Difference between Java IO and Java NIO
Last Updated :
22 May, 2020
Java IO(Input/Output) is used to perform read and write operations. The java.io package contains all the classes required for input and output operation. Whereas, Java NIO (New IO) was introduced from JDK 4 to implement high-speed IO operations. It is an alternative to the standard IO API’s. In this article, the difference between these two IO packages is discussed.
Before getting into the difference between java IO and Java NIO, we need to understand a few key concepts which differentiate both the I/O packages:
- Stream oriented vs Buffer Oriented Packages:
Java IO is a stream-oriented package which means that it can be read one or more bytes at a time from a stream. It uses a stream for transferring the data between data source/sink and java program. It is a unidirectional data transfer. The following image illustrates a stream-oriented package:
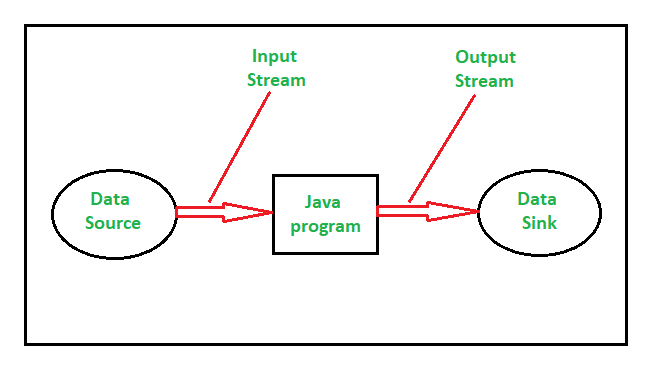
Unlike Java IO, Java NIO is a buffer oriented package. This means that the data is read into a buffer from which it is further processed using a channel. For example, a thread asking a channel to read data into a buffer and while the channel is reading data to the buffer simultaneously the thread can go for some other work. Once the data is read into the buffer, the thread can then continue to process the work which it had left during the read operation. Therefore, NIO is a bi-directional data transfer. The following image illustrates a buffer-oriented package:

- Blocking IO vs Non Blocking IO Packages:
Java IO is a blocking IO. This means that if a thread is invoking a read() or write() operation, that thread is blocked until there is some data to read or the data is fully written. That’s why it is synchronous IO or blocking IO.
Unlike Java IO, Java NIO is a non-blocking IO. This means that if a thread is invoking a read() or write() operation, that thread is not blocked until there is some data to read or the data is fully written rather the thread go on something else. That’s why it is an asynchronous IO or non-blocking IO.
- Channels:
A channel is a medium for efficient data transmission between entity and buffer. It acts as a gateway for open connection with data source/sink.
- Selector:
The selector selects the channel among the multiple IO channels using the single thread.
The following table illustrates the differences between the Java IO and Java NIO:
| Java IO |
Java NIO |
| Java IO stands for Java Input Output |
Java NIO stands for Java New Input Output |
| Java IO operates inside java.io package |
Java NIO operates inside java.nio package |
| Java IO is Stream oriented |
Java NIO is Buffer oriented |
| Blocking IO operation |
Non-blocking IO operation |
| Channels are not available |
Channels are available |
It deals with data in stream |
It deals with data in blocks |
| Does not contain the concept of Selectors |
Contains the concept of Selectors |
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...