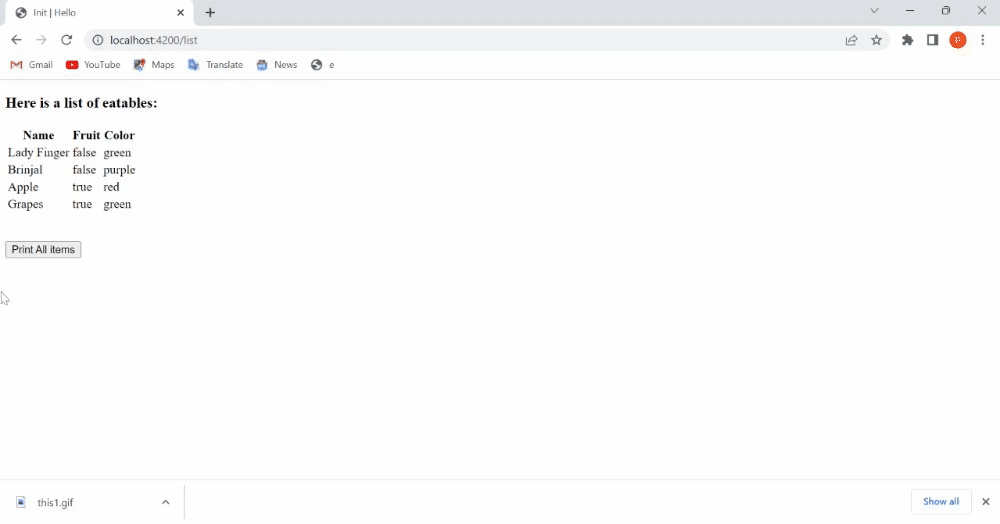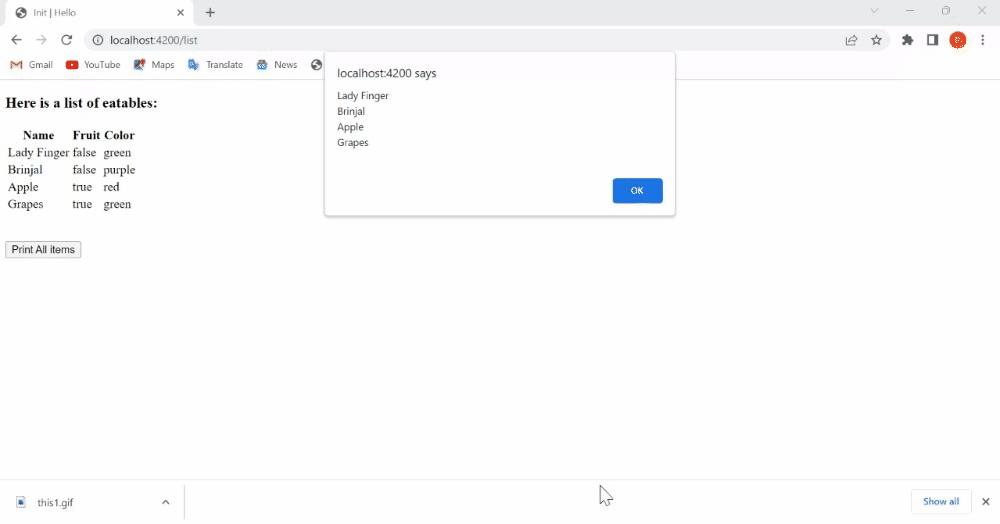
<h3>Here is a list of eatables: </h3>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Fruit</th>
<th>Color</th>
</tr>
{{#each this.fruits as |detail|}}
<tr>
<td>{{detail.name}}</td>
<td>{{detail.isFruit}}</td>
<td>{{detail.color}}</td>
</tr>
{{/each}}
</table>
<br /><br />
<div>
<input
type="button"
id="print-item"
value="Print All items"
{{action "print" }}
/>
</div>
{{outlet}}
|
Output:
Ember.js Route init() Method
Reference: https://api.emberjs.com/ember/4.6/classes/Route/methods/init?anchor=init
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...