Discrete logarithm (Find an integer k such that a^k is congruent modulo b)
Last Updated :
29 Dec, 2021
Given three integers a, b and m. Find an integer k such that 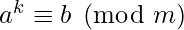 where a and m are relatively prime. If it is not possible for any k to satisfy this relation, print -1.
where a and m are relatively prime. If it is not possible for any k to satisfy this relation, print -1.
Examples:
Input: 2 3 5
Output: 3
Explanation:
a = 2, b = 3, m = 5
The value which satisfies the above equation
is 3, because
=> 23 = 2 * 2 * 2 = 8
=> 23 (mod 5) = 8 (mod 5)
=> 3
which is equal to b i.e., 3.
Input: 3 7 11
Output: -1
A Naive approach is to run a loop from 0 to m to cover all possible values of k and check for which value of k, the above relation satisfies. If all the values of k exhausted, print -1. Time complexity of this approach is O(m)
An efficient approach is to use baby-step, giant-step algorithm by using meet in the middle trick.
Baby-step giant-step algorithm
Given a cyclic group G of order ‘m’, a generator ‘a’ of the group, and a group element ‘b’, the problem is to find an integer ‘k’ such that 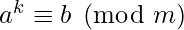
So what we are going to do(according to Meet in the middle trick) is to split the problem in two parts of  each and solve them individually and then find the collision.
each and solve them individually and then find the collision.
Now according to the baby-step giant-step
algorithm, we can write 'k' as
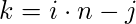 with
with 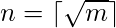 and
and 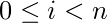 and
and 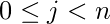 .
Therefore, we have:
.
Therefore, we have:
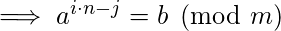
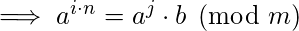 Therefore in order to solve, we precompute
Therefore in order to solve, we precompute
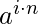 for different values of 'i'.
Then fix 'b' and tries values of 'j'
In RHS of the congruence relation above. It
tests to see if congruence is satisfied for
any value of 'j', using precomputed
values of LHS.
for different values of 'i'.
Then fix 'b' and tries values of 'j'
In RHS of the congruence relation above. It
tests to see if congruence is satisfied for
any value of 'j', using precomputed
values of LHS.
Let’s see how to use above algorithm for our question:-
First of all we have to write 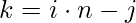 , where
, where 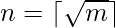 Obviously, any value of k in the interval [0, m) can be represented in this form, where
Obviously, any value of k in the interval [0, m) can be represented in this form, where 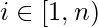 and
and 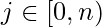
Replace the ‘k’ in above equality, we get:-
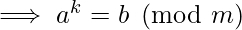
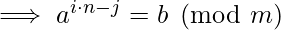
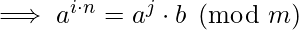
- The term left and right can take only n distinct values as
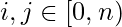 . Therefore we need to generate all these terms for either left or right part of equality and store them in an array or data structure like map/unordered_map in C/C++ or Hashmap in java.
. Therefore we need to generate all these terms for either left or right part of equality and store them in an array or data structure like map/unordered_map in C/C++ or Hashmap in java. - Suppose we have stored all values of LHS. Now iterate over all possible terms on the RHS for different values of j and check which value satisfies the LHS equality.
- If no value satisfies in above step for any candidate of j, print -1.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int powmod(int x, int y, int p)
{
int res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0)
{
if (y & 1)
res = (res*x) % p;
y = y>>1;
x = (x*x) % p;
}
return res;
}
int discreteLogarithm(int a, int b, int m) {
int n = (int) sqrt (m) + 1;
unordered_map<int, int> value;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; --i)
value[ powmod (a, i * n, m) ] = i;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
int cur = (powmod (a, j, m) * b) % m;
if (value[cur])
{
int ans = value[cur] * n - j;
if (ans < m)
return ans;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int a = 2, b = 3, m = 5;
cout << discreteLogarithm(a, b, m) << endl;
a = 3, b = 7, m = 11;
cout << discreteLogarithm(a, b, m);
}
|
Java
class GFG{
static int powmod(int x, int y, int p)
{
int res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0)
{
if ((y & 1)>0)
res = (res*x) % p;
y = y>>1;
x = (x*x) % p;
}
return res;
}
static int discreteLogarithm(int a, int b, int m) {
int n = (int) (Math.sqrt (m) + 1);
int[] value=new int[m];
for (int i = n; i >= 1; --i)
value[ powmod (a, i * n, m) ] = i;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
int cur = (powmod (a, j, m) * b) % m;
if (value[cur]>0)
{
int ans = value[cur] * n - j;
if (ans < m)
return ans;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 2, b = 3, m = 5;
System.out.println(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
a = 3;
b = 7;
m = 11;
System.out.println(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
}
}
|
Python3
import math;
def powmod(x, y, p):
res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0):
if (y & 1):
res = (res * x) % p;
y = y >> 1;
x = (x * x) % p;
return res;
def discreteLogarithm(a, b, m):
n = int(math.sqrt(m) + 1);
value = [0] * m;
for i in range(n, 0, -1):
value[ powmod (a, i * n, m) ] = i;
for j in range(n):
cur = (powmod (a, j, m) * b) % m;
if (value[cur]):
ans = value[cur] * n - j;
if (ans < m):
return ans;
return -1;
a = 2;
b = 3;
m = 5;
print(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
a = 3;
b = 7;
m = 11;
print(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static int powmod(int x, int y, int p)
{
int res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0)
{
if ((y & 1)>0)
res = (res*x) % p;
y = y>>1;
x = (x*x) % p;
}
return res;
}
static int discreteLogarithm(int a, int b, int m) {
int n = (int) (Math.Sqrt (m) + 1);
int[] value=new int[m];
for (int i = n; i >= 1; --i)
value[ powmod (a, i * n, m) ] = i;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
int cur = (powmod (a, j, m) * b) % m;
if (value[cur]>0)
{
int ans = value[cur] * n - j;
if (ans < m)
return ans;
}
}
return -1;
}
static void Main()
{
int a = 2, b = 3, m = 5;
Console.WriteLine(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
a = 3;
b = 7;
m = 11;
Console.WriteLine(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function powmod($x, $y, $p)
{
$res = 1;
$x = $x % $p;
while ($y > 0)
{
if ($y & 1)
$res = ($res * $x) % $p;
$y = $y >> 1;
$x = ($x * $x) % $p;
}
return $res;
}
function discreteLogarithm($a, $b, $m)
{
$n = (int)sqrt($m) + 1;
$value = array_fill(0, $m, NULL);
for ($i = $n; $i >= 1; --$i)
$value[ powmod ($a, $i * $n, $m) ] = $i;
for ($j = 0; $j < $n; ++$j)
{
$cur = (powmod ($a, $j, $m) * $b) % $m;
if ($value[$cur])
{
$ans = $value[$cur] * $n - $j;
if ($ans < $m)
return $ans;
}
}
return -1;
}
$a = 2;
$b = 3;
$m = 5;
echo discreteLogarithm($a, $b, $m), "\n";
$a = 3;
$b = 7;
$m = 11;
echo discreteLogarithm($a, $b, $m), "\n";
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function powmod(x, y, p)
{
let res = 1;
x = x % p;
while (y > 0)
{
if ((y & 1)>0)
res = (res*x) % p;
y = y>>1;
x = (x*x) % p;
}
return res;
}
function discreteLogarithm(a, b, m) {
let n = (parseInt(Math.sqrt(m), 10) + 1);
let value = new Array(m);
value.fill(0);
for (let i = n; i >= 1; --i)
value[ powmod (a, i * n, m) ] = i;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
let cur = (powmod (a, j, m) * b) % m;
if (value[cur]>0)
{
let ans = value[cur] * n - j;
if (ans < m)
return ans;
}
}
return -1;
}
let a = 2, b = 3, m = 5;
document.write(
discreteLogarithm(a, b, m) + "</br>"
);
a = 3;
b = 7;
m = 11;
document.write(
discreteLogarithm(a, b, m) + "</br>"
);
</script>
|
Output:
3
-1
Time complexity: O(sqrt(m)*log(b))
Auxiliary space: O(sqrt(m))
A possible improvement is to get rid of binary exponentiation or log(b) factor in the second phase of the algorithm. This can be done by keeping a variable that multiplies by ‘a’ each time as ‘an’. Let’s see the program to understand more.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int discreteLogarithm(int a, int b, int m)
{
int n = (int) sqrt (m) + 1;
int an = 1;
for (int i = 0; i<n; ++i)
an = (an * a) % m;
unordered_map<int, int> value;
for (int i = 1, cur = an; i<= n; ++i)
{
if (! value[ cur ])
value[ cur ] = i;
cur = (cur * an) % m;
}
for (int i = 0, cur = b; i<= n; ++i)
{
if (value[cur])
{
int ans = value[cur] * n - i;
if (ans < m)
return ans;
}
cur = (cur * a) % m;
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int a = 2, b = 3, m = 5;
cout << discreteLogarithm(a, b, m) << endl;
a = 3, b = 7, m = 11;
cout << discreteLogarithm(a, b, m);
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static int discreteLogarithm(int a, int b, int m)
{
int n = (int) (Math.sqrt (m) + 1);
int an = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
an = (an * a) % m;
int[] value=new int[m];
for (int i = 1, cur = an; i <= n; ++i)
{
if (value[ cur ] == 0)
value[ cur ] = i;
cur = (cur * an) % m;
}
for (int i = 0, cur = b; i <= n; ++i)
{
if (value[cur] > 0)
{
int ans = value[cur] * n - i;
if (ans < m)
return ans;
}
cur = (cur * a) % m;
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 2, b = 3, m = 5;
System.out.println(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
a = 3;
b = 7;
m = 11;
System.out.println(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
}
}
|
Python3
import math;
def discreteLogarithm(a, b, m):
n = int(math.sqrt (m) + 1);
an = 1;
for i in range(n):
an = (an * a) % m;
value = [0] * m;
cur = an;
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if (value[ cur ] == 0):
value[ cur ] = i;
cur = (cur * an) % m;
cur = b;
for i in range(n + 1):
if (value[cur] > 0):
ans = value[cur] * n - i;
if (ans < m):
return ans;
cur = (cur * a) % m;
return -1;
a = 2;
b = 3;
m = 5;
print(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
a = 3;
b = 7;
m = 11;
print(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int discreteLogarithm(int a, int b, int m)
{
int n = (int) (Math.Sqrt (m) + 1);
int an = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
an = (an * a) % m;
int[] value = new int[m];
for (int i = 1, cur = an; i<= n; ++i)
{
if (value[ cur ] == 0)
value[ cur ] = i;
cur = (cur * an) % m;
}
for (int i = 0, cur = b; i<= n; ++i)
{
if (value[cur] > 0)
{
int ans = value[cur] * n - i;
if (ans < m)
return ans;
}
cur = (cur * a) % m;
}
return -1;
}
static void Main()
{
int a = 2, b = 3, m = 5;
Console.WriteLine(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
a = 3;
b = 7;
m = 11;
Console.WriteLine(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function discreteLogarithm($a, $b, $m)
{
$n = (int)sqrt ($m) + 1;
$an = 1;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; ++$i)
$an = ($an * $a) % $m;
$value = array_fill(0, $m, NULL);
for ($i = 1, $cur = $an; $i<= $n; ++$i)
{
if (! $value[ $cur ])
$value[ $cur ] = $i;
$cur = ($cur * $an) % $m;
}
for ($i = 0, $cur = $b; $i<= $n; ++$i)
{
if ($value[$cur])
{
$ans = $value[$cur] * $n - $i;
if ($ans < $m)
return $ans;
}
$cur = ($cur * $a) % $m;
}
return -1;
}
$a = 2;
$b = 3;
$m = 5;
echo discreteLogarithm($a, $b, $m), "\n";
$a = 3;
$b = 7;
$m = 11;
echo discreteLogarithm($a, $b, $m);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function discreteLogarithm(a, b, m)
{
let n = parseInt(Math.sqrt(m), 10) + 1;
let an = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i)
an = (an * a) % m;
let value = new Array(m);
value.fill(0);
for (let i = 1, cur = an; i<= n; ++i)
{
if (value[ cur ] == 0)
value[ cur ] = i;
cur = (cur * an) % m;
}
for (let i = 0, cur = b; i<= n; ++i)
{
if (value[cur] > 0)
{
let ans = value[cur] * n - i;
if (ans < m)
return ans;
}
cur = (cur * a) % m;
}
return -1;
}
let a = 2, b = 3, m = 5;
document.write(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m) + "</br>");
a = 3;
b = 7;
m = 11;
document.write(discreteLogarithm(a, b, m));
</script>
|
Output:
3
-1
Time complexity: O(sqrt(m))
Auxiliary space: O(sqrt(m))
Reference:
http://e-maxx-eng.appspot.com/algebra/discrete-log.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baby-step_giant-step
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...