Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM)
Last Updated :
22 Jul, 2020
In the last two decades, a massive range of modifications took place in an object-oriented and distributed component-oriented paradigm. To fulfill this demand, Microsoft developed Distributed Component Object Model. DCOM can be defined as COM with inclusion of a long wire and this is an extension to Component Object Model (COM). DCOM- Distributed Component Object Model– helps remote object via running on a protocol known as the.
Object Remote Procedure Call (ORPC). 10 million people use of Windows every day in networked environments DCOM emerge as extensively used primary purpose of DCOM is to support development of components that can be dynamically activated and that can engage with every other. DCOM object model is based on implementations of interfaces.
(DCOM) both object and component paradigm consists of a number of issues.
1. Interoperability
2. Versioning
3. Language independence
4. Size and complexity of system
Dynamic Data Exchange :
Dynamic Data Exchange or DDE, used to be designed for Microsoft Windows to enable applications to exchange information of any specific type. As DDE protocol is actually a little complicated and this complexity used to be interpreted by using many software program vendors, Dynamic Data Exchange Management Library (DDEML) was created. This library simplified interfacing with DDE protocol as well as furnished a frequent interface for all developers.
DCOM Architecture :
DCOM structure is designed for promoting software interoperability.
- The architecture supports a “software bus” on which reusable software program components can be used and built-in with one any other seamlessly.
- In order to furnish support for this reusable software component, complete object model is based totally on an object-based programming model.
- Object model used to be selected due to fact of its incapability to provide inheritance.
- This means that architecture is successful in keeping off fragile base class syndrome which exists in different models.
- The fragile base class syndrome seems when one class inherits members and behavior of any other class.
- Class which offers behavior and member functions is recognized as base class while other class is recognized as derived class.
- If the member and functionality of base class modifications then behavior and member functions of derived class additionally change.
- Changes like this end result in having to alter base class which in turn requires compilation of all dependent classes.
- DCOM architecture shown in fig 1.0 possesses a special infrastructure as it helps continual storage.
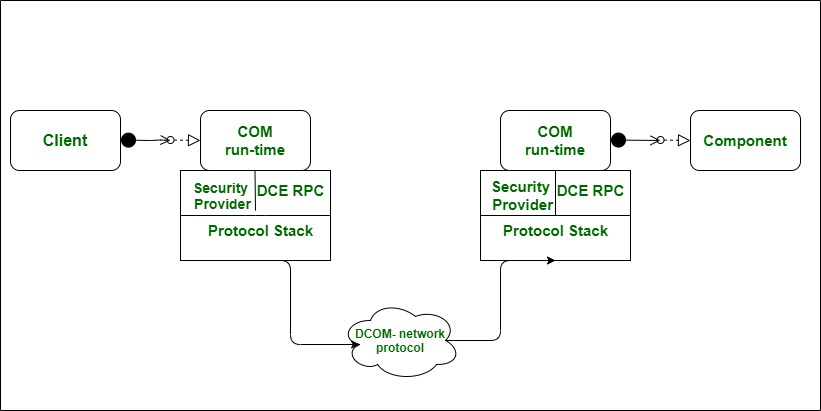
Working of DCOM :
For working of DCOM, COM object desires to be configured effectively on both computer systems and you hardly had to uninstall and reinstall objects numerous times to get them to work effectively on a particular task. Windows Registry consists of DCOM configuration information in three identifiers i.e. CLSID, PROGID, and APPID.
- CLSID –
Class Identifier or CLSID is a Global Unique Identifier or GUID to create a unique identity for an entity. Windows stores this CLSID for every setup class in a program for performing a particular task. When you want to run a class, you need right CLSID, so Windows is aware of place to go and locate program.
- PROGID –
Programmatic Identifier or PROGID is a non-obligatory or you can say an optional identifier a programmer can use as an alternative for any complex and strict CLSID. PROGIDs are generally less complicated to read and can be easily understood. There are no restrictions on how many PROGIDs can have an identical name, which motives problems on occasion.
- APPID –
Application Identifier or APPID is a type of unique identifier for every available app also called App IDs hel ps in securing and authenticating your apps. It identifies all of classes that are part of identical executable andpermissions required to get entry to it. DCOM can’t work if APPID isn’t correct i.e. for DCOM to work perfectly you need to have a correct APPID. You will likely get permissions errors making an attempt to create remote object, in my experience.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...