Difference between RAID 0 and RAID 1
Last Updated :
02 May, 2023
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disk, is the technique used for disk organisation for reliability and performance. Both RAID 0 stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 0 and RAID 1 stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 1 are the categories of RAID. The main difference between the RAID 0 and RAID 1 is that, In RAID 0 technology, Disk stripping is used. On the other hand, in RAID 1 technology, Disk mirroring is used.

| S.NO |
RAID 0 |
RAID 1 |
| 1. |
RAID 0 stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 0. |
While RAID 1 stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 1. |
| 2. |
In RAID 0 technology, Disk stripping is used. |
While in RAID 1 technology, Disk mirroring is used. |
| 3. |
The cost of RAID 0 technology is low. |
While RAID 1 is costly or expensive. |
| 4. |
In RAID 0, There is no write penalty. |
While in RAID 1, There is write penalty. |
| 5. |
The Relative storage efficiency of RAID 0 is 100%. |
While the relative storage efficiency of RAID 1 is 50%. |
| 6. |
The write performance of RAID 0 is better than RAID 1. |
While the write performance of RAID 1 is slower than RAID 0. |
| 7. |
RAID 0 emphasis on data accessing speed. |
While in RAID 1, data availability is emphasized. |
| 8. |
RAID 0 is well in read performance. |
While RAID 1 is moderate in read performance. |
| 9. |
In RAID 0, there is no protection available. |
In RAID 1, mirror protection is provided. |
| 10 |
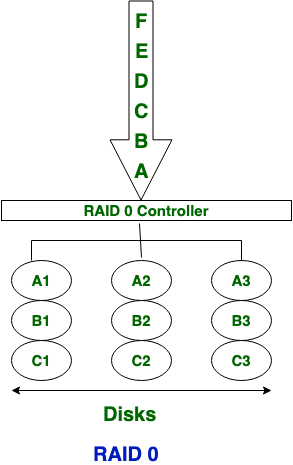
RAID 0, also known as disk striping, involves the splitting of data into small blocks and spreading it across multiple disks in a way that allows for simultaneous read and write operations. In this configuration, each disk contains a portion of the data, and data is written to and read from the disks in parallel. RAID 0 does not provide fault tolerance, as there is no redundancy or backup copy of the data. If one disk fails, all data on the array is lost. |
RAID 1, also known as disk mirroring, involves the duplication of data on two or more disks. In this configuration, all data is written to two or more disks simultaneously, so that each disk contains an identical copy of the data. This provides fault tolerance, as if one disk fails, the system can continue to operate with the remaining disk(s) until the failed disk is replaced. |
In summary, RAID 0 may be a good choice for applications that require high performance and do not require data redundancy, while RAID 1 is a better choice for applications that require fault tolerance and data redundancy.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...