Difference between Direct and Implied Addressing Modes
Last Updated :
16 Jun, 2020
Prerequisite – Addressing Modes
1. Direct Addressing Mode :
In direct addressing mode, the address field contains the address of the operand.
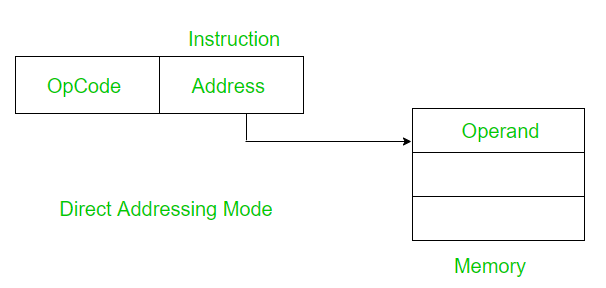
Effective Address(EA) = address field of operand
Example –
Add the contents of register A to the accumulator.
ADD A
Look in memory at address A for operand. Only a single memory reference is required to access data. So, no additional calculations are required to work out effective address.
2. Implied Addressing Mode :
Operand is specified implicitly in the definition of the instruction. It is normally used for zero or single address instructions.
Example-1:
Increment the contents of register A.
INC A
Here it is implicitly specified that register A is both the source as well as the destination.
Example-2:
Clear the contents of flag register.
CLC
The above instruction is an example of zero address instruction.
Difference between Direct and Implied Addressing Modes :
| DIRECT ADDRESSING MODE |
IMPLIED ADDRESSING MODE |
| Address fields contains the effective address of operand. |
Effective address of operand is specified implicitly. |
| Instruction size is larger since operand has to be explicitly specified. |
Instruction size is smaller since operand is specified implicitly. |
| It requires one reference to memory. |
No memory references are required. |
| Mostly used in 2 address instructions and more. |
Mostly used in zero address and single address instructions. |
| It is slower compared to implied mode. |
It is a faster method. |
| It has more range than implied mode. |
It has less range than direct mode. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...