Difference Between Hardware RAID vs Software RAID
Last Updated :
03 Feb, 2022
Redundant Array of Independent Disks(RAID) is virtual disk technology that combines multiple physical drives into one unit. This is a method of improving the performance and reliability of the storage media by using multiple drives. The drives are configured so that the data is either divided between disks to distribute the load, or duplicated to ensure that it can be recovered once a disk fails. The execution of RAID can be done either using a special controller (hardware RAID) or by an operating system driver (software RAID).
RAID Mechanism
Types of RAID:
RAID is classified into the following types:
| Types |
Description
|
| RAID-0 |
It is the fastest and most effective array type but offers no fault tolerance. |
| RAID-1 |
It is the array of choices for a critical, fault-tolerant environment. |
| RAID-2 |
It is used today because ECC is embedded in most modern disk drives. |
| RAID-3 |
It is used in a single environment that accesses long sequential records to speed up data transfer. |
| RAID-4 |
It offers no advantages over RAID-5 and doesn’t support multiple simultaneous write operations. |
| RAID-5 |
It is the simplest choice in a multi-user environment. However, a minimum of three drives are required for the RAID-5 array. |
Hardware RAID:
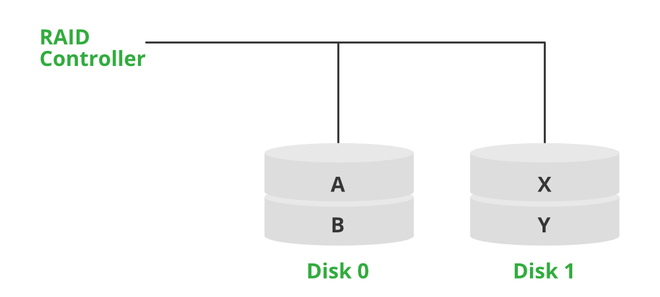
Hardware RAID is a customized processing system, using different controllers or RAID cards to manage the RAID design independently from the OS. The RAID controller doesn’t take processing power far away from the disks it manages. It handles the drives so that the processes are almost transparent to the host computer. It has more RAID configuration options including hybrid configurations which may not be available with certain OS options. The hardware RAID is typically expensive and adds a substantial amount to the cost of the whole system.

Hardware RAID Mechanism
Software RAID:
Software RAID may be a newer sort of RAID where no specialized hardware is required, and therefore the host computer is liable for the drives. When storage drives are connected to the pc or server without a RAID controller, RAID configuration is managed by utility software within the OS, which is mentioned as a software RAID setup. Software RAID permits users to reconfigure arrays without being restricted by the hardware RAID controller. The cost is low because no additional hardware RAID controller is required. Numerous operating systems support RAID configuration, including those from Apple, Microsoft, various Linux flavors also as OpenBSD, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and Solaris Unix.

Software RAID Mechanism
Hardware RAID vs Software RAID :
| S. No |
Hardware RAID
|
Software RAID
|
| 1. |
Hardware RAID is a customized processing system, using different controllers or RAID cards to manage the RAID design independently from the OS. |
Software RAID uses the processing power of that computer’s operating system in which the RAID disks are installed. |
| 2. |
Hardware RAID is more reliable and expensive. |
The cost is low because no additional hardware RAID controller is required. |
| 3. |
Inconsistent performance for certain hardware RAID setups that use flash storage (SSD), HDD arrays. |
In Software RAID the processors can easily handle RAID 0 & 1 processing with no noticeable performance hit. |
| 4. |
Replacing failed disk is simple – Just take it out and put in a new one |
Replacing a failed disk in the software RAID is a bit more complex. We have to first tell our system to stop using the disk and then replace the disk. |
| 5. |
When the RAID controller goes down, it should get replaced with an identical model to avoid malfunction. |
We can implement Software RAID configuration on one operating system (e.g. Ubuntu) and use it across other systems. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...