Introduction to Dimensionality Reduction
Last Updated :
06 May, 2023
Machine Learning: As discussed in this article, machine learning is nothing but a field of study which allows computers to “learn” like humans without any need of explicit programming.
What is Predictive Modeling: Predictive modeling is a probabilistic process that allows us to forecast outcomes, on the basis of some predictors. These predictors are basically features that come into play when deciding the final result, i.e. the outcome of the model.
Dimensionality reduction is the process of reducing the number of features (or dimensions) in a dataset while retaining as much information as possible. This can be done for a variety of reasons, such as to reduce the complexity of a model, to improve the performance of a learning algorithm, or to make it easier to visualize the data. There are several techniques for dimensionality reduction, including principal component analysis (PCA), singular value decomposition (SVD), and linear discriminant analysis (LDA). Each technique uses a different method to project the data onto a lower-dimensional space while preserving important information.
What is Dimensionality Reduction?
Dimensionality reduction is a technique used to reduce the number of features in a dataset while retaining as much of the important information as possible. In other words, it is a process of transforming high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space that still preserves the essence of the original data.
In machine learning, high-dimensional data refers to data with a large number of features or variables. The curse of dimensionality is a common problem in machine learning, where the performance of the model deteriorates as the number of features increases. This is because the complexity of the model increases with the number of features, and it becomes more difficult to find a good solution. In addition, high-dimensional data can also lead to overfitting, where the model fits the training data too closely and does not generalize well to new data.
Dimensionality reduction can help to mitigate these problems by reducing the complexity of the model and improving its generalization performance. There are two main approaches to dimensionality reduction: feature selection and feature extraction.
Feature Selection:
Feature selection involves selecting a subset of the original features that are most relevant to the problem at hand. The goal is to reduce the dimensionality of the dataset while retaining the most important features. There are several methods for feature selection, including filter methods, wrapper methods, and embedded methods. Filter methods rank the features based on their relevance to the target variable, wrapper methods use the model performance as the criteria for selecting features, and embedded methods combine feature selection with the model training process.
Feature Extraction:
Feature extraction involves creating new features by combining or transforming the original features. The goal is to create a set of features that captures the essence of the original data in a lower-dimensional space. There are several methods for feature extraction, including principal component analysis (PCA), linear discriminant analysis (LDA), and t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE). PCA is a popular technique that projects the original features onto a lower-dimensional space while preserving as much of the variance as possible.
Why is Dimensionality Reduction important in Machine Learning and Predictive Modeling?
An intuitive example of dimensionality reduction can be discussed through a simple e-mail classification problem, where we need to classify whether the e-mail is spam or not. This can involve a large number of features, such as whether or not the e-mail has a generic title, the content of the e-mail, whether the e-mail uses a template, etc. However, some of these features may overlap. In another condition, a classification problem that relies on both humidity and rainfall can be collapsed into just one underlying feature, since both of the aforementioned are correlated to a high degree. Hence, we can reduce the number of features in such problems. A 3-D classification problem can be hard to visualize, whereas a 2-D one can be mapped to a simple 2-dimensional space, and a 1-D problem to a simple line. The below figure illustrates this concept, where a 3-D feature space is split into two 2-D feature spaces, and later, if found to be correlated, the number of features can be reduced even further.
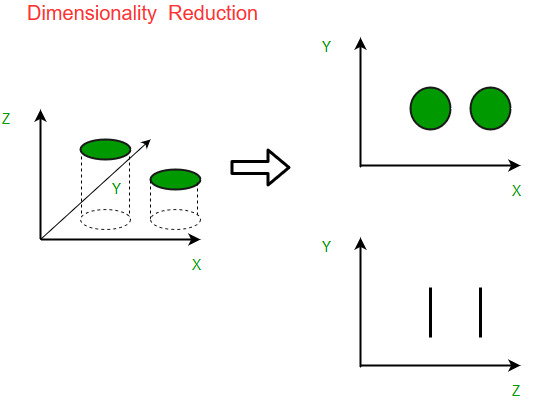
Components of Dimensionality Reduction
There are two components of dimensionality reduction:
- Feature selection: In this, we try to find a subset of the original set of variables, or features, to get a smaller subset which can be used to model the problem. It usually involves three ways:
- Filter
- Wrapper
- Embedded
- Feature extraction: This reduces the data in a high dimensional space to a lower dimension space, i.e. a space with lesser no. of dimensions.
Methods of Dimensionality Reduction
The various methods used for dimensionality reduction include:
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
- Generalized Discriminant Analysis (GDA)
Dimensionality reduction may be both linear and non-linear, depending upon the method used. The prime linear method, called Principal Component Analysis, or PCA, is discussed below.
Principal Component Analysis
This method was introduced by Karl Pearson. It works on the condition that while the data in a higher dimensional space is mapped to data in a lower dimension space, the variance of the data in the lower dimensional space should be maximum.
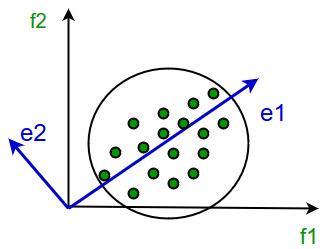
It involves the following steps:
- Construct the covariance matrix of the data.
- Compute the eigenvectors of this matrix.
- Eigenvectors corresponding to the largest eigenvalues are used to reconstruct a large fraction of variance of the original data.
Hence, we are left with a lesser number of eigenvectors, and there might have been some data loss in the process. But, the most important variances should be retained by the remaining eigenvectors.
Advantages of Dimensionality Reduction
- It helps in data compression, and hence reduced storage space.
- It reduces computation time.
- It also helps remove redundant features, if any.
- Improved Visualization: High dimensional data is difficult to visualize, and dimensionality reduction techniques can help in visualizing the data in 2D or 3D, which can help in better understanding and analysis.
- Overfitting Prevention: High dimensional data may lead to overfitting in machine learning models, which can lead to poor generalization performance. Dimensionality reduction can help in reducing the complexity of the data, and hence prevent overfitting.
- Feature Extraction: Dimensionality reduction can help in extracting important features from high dimensional data, which can be useful in feature selection for machine learning models.
- Data Preprocessing: Dimensionality reduction can be used as a preprocessing step before applying machine learning algorithms to reduce the dimensionality of the data and hence improve the performance of the model.
- Improved Performance: Dimensionality reduction can help in improving the performance of machine learning models by reducing the complexity of the data, and hence reducing the noise and irrelevant information in the data.
Disadvantages of Dimensionality Reduction
- It may lead to some amount of data loss.
- PCA tends to find linear correlations between variables, which is sometimes undesirable.
- PCA fails in cases where mean and covariance are not enough to define datasets.
- We may not know how many principal components to keep- in practice, some thumb rules are applied.
- Interpretability: The reduced dimensions may not be easily interpretable, and it may be difficult to understand the relationship between the original features and the reduced dimensions.
- Overfitting: In some cases, dimensionality reduction may lead to overfitting, especially when the number of components is chosen based on the training data.
- Sensitivity to outliers: Some dimensionality reduction techniques are sensitive to outliers, which can result in a biased representation of the data.
- Computational complexity: Some dimensionality reduction techniques, such as manifold learning, can be computationally intensive, especially when dealing with large datasets.
Important points:
- Dimensionality reduction is the process of reducing the number of features in a dataset while retaining as much information as possible.
This can be done to reduce the complexity of a model, improve the performance of a learning algorithm, or make it easier to visualize the data.
- Techniques for dimensionality reduction include: principal component analysis (PCA), singular value decomposition (SVD), and linear discriminant analysis (LDA).
- Each technique projects the data onto a lower-dimensional space while preserving important information.
- Dimensionality reduction is performed during pre-processing stage before building a model to improve the performance
- It is important to note that dimensionality reduction can also discard useful information, so care must be taken when applying these techniques.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...