Difference between RAID 2 and RAID 3
Last Updated :
03 May, 2023
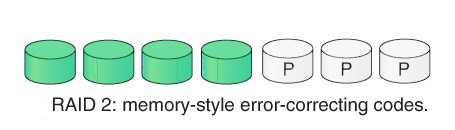
1. RAID 2: It consist of Bit-level Striping. RAID 2 records Error Correction Code (ECC) using hamming code parity. In this level each data bit in a word is recorded on a separate disk and ECC codes of the data words are stored on a different set of disk. Advantage –
- In case of Error Correction it uses hamming code.
- It Uses one designated drive to store parity.
Disadvantage –
- It has complex structure and high cost due to extra drive.
- It require extra drive for error detection.
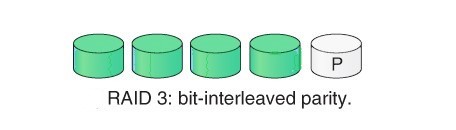
2. RAID 3: RAID 3 consists of Byte-level Striping. It stripes the data onto multiple disk. The parity bit generated for each disk section and stored on a different dedicated disk. This level overcome the single disk failure. Advantages –
- Data can be transferred in bulk.
- Data can be accessed in parallel.
Disadvantages –
- It require an additional drive for parity.
- In case of small size files it performs slowly.
Difference between RAID 2 and RAID 3 :
| SR.No. |
RAID 2 |
RAID 3 |
| 1. |
RAID 2 stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 2. |
RAID 3 stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 3. |
| 2. |
In RAID 2 technology, Bit-level Striping is used. |
In RAID 3 technology, Byte-level Striping is used. |
| 3. |
In this level, One group of disk are used to write the data and other group is used to write the ECC. |
In this level, Multiple disks are used for storing data and one dedicated disk is used to store parity |
| 4. |
Hamming code is used for Error detection. |
Hamming code is not used. |
| 5. |
It require extra drive for Error Code. |
It require extra drive for Parity. |
| 6. |
If one of the disk fails, the remaining bits of the byte and the associated ECC bits can be used to reconstruct the data. |
In case of drive failure the parity bits is accessed and data is reconstructed from the remaining drive. |
| 7 |
In RAID 2, data is divided into individual bits and then striped across multiple disks, with a dedicated parity disk that stores the parity information for all the data disks. The parity information is generated using Hamming code, which allows for single-bit error correction and double-bit error detection. This means that if a disk fails, the data can be reconstructed using the parity information from the dedicated parity disk. |
In RAID 3, data is striped across multiple disks, with one dedicated parity disk that stores the parity information for all the data disks. Unlike RAID 2, the data is not divided into individual bits, but rather into larger data blocks. This means that if a disk fails, the data can be reconstructed using the parity information from the dedicated parity disk. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...