Difference Between Purines and Pyrimidines
Last Updated :
07 Mar, 2024
Purines and pyrimidines are the two types of nitrogenous bases that make up the building blocks of DNA and RNA. These bases are responsible for encoding genetic information. Learning the differences between purines and pyrimidines is crucial in understanding the structure and function of DNA and RNA. In this article, we will compare and discuss the similarities and differences between purines and pyrimidines.
What are Purines?
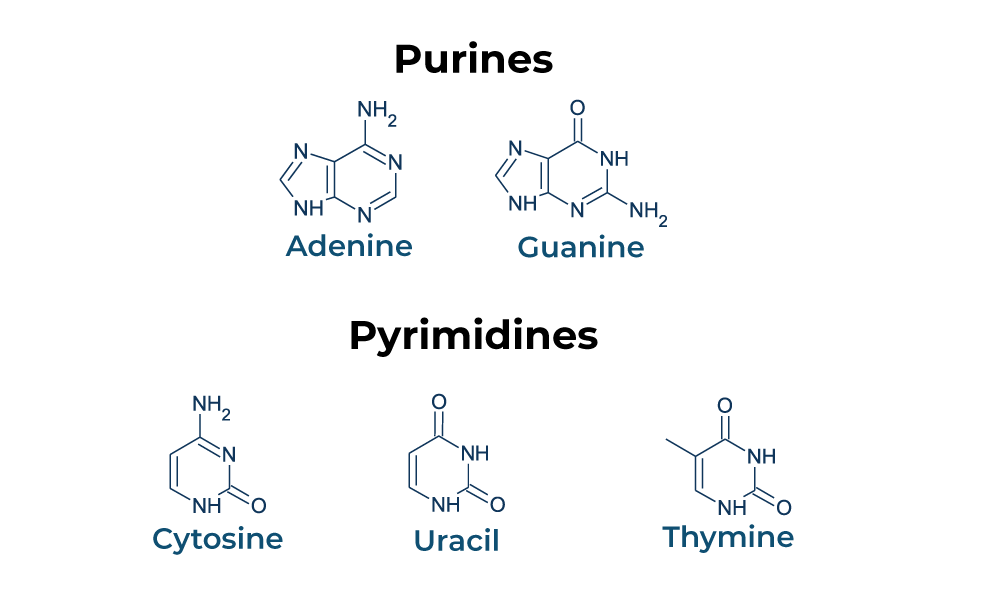
Purines are one of the two types of nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA. They have a double-ring structure consisting of a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring. The two purines found in DNA and RNA are adenine (A) and guanine (G). These nitrogenous bases are essential for the formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs, which help stabilize the double helix structure of DNA.
What are Pyrimidines?
Pyrimidines are the other type of nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA. They have a single-ring structure consisting of a six-membered ring. The three pyrimidines found in DNA and RNA are cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Cytosine and thymine are found in DNA, while cytosine and uracil are found in RNA. The nitrogenous base pairing rules dictate that adenine pairs with thymine (or uracil in RNA) and cytosine pairs with guanine.
Difference between Purines and Pyrimidines
Difference between Purines and Pyrimidines class 12 are as follows:
| Characteristics |
Purines
|
Pyrimidines
|
| Structure |
Contain two carbon-nitrogen rings fused together |
Contain a single carbon-nitrogen ring |
| Nitrogenous Bases in DNA |
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) |
Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Uracil (U) |
| Nitrogenous Bases in RNA |
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) |
Cytosine (C), Uracil (U) |
| Base Pairing |
A pairs with T (DNA) or U (RNA) and G pairs with C |
C pairs with G and T (DNA) or U (RNA) pairs with A |
| Number of Nitrogen Atoms |
Contain four nitrogen atoms in their structure |
Contain two nitrogen atoms in their structure |
| Function in DNA/RNA |
Serve as the building blocks for genetic material |
Serve as the building blocks for genetic material |
| Hydrogen Bonding |
Can form hydrogen bonds with pyrimidines |
Can form hydrogen bonds with purines |
Similarities of Purines and Pyrimidines
Table comparing the similarities between purines and pyrimidines is given below:
| Features |
Purines
|
Pyrimidines
|
| Nitrogenous Bases in DNA |
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) |
Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Uracil (U) |
| Chemical Composition |
Contain two carbon-nitrogen rings fused together |
Contain a single carbon-nitrogen ring |
| Nitrogenous Bases in RNA |
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) |
Cytosine (C), Uracil (U) |
| Hydrogen Bonding |
Can form hydrogen bonds with pyrimidines |
Can form hydrogen bonds with purines |
| Function in DNA/RNA |
Serve as the building blocks for genetic material |
Serve as the building blocks for genetic material |
| Number of Nitrogen Atoms |
Contain four nitrogen atoms in their structure |
Contain two nitrogen atoms in their structure |
Conclusion – Difference Between Purines And Pyrimidines
Purines and pyrimidines are the two types of nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA. Purines have a double-ring structure and consist of adenine and guanine, while pyrimidines have a single-ring structure and consist of cytosine, thymine, and uracil. Learinng the difference between purines and pyrimidines is crucial in understanding the structure and function of DNA and RNA. The base pairing rules between purines and pyrimidines are essential for the replication and transcription of genetic material.
Also Read:
FAQs on Difference Between Purines And Pyrimidines
What are Purines and Pyrimidines?
Purines and pyrimidines are important molecules that make up the genetic material in living organisms.
What is the Main Difference Between Purines and Pyrimidines?
Purines have two rings in their structure while pyrimidines have one ring. Purines are also heavier and contain more nitrogen and carbon atoms.
What is the Function of Purines and Pyrimidines in DNA and RNA?
Purines and pyrimidines are the building blocks of genetic material and are essential for the proper functioning and replication of DNA and RNA.
Are Purines and Pyrimidines Found in Other Biological Molecules?
Yes, purines and pyrimidines are found in other molecules like ATP, which is a molecule that provides energy to cells.
What is the Difference Between Purine and Pyrimidine Synthesis?
Purine and pyrimidine are mainly synthesise via both de novo and salvage pathway. But purine mainly synthesised by salvage and pyrimidine via de-novo synthesis.
What are the Common Purine and Pyrimidine Bases?
The common purine bases are adenine and guanine, while the common pyrimidine bases are cytosine, thymine (in DNA), and uracil (in RNA).
Are Purine the Same in both DNA and RNA?
Yes, purines are present in both DNA and RNA, with adenine and guanine being the common purine bases in both nucleic acids.
What are the 2 Bases of Purines?
The two bases of purines are adenine and guanine, which are essential components of nucleotides in DNA and RNA.
Describe the Difference Between Purines And Pyrimidines Class 11?
Purines are double-ringed nitrogenous bases (adenine and guanine), while pyrimidines are single-ringed bases (cytosine, thymine, and uracil). They form the building blocks of nucleic acids.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...