Different Phases of Formal Review
Last Updated :
01 Feb, 2024
Formal Review generally takes place in piecemeal approach that consists of six different steps that are essential. Formal review generally obeys formal process. It is also one of the most important and essential techniques required in static testing.
Six steps are extremely essential as they allow team of developers simply to ensure and check software quality, efficiency, and effectiveness. These steps are given below :
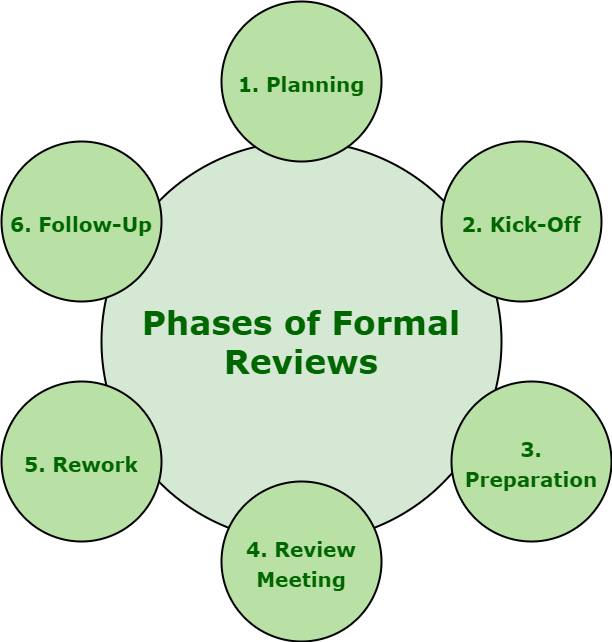
Phases of Formal Reviews
- Planning : For specific review, review process generally begins with ‘request for review’ simply by author to moderator or inspection leader. Individual participants, according to their understanding of document and role, simply identify and determine defects, questions, and comments. Moderator also performs entry checks and even considers exit criteria.
- Kick-Off : Getting everybody on the same page regarding document under review is the main goal and aim of this meeting. Even entry result and exit criteria are also discussed in this meeting. It is basically an optional step. It also provides better understanding of team about relationship among document under review and other documents. During kick-off, Distribution of document under review, source documents, and all other related documentation can also be done.
- Preparation : In preparation phase, participants simply work individually on document under review with the help of related documents, procedures, rules, and provided checklists. Spelling mistakes are also recorded on document under review but not mentioned during meeting. These reviewers generally identify and determine and also check for any defect, issue or error and offer their comments, that later combined and recorded with the assistance of logging form, while reviewing document.
- Review Meeting : This phase generally involves three different phases i.e. logging, discussion, and decision. Different tasks are simply related to document under review is performed.
- Rework : Author basically improves document that is under review based on the defects that are detected and improvements being suggested in review meeting. Document needs to be reworked if total number of defects that are found are more than an unexpected level. Changes that are done to document must be easy to determine during follow-up, therefore author needs to indicate changes are made.
- Follow-Up : Generally, after rework, moderator must ensure that all satisfactory actions need to be taken on all logged defects, improvement suggestions, and change requests. Moderator simply makes sure that whether author has taken care of all defects or not. In order to control, handle, and optimize review process, moderator collects number of measurements at every step of process. Examples of measurements include total number of defects that are found, total number of defects that are found per page, overall review effort, etc.
- Individual Assessment: The stage prior to the official group meeting during which each reviewer conducts an independent examination of the artefacts.
- Meeting for Group Review: The cooperative stage in which the review panel discusses over results, resolves conflicts and makes choices regarding the examined artifacts.
- Finalization and Record-Keeping: Completing the formal review procedure, recording the results and being ready for any necessary follow-up measures.
- Metrics and Ongoing Improvement: Finding opportunities for ongoing improvement and evaluating the success of the formal review process through the tracking and analysis of review metrics.
Importance of Different Phases of Formal Review
- Early Defect Detection: By catching errors early in the development process, formal reviews lower the effort and expense involved in fixing them.
- Knowledge Sharing: Team members collaborate and share knowledge during various stages, which promotes a culture of ongoing learning and development.
- Process Improvement: Through the formal review process, reoccurring issues are found, which helps development processes become more refined and improved over time.
- Quality Assurance: By verifying that the programme complies with established standards and criteria, formal reviews make an important contribution to quality assurance.
Conclusion
The many stages of formal review are essential for guaranteeing effectiveness, integrity, and quality of the software development process. In the pursuit of software development excellence, it is imperative for organizations to embrace and optimize the various stages of formal review in order to produce software products that are strong, dependable and of superior quality.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...