Dyck path
Last Updated :
11 Apr, 2023
Consider a n x n grid with indexes of top left corner as (0, 0). Dyck path is a staircase walk from bottom left, i.e., (n-1, 0) to top right, i.e., (0, n-1) that lies above the diagonal cells (or cells on line from bottom left to top right).
The task is to count the number of Dyck Paths from (n-1, 0) to (0, n-1).
Examples :
Input : n = 1
Output : 1
Input : n = 2
Output : 2
Input : n = 3
Output : 5
Input : n = 4
Output : 14

The number of Dyck paths from (n-1, 0) to (0, n-1) can be given by the Catalan numberC(n).
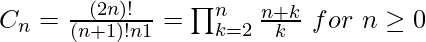
Below are the implementations to find count of Dyck Paths (or n’th Catalan number).
C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int countDyckPaths(unsigned int n)
{
int res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
res *= (2 * n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res / (n+1);
}
int main()
{
int n = 4;
cout << "Number of Dyck Paths is "
<< countDyckPaths(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
public static int countDyckPaths(int n)
{
int res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
res *= (2 * n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res / (n + 1);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = 4;
System.out.println("Number of Dyck Paths is " +
countDyckPaths(n));
}
}
|
Python3
def countDyckPaths(n):
res = 1
for i in range(0, n):
res *= (2 * n - i)
res /= (i + 1)
return res / (n+1)
n = 4
print("Number of Dyck Paths is ",
str(int(countDyckPaths(n))))
|
Javascript
<script>
function countDyckPaths(n)
{
let res = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
res *= (2 * n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res / (n + 1);
}
let n = 4;
document.write("Number of Dyck Paths is " +
countDyckPaths(n));
</script>
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int countDyckPaths(int n)
{
int res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
res *= (2 * n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res / (n + 1);
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 4;
Console.WriteLine("Number of "
+ "Dyck Paths is " +
countDyckPaths(n));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function countDyckPaths( $n)
{
$res = 1;
for ( $i = 0; $i < $n; ++$i)
{
$res *= (2 * $n - $i);
$res /= ($i + 1);
}
return $res / ($n + 1);
}
$n = 4;
echo "Number of Dyck Paths is " ,
countDyckPaths($n);
?>
|
OutputNumber of Dyck Paths is 14
Time complexity: O(n).
Auxiliary space: O(1).
Exercise :
- Find number of sequences of 1 and -1 such that every sequence follows below constraints :
a) The length of a sequence is 2n
b) There are equal number of 1’s and -1’s, i.e., n 1’s, n -1s
c) Sum of prefix of every sequence is greater than or equal to 0. For example, 1, -1, 1, -1 and 1, 1, -1, -1 are valid, but -1, -1, 1, 1 is not valid. - Number of paths of length m + n from (m-1, 0) to (0, n-1) that are restricted to east and north steps.
Approach 2:-approach to count the number of Dyck paths –In this implementation, we generate all possible Dyck paths of length n by generating all binary numbers with n bits. We then traverse through each bit in the binary representation of the number and update the depth accordingly. If at any point the depth becomes negative, then the path is not a Dyck path, so we break out of the loop. If we reach the end of the path and the depth is zero, then the path is a Dyck path, so we increment the count. Finally, we return the count of Dyck paths.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int factorial(int n) {
int fact = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fact *= i;
}
return fact;
}
int dyck_paths_2(int n) {
int numerator = factorial(2 * n);
int denominator = factorial(n + 1) * factorial(n);
return numerator / denominator;
}
int main() {
int n = 4;
cout << "Number of Dyck paths is " << n << ": " << dyck_paths_2(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class DyckPaths
{
public static int factorial(int n)
{
int fact = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fact *= i;
}
return fact;
}
public static int dyck_paths_2(int n)
{
int numerator = factorial(2 * n);
int denominator = factorial(n + 1) * factorial(n);
return numerator / denominator;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
System.out.println("Number of Dyck paths is " + n
+ ": " + dyck_paths_2(n));
}
}
|
Python3
def factorial(n):
fact = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
fact *= i
return fact
def dyck_paths_2(n):
numerator = factorial(2 * n)
denominator = factorial(n + 1) * factorial(n)
return numerator // denominator
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 4
print("Number of Dyck paths is {}: {}".format(n, dyck_paths_2(n)))
|
Javascript
function factorial(n) {
let fact = 1;
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fact *= i;
}
return fact;
}
function dyckPaths2(n) {
const numerator = factorial(2 * n);
const denominator = factorial(n + 1) * factorial(n);
return numerator / denominator;
}
const n = 4;
console.log(`Number of Dyck paths is ${n}: ${dyckPaths2(n)}`);
|
C#
using System;
class Program {
static int Factorial(int n)
{
int fact = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fact *= i;
}
return fact;
}
static int DyckPaths2(int n)
{
int numerator = Factorial(2 * n);
int denominator = Factorial(n + 1) * Factorial(n);
return numerator / denominator;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 4;
Console.WriteLine("Number of Dyck paths is " + n
+ ": " + DyckPaths2(n));
}
}
|
OutputNumber of Dyck paths is 4: 14
Time complexity: O(n).
Auxiliary space: O(1).
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...