Java Convert int to String | Different Ways Of Conversion
Last Updated :
15 Dec, 2023
Converting Integers to Strings involves using the Integer classes toString() or String.valueOf() for direct conversion. String.format() is another method offering flexible formatting options. Using StringBuilder or StringBuffer for appending integer values as strings is efficient for extensive string manipulation.
We generally counter with such conversion articles because many operations can be performed over a string while we are limited to when it comes to integers. We have a wide varied list of in-built methods in the String class that helps us perform hassle-free operations.
Suppose we are required to concatenate two integers then it would become a tedious job as we need to go through as we need to deal with the number system corresponding to which we will be playing mathematics within the number system. But in order to convert integers to strings in Java, we have some inbuilt methods and classes which make our work too easy.
Tip: We generally convert primitive class data members types though we have the concept of Wrapper classes to Strings because in practical programming in java we deal with strings.
How to convert int to string in Java?
There are certain methods for Integer to String conversions are mentioned below:
- Using the toString() method of the Integer class
- Using the valueOf() method of the String class
- Using Integer(int).toString() method of Integer class
- Using concatenation with an empty string.
Using toString Method of Integer Class
The Integer class has a static method toString() that returns a String object representing the specified int parameter. The argument is converted and returned as a string instance. If the number is negative, the sign will be preserved.
Example:
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a = 1234;
int b = -1234;
String str1 = Integer.toString(a);
String str2 = Integer.toString(b);
System.out.println("String str1 = " + str1);
System.out.println("String str2 = " + str2);
}
}
|
Output
String str1 = 1234
String str2 = -1234
Using valueOf() method of String Class
The String class has a static method valueOf() that can be used to convert the Integer to String as shown below:
Below is the implementation of the above method:
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int c = 1234;
String str3 = String.valueOf(c);
System.out.println("String str3 = " + str3);
}
}
|
Output
String str3 = 1234
Using toString() method of the Integer class
It is different from method 1 as proposed above, as in this method we use an instance of the Integer class to invoke its toString() method.
Below is the Implementation of the above method:
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int d = 1234;
String str4 = new Integer(d).toString();
System.out.println("String str4 = " + str4);
}
}
|
Output
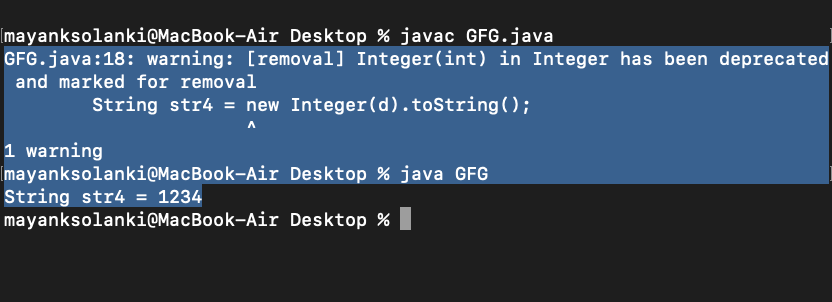
Output explanation: If the variable is of primitive type (int), it is better to use Integer.toString(int) or String.valueOf(int). But if the variable is already an instance of Integer (wrapper class of the primitive type int), it is better to just invoke its toString() method as shown above.
Note: This method is not efficient as an instance of the Integer class is created before conversion is performed.
Using concatenation with an empty string
Approach: Here we will declare an empty string and using the ‘+’ operator, we will simply store the resultant as a string. Now by this, we are successfully able to append and concatenate these strings.
Below is the implementation of the above method:
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a = 1234;
int b = -1234;
String str1 = "" + a;
String str2 = "" + b;
System.out.println("String str1 = " + str1);
System.out.println("String str2 = " + str2);
}
}
|
Output
String str1 = 1234
String str2 = -1234
Advanced Methods to Convert int to String Java
There are certain advance Methods are mentioned below:
- Using DecimalFormat Class
- Using StringBuffer class
- using StringBuilder class
- Using special radix and custom radix
DecimalFormat is a class that formats a number to a String.
Below is the implementation of the above method:
Java
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int e = 12345;
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#,###");
String Str5 = df.format(e);
System.out.println(Str5);
}
}
|
Output
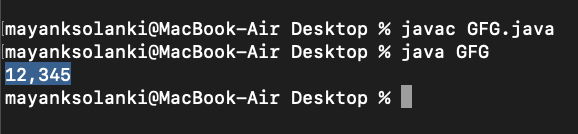
Tip: Using this method, you can specify the number of decimal places and comma separator for readability.
Using StringBuffer class
StringBuffer is a class that is used to concatenate multiple values into a String.
Example 1:
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int f = 1234;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append(f);
String str6 = sb.toString();
System.out.println("String str6 = " + str6);
}
}
|
Output
String str6 = 1234
Example 2:
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String str6
= new StringBuffer().append(1234).toString();
System.out.println("String str6 = " + str6);
}
}
|
Output
String str6 = 1234
Using StringBuilder Class
StringBuilder works similarly but is not thread-safe like StringBuffer.
Example 1:
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int g = 1234;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(g);
String str7 = sb.toString();
System.out.println("String str7 = " + str7);
}
}
|
Output
String str7 = 1234
Example 2:
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String str7
= new StringBuilder().append(1234).toString();
System.out.println("String str7 = " + str7);
}
}
|
Output
String str7 = 1234
Note: All the examples above use the base (radix) 10. Following are convenient methods to convert to binary, octal, and hexadecimal systems. The arbitrary custom number system is also supported.
A. Using special radix
Example: Binary
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int h = 255;
String binaryString = Integer.toBinaryString(h);
System.out.println(binaryString);
}
}
|
Output Explanation: 11111111 is the binary representation of the number 255.
Example: Octal
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 255;
String octalString = Integer.toOctalString(i);
System.out.println(octalString);
}
}
|
377 is the octal representation of the number 255.
Example: Hexadecimal
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int j = 255;
String hexString = Integer.toHexString(j);
System.out.println(hexString);
}
}
|
The ff is the hexadecimal representation of the number 255.
B. Custom Base/Radix
Approach: We are using the toString() method of the Integer class to get it converted into a string where additionally we will be passing a value as an argument known as radix. One can use any other custom base/radix when converting an int to a string. In the example below, we are considering the base 7 number system for illustration purposes.
Example:
Java
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int k = 255;
String customString = Integer.toString(k, 7);
System.out.println(customString);
}
}
|
Output

Note: 513 is the representation of the number 255 when written in the base 7 system.
Summary
The process of converting integers to strings in Java involves methods using the toString() and valueOf() methods from the Integer class for direct conversions, String.format() for customizable formatting options, and StringBuilder or StringBuffer for efficient string integration.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...