Difference between Queue and Deque in C++
Last Updated :
20 Jun, 2022
Queue: A Queue is a linear data structure that follows a First In First Out (FIFO) order in which the operations are performed. It is a type of container adaptor where elements are inserted into one end of the container and deleted from the other.
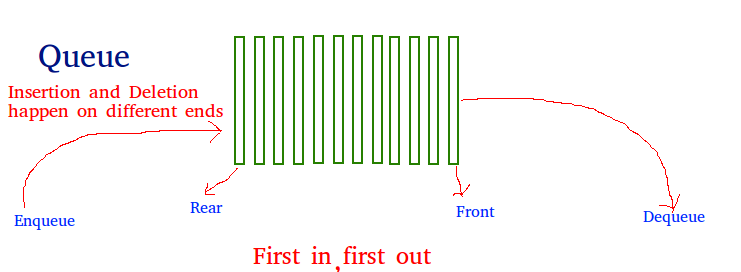
Functions:
- empty(): Tests whether the queue is empty.
- size(): Returns the unsigned int, size of the queue.
- queue::front() and queue::back(): front() function returns a reference to the first element or the oldest of the queue. back() function returns a reference to the last or the newest element of the queue.
- push(k) and pop(): push() function adds the element ‘k’ at the end of the queue. pop() function deletes the element from the beginning of the queue and reduces its size by 1.
- swap(): exchanges the elements of two different queues of the same type but may or may not of the same size.
- emplace(): it is used to insert a new element at end of the queue.
Syntax:
queue <data_type> q
Below is the program to illustrate the same:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(10);
q.push(5);
q.push(15);
q.push(1);
q.pop();
q.pop();
cout << "Elements in Queue are: ";
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << q.front() << ' ';
q.pop();
}
return 0;
}
|
Output:
Elements in Queue are: 15 1
Deque: Deque is a sequence container with the ability of expansion and contraction on both ends. It is a template of Standard Template Library or STL in C++is. It is similar to vectors but are more efficient for the insertion and deletion of elements. Contiguous storage allocation in deque may not be guaranteed as in vectors.
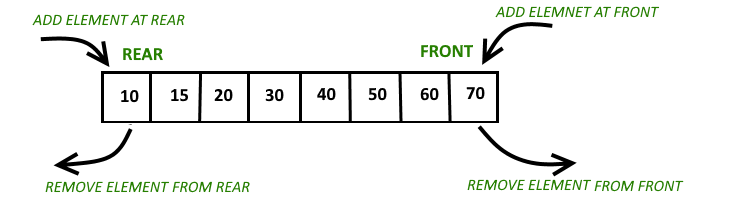
Functions:
- max_size(): Returns the maximum number of elements deque can contain.
- push_back() and push_front(): push_front( ) push the elements into a deque from the front and push_back( ) push elements into a deque from the back.
- pop_front() and pop_back(): pop_front() function is used to pop elements from a deque from the front and pop_back( ) function is used to pop elements from a deque from the back.
- clear() and erase(): clear is used to remove all the elements from the deque and erase is used to remove some specified elements.
- insert(): increases the container side by inserting element in the specified position.
- resize(): changes the size of the element’s container as per requirement.
- rbegin() and rend(): rbegin() points to the last element of the deque whereas rend points to the position before the beginning of the deque.
- at() and swap(): at() points to the position of the element given in the parameter and swap( ) is used two swap elements of two deques.
- emplace_front() and emplace_back(): these two functions are used to insert new elements in the container at the beginning and at the end of deque respectively.
Syntax:
deque<data_type> dq
Below is the program to illustrate the same:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
deque<int> dq;
dq.push_front(10);
dq.push_front(5);
dq.push_front(3);
dq.pop_front();
dq.pop_front();
dq.push_back(1);
dq.push_back(50);
dq.push_back(2);
dq.pop_back();
dq.pop_back();
cout << "Elements in deque are: ";
while (!dq.empty()) {
cout << " " << dq.front();
dq.pop_front();
}
return 0;
}
|
Output:
Elements in deque are: 10 1
Below is the tabular difference between the queue and deque:
| S.No. |
Queue
|
Deque
|
| 1 |
Insertion can be done through the rear end only. |
Insertion is possible through both ends. |
| 2 |
Deletion of elements is possible through the front end only. |
Deletion of elements possible through both ends. |
| 3 |
Elements can not be accessed through iterators. |
Elements can be accessed through iterators. |
| 4 |
Implemented as container adaptors. |
Implemented generally as some form of a dynamic array. |
| 5 |
The stack can not be implemented using a queue. |
A stack can be implemented using deque. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...