Difference between VGA and SVGA
Last Updated :
07 Apr, 2020
1. Video Graphics Array (VGA) :
Video Graphics Array standard was first developed by IBM. It uses analog signals, delivers 640×480 resolution screen with 16 colors at a time and a refresh rate of 16 colors. It displays a maximum of 256 colours at a time from the 262, 144 colours collection. It consists of a 6-Bit Digital to Analog converter to convert analog red, green and blue (RGB) signals.
Function of the Digital to Analog converter –
A 6-bit converter generates
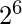
(64) possible values. So, for each colour, it produces total of 64x64x64 possible combinations for 3 signals(RGB) of the 262, 144 colour collection. It consists of 256 colour registers, making it possible to save 256 colours combination at a time. To select one of the 256 colour registers, it has a 8-bit value/address which can produce any desired address.
2. Super Video Graphics Arrays (SVGA) :
Video Graphics Array standard was first developed by NEC home electronics. It is an extension of VGA and also called ultra VGA. The super VGA provides higher resolution with more colours. Depending on the video memory installed in the computer, either 256 simultaneous colors or 16 million colors is supported by the system. Memory utilization in SVGA is high.
The basic difference between VGA and SVGA is that VGA provides a resolution of 640×480 pixels whereas SVGA provides a resolution of 1024×760 pixels.
Differences between VGA and SVGA :
|
VGA |
SVGA |
| Full Form |
Video Graphics Arrays. |
Super Video Graphics Arrays. |
| Development |
IBM. |
NEC Home Electronics. |
| Supporting |
Smaller resolution videos and images. |
Larger resolution videos and images. |
| Resolution |
Maximum 640×480 |
Maximum 1024×760 |
| Memory |
Upto 256k. |
Upto 1024k. |
| Supplementary Memory |
Not Included |
Included |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...